HP All-flash array and 10 more major changes to 3PAR storage systems (part 1)
Today, HP has passed a big announcement in the department of storage systems, I want to share this information. Models of storage systems of the middle class, optimized for work with flash-carriers - HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450, were announced, and also the functionality of current 7000/10000 systems was expanded.
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450

Virtually any storage system currently on the market supports SSDs.
Traditionally, high performance requirements from the disk subsystem have been achieved by adding a large number of rotating spindles, usually with minimal utilization of their volume (Figure 1).
The use of SSD drives has reduced the number of rotating spindles, while raising the performance of data arrays.
')

Fig.1. Achieving high performance in traditional arrays and modern arrays
While traditional arrays dominate the market with almost 20-year-old architecture, or super-expensive all-flash startups, HP offers an array with a completely different architecture, specially designed to work simultaneously with different types of data. The key features of the 3PAR 7450 array are that controllers are not a bottleneck in performance. This ensures a near linear increase in performance as new disks are added.
Technologically, these arrays are similar to the current 3PAR 7400 with improved cache characteristics and interconnect connections between controllers. Like the HP 3PAR 7400 model, the new 7450 can expand to an array of 4 fully-connected controllers with write-mirroring cache, while the uniqueness of the array is that each array controller is active for all volumes — which gives fair load balancing between all nodes and all disk array. This unique technology allows you to maintain high performance even when a single controller fails.
7450 arrays have a large cache size - 64GB for a dual-controller system and 128GB for 4 controllers, while the write cache has its own channels, so the array operating system cannot “eat off” the write cache for its needs and is fully accessible for input operations / output.
Due to such a large cache level, the use of ASIC chips and eight-core Intel E5-2470 2.3GHz processors, the array can accelerate to 520,000 IOPs using only SSD drives (4k random read), which is important when the delay is less than 1ms. And to obtain such large numbers, only a few shelves with SSD carriers are sufficient. Large IOPS require large bandwidth arrays. Due to the use of ASIC chips, the central processor of each controller is greatly relieved, this allows to obtain very high throughput rates - up to 5.2 GB / s. Thus, the raw computing power of each controller has increased by more than 55%.
To cope with such heavy loads and maintain clustering, bus bandwidth between controllers has been increased.
Since Since most traditional disk arrays are built on a 20-year-old architecture, the use of SSD drives in them does not bring significant performance, but only leads to a short-term improvement in reading performance. Controllers of such arrays have significant limitations on the number of supported SSD drives.
The features of the 3PAR array architecture are such that they allow to obtain high performance even when adding a large number of SSDs (120 SSD for 3PAR 7200, 240 SSD for 3PAR 7400/7450 models).
To assess the wear of SSD disks, the advanced Flash Wear Gauge mechanism is used, which will inform in time about possible problems with the carriers.
Adaptive cache
For the 3PAR 7450 array, the microcode for working with the controller cache has been revised.
The minimum page size stored in the cache of most storage systems is 16KB. The 3PAR array has a “smart” cache - each disk type, depending on their size and number, is allocated a specific cache area for writing. Further, if sequential and random references go in parallel to this type of disks, the pages of this part of the cache are adapted to the types of requests. For example, with several consecutive read operations, the cache immediately reads several blocks of 16K, thus reducing the load on the media and decreasing the response time. As soon as consecutive calls have stopped, only the actual pages remain in the cache.
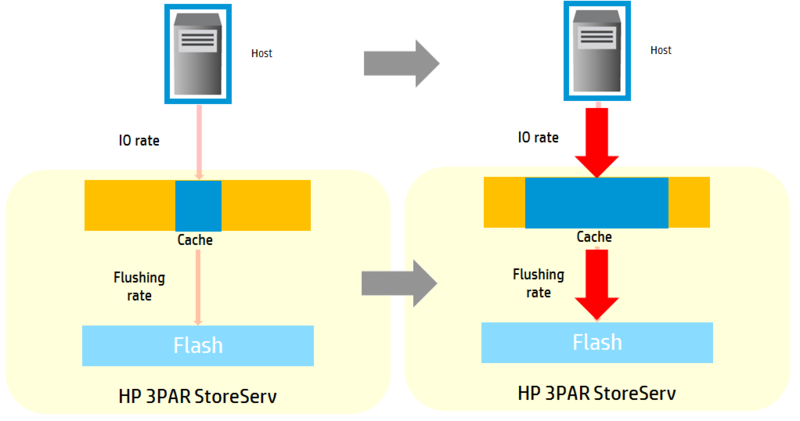
Fig. 2 Adaptive Cache in 3PAR 7450 Storage System
Consider an example when a host requests 4KB for reading. For traditional arrays from the cache to the disks are characterized by treatment in blocks of 16KB. This is done because there is a delay for rotating disks, so a larger block is immediately placed in the cache in order to predict further references to neighboring blocks. This approach will increase the speed of accessing the array, but will greatly load the data cache. SSD drives are characterized by ten times less response time, so the 3PAR 7450 arrays use an adaptive mode of operation - the array cache requests a block from the SSD carrier that is almost the same size as the I / O unit requested from the host, which makes the cache and SSD less load.

