In Switzerland, created a cheetah-sized robot the size of a cat
A small cat-sized robot from the bionics laboratory of the Federal Polytechnic School of Lausanne ( EPFL ), although inferior to the full-size “cheetahs” of Boston Dynamics and MIT in size and absolute speed, can run independently and overcome small obstacles. And in relation to speed and own size, this is the fastest four-legged robot in the world in the weight category up to 30 kg. With a length of only 20 cm and a weight of 1100 grams, the cheetah , as the robot is called by its creators, can run at a speed of almost one and a half meters per second.
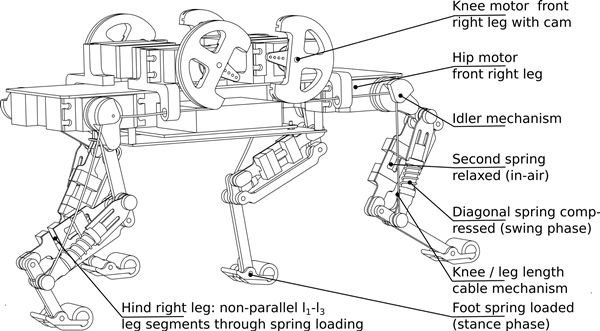
The robots set in motion eight servomotors - two for each leg. The femur joints are attached directly to the engines, and the knee joints are connected through a system of cables. On the legs of the robot there are springs that are chosen to work like the muscles and tendons of a real animal. It is thanks to the successful design of the legs that the robot is able to run over a slightly rugged terrain - it keeps balance only due to mechanical self-stabilization, working in the open-loop mode.
')
Unlike large four-legged robots from Massachusetts, the cheetah has almost no unique complex details (the MIT cheetah uses specially designed electric motors , and there is practically no data about the Cheetah design of Boston Dynamics that is not publicly available). As its designers say, the robot is cheap enough, affordable and safe, which makes it an ideal candidate for research in the field of robotics rather poor institutions and even single enthusiasts.
Scientific work with detailed information about the robot should be published today in The International Journal of Robotics Research .
The robots set in motion eight servomotors - two for each leg. The femur joints are attached directly to the engines, and the knee joints are connected through a system of cables. On the legs of the robot there are springs that are chosen to work like the muscles and tendons of a real animal. It is thanks to the successful design of the legs that the robot is able to run over a slightly rugged terrain - it keeps balance only due to mechanical self-stabilization, working in the open-loop mode.

')
Unlike large four-legged robots from Massachusetts, the cheetah has almost no unique complex details (the MIT cheetah uses specially designed electric motors , and there is practically no data about the Cheetah design of Boston Dynamics that is not publicly available). As its designers say, the robot is cheap enough, affordable and safe, which makes it an ideal candidate for research in the field of robotics rather poor institutions and even single enthusiasts.
Scientific work with detailed information about the robot should be published today in The International Journal of Robotics Research .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/183540/
All Articles