Fig. 3 Adaptive read cache in 3PAR 7450 array
Writing requests complicate matters. It is known that SSD media processes the recording in blocks of 4/8 KB in size from the host, but the SSD of the media is overwritten in blocks of 64KB, for early models of SSD drives - 512KB (rewriting cycles for SSD are always limited). Traditional arrays approach - 16KB pages are stored in the cache and blocks of the same size are recorded on SSD carriers, even if the server sends 4 / 8KB blocks, i.e. An incomplete page will be cached until full, only after that it will be recorded on SSD media. But most often an incomplete page will be dropped on SSD carriers, since in the arrays, policies of forced flushing of the cache to disks are applied upon reaching a certain timeout for saving data (even if only 4KB is written in the controller cache, the block is reset to 16 KB, of which 12KB will be filled with zeros). In this approach, the efficiency of using SSD carriers and their lifespan is greatly reduced. This behavior is typical for most arrays of the traditional type.
Approach used in 3PAR storage systems - smaller blocks (up to 4KB) are dropped to cache disks; this approach has several advantages:

Fig. 4 The principle of the cache 3PAR 7450 write
If the host receives write requests in large blocks (for example, 128KB), then the 3PAR array cache breaks them into smaller blocks and divides the load between the carriers. In this approach, each SSD media wears much less. In addition, the controller can simultaneously handle requests of different types: sequential and random. Each type of request is processed in parallel by ASIC chips, thereby reducing the queue and increasing the speed of the array in mixed loads. In traditional arrays on mixed loads, large queues of requests are characteristic.
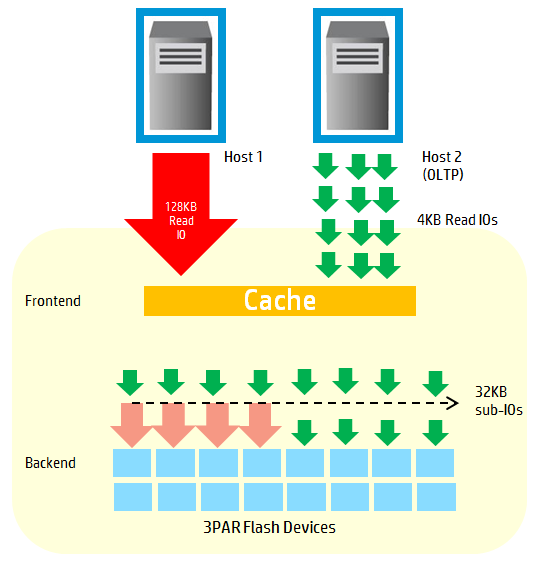
Fig. 5 The principle of the 3PAR array cache in mixed loads
What are the advantages of such storage system, along with numerous projects of Flash-arrays that appeared in the near future?
Disaster Recovery Support
In addition to performance improvements, the ability to build fault-tolerant solutions has increased in 3PAR arrays. In particular, the work of Peer Persistence technology, which is aimed at working together with VMware solutions, has improved. Several improvements:
The volume is replicated between arrays and fault-tolerant paths are presented to it, presented to the host. Disk arrays located at different sites will be interconnected by replication implemented using 3PAR Remote Copy. Due to the fact that both sites are active, replication will be two-way. 3PAR Peer Persistence technology provides vMSC cluster nodes with uniform access to two storage systems at data center sites, while each logical drive (LUN) of each 3Par storage system has a synchronous copy on another site (as reflected in the diagram below). This copy is presented to the VMware virtual environment passively to the main LUN, since it has the same WWN identifier (a unique device identifier on SANs). In the event of a failure of the main LUN, its backup remains visible to hosts, thus allowing the hypervisor to migrate virtual machines using conventional vMotion, High-Availability or Fault-Tollerance technologies. Switching between sites is performed by quorum, i.e. This is a fully automatic operation.
Most traditional technologies (such as, for example, the automated solution of VMware Site Recovery Manager) in the event of a storage system failure can transfer the entire virtual environment to a backup site, but this will require a reboot of the virtual machines. Due to the above-described Peer Persistence technology, storage is available for a virtual cluster even when the disk array of one of the sites has failed. At the same time, switching to the backup site occurs without the use of third-party mechanisms, which makes it possible to transfer virtual machines to another platform without stopping them and, at the same time, does not complicate the management of the infrastructure.
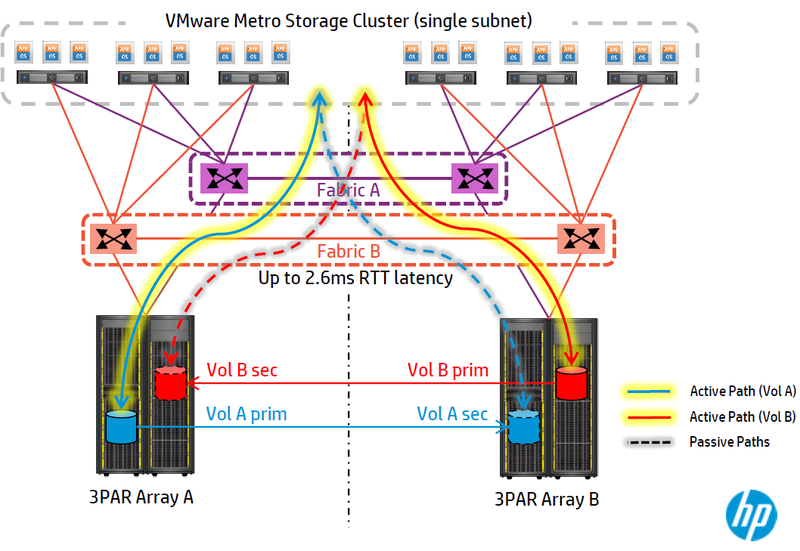
Fig. 6 Disaster Recovery Technology in VMware Environment
For physical machines, application clustering software that works in conjunction with 3PAR arrays is still available - HP Cluster Extension for Linux and Windows and MetroCluster for HP-UX.
Data encryption system in 3PAR StoreServ 7000/10000 arrays
Since June, customers have the opportunity to order arrays with the function of data encryption in addition to standard 3PAR 7000/10000 arrays. The difference of these arrays in the presence of special disks SED (Self-Encrypted Disk), each of which has an encryption chip. The AES-128 / RSA-2048 / SHA-256 / RNG FIPS-186 / SP 800-90DRBG encryption protocols are supported. Due to the low latency of the chip, the speed of the SED disk is almost the same as the speed of a regular disk. During the first initialization, the encryption key is recognized by the Local Key Manager, which is part of the array's operating system and runs on each controller. During the first initialization of the array, you will be asked to save a copy of the key. In the event of a power failure on the disks or array, the data is blocked and data access can be resumed by re-entering the encryption key in the Local Key Manager console. If the IT specialist leaves the organization, you can change the key. When migrating to an array without the encryption function, the data will be decrypted; when migrating in the opposite direction, it will be encrypted. There are important nuances:
Several types of SEDs will be available for encryption - 400GB MLC SSD, 450GB 10k, 900GB 10k, 1TB 7.2k 2.5 ”.

Fig. 7 Scheme of data encryption in 3PAR array
Encryption is enabled very quickly, in several parallel streams, for example, on a 160-disk system, encryption is applied in ~ 30 seconds.
What media is the HP 3PAR 7450 array for?
Firstly, these are the technology OLTP / WEB 2.0, for which the response time and speed of the array is crucial, and for the enterprise it directly affects the profit.
Secondly, these are the VDI technologies that have become widely demanded, which are characterized by the presence of an avalanche-like growth of calls to the array over a very short period of time (boot storm). The use of the 3PAR 7450 fast array will allow you to squeeze the maximum performance out of SSD drives (up to 10,000 IOPS from the carrier), thus reducing their number.

Fig. 9 Pattern of typical array calls for VDI
Thirdly, it is a business analyst. Quick analysis of large amounts of data - quick response to changes and high profits.
Which announcements are still worth mentioning:
UPD: Appeared test protocol functional 3PAR Peer Persistence on the site VMware . Pay particular attention to the test script table of virtual machines in the cluster.
Bibliography:
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450

Virtually any storage system currently on the market supports SSDs.
Traditionally, high performance requirements from the disk subsystem have been achieved by adding a large number of rotating spindles, usually with minimal utilization of their volume (Figure 1).
The use of SSD drives has reduced the number of rotating spindles, while raising the performance of data arrays.
')

Fig.1. Achieving high performance in traditional arrays and modern arrays
While traditional arrays dominate the market with almost 20-year-old architecture, or super-expensive all-flash startups, HP offers an array with a completely different architecture, specially designed to work simultaneously with different types of data. The key features of the 3PAR 7450 array are that controllers are not a bottleneck in performance. This ensures a near linear increase in performance as new disks are added.
Technologically, these arrays are similar to the current 3PAR 7400 with improved cache characteristics and interconnect connections between controllers. Like the HP 3PAR 7400 model, the new 7450 can expand to an array of 4 fully-connected controllers with write-mirroring cache, while the uniqueness of the array is that each array controller is active for all volumes — which gives fair load balancing between all nodes and all disk array. This unique technology allows you to maintain high performance even when a single controller fails.
7450 arrays have a large cache size - 64GB for a dual-controller system and 128GB for 4 controllers, while the write cache has its own channels, so the array operating system cannot “eat off” the write cache for its needs and is fully accessible for input operations / output.
Due to such a large cache level, the use of ASIC chips and eight-core Intel E5-2470 2.3GHz processors, the array can accelerate to 520,000 IOPs using only SSD drives (4k random read), which is important when the delay is less than 1ms. And to obtain such large numbers, only a few shelves with SSD carriers are sufficient. Large IOPS require large bandwidth arrays. Due to the use of ASIC chips, the central processor of each controller is greatly relieved, this allows to obtain very high throughput rates - up to 5.2 GB / s. Thus, the raw computing power of each controller has increased by more than 55%.
To cope with such heavy loads and maintain clustering, bus bandwidth between controllers has been increased.
Since Since most traditional disk arrays are built on a 20-year-old architecture, the use of SSD drives in them does not bring significant performance, but only leads to a short-term improvement in reading performance. Controllers of such arrays have significant limitations on the number of supported SSD drives.
The features of the 3PAR array architecture are such that they allow to obtain high performance even when adding a large number of SSDs (120 SSD for 3PAR 7200, 240 SSD for 3PAR 7400/7450 models).
To assess the wear of SSD disks, the advanced Flash Wear Gauge mechanism is used, which will inform in time about possible problems with the carriers.
Adaptive cache
For the 3PAR 7450 array, the microcode for working with the controller cache has been revised.
The minimum page size stored in the cache of most storage systems is 16KB. The 3PAR array has a “smart” cache - each disk type, depending on their size and number, is allocated a specific cache area for writing. Further, if sequential and random references go in parallel to this type of disks, the pages of this part of the cache are adapted to the types of requests. For example, with several consecutive read operations, the cache immediately reads several blocks of 16K, thus reducing the load on the media and decreasing the response time. As soon as consecutive calls have stopped, only the actual pages remain in the cache.

Fig. 2 Adaptive Cache in 3PAR 7450 Storage System
Consider an example when a host requests 4KB for reading. For traditional arrays from the cache to the disks are characterized by treatment in blocks of 16KB. This is done because there is a delay for rotating disks, so a larger block is immediately placed in the cache in order to predict further references to neighboring blocks. This approach will increase the speed of accessing the array, but will greatly load the data cache. SSD drives are characterized by ten times less response time, so the 3PAR 7450 arrays use an adaptive mode of operation - the array cache requests a block from the SSD carrier that is almost the same size as the I / O unit requested from the host, which makes the cache and SSD less load.

Fig. 3 Adaptive read cache in 3PAR 7450 array
Writing requests complicate matters. It is known that SSD media processes the recording in blocks of 4/8 KB in size from the host, but the SSD of the media is overwritten in blocks of 64KB, for early models of SSD drives - 512KB (rewriting cycles for SSD are always limited). Traditional arrays approach - 16KB pages are stored in the cache and blocks of the same size are recorded on SSD carriers, even if the server sends 4 / 8KB blocks, i.e. An incomplete page will be cached until full, only after that it will be recorded on SSD media. But most often an incomplete page will be dropped on SSD carriers, since in the arrays, policies of forced flushing of the cache to disks are applied upon reaching a certain timeout for saving data (even if only 4KB is written in the controller cache, the block is reset to 16 KB, of which 12KB will be filled with zeros). In this approach, the efficiency of using SSD carriers and their lifespan is greatly reduced. This behavior is typical for most arrays of the traditional type.
Approach used in 3PAR storage systems - smaller blocks (up to 4KB) are dropped to cache disks; this approach has several advantages:
- Wear of SSD carriers decreases, since Only small data blocks will be recorded.
- Improved mechanisms for finding free space on the SSD, after filling the media: the array is easier to find a free block in 4KB than a block in 16KB
- On the basis of paragraph 2, the utilization of SSD media is improved - only blocks with data are stored, blocks filled with zeros are excluded
- For RAID1 volumes, delays and penalties associated with the sequence of “read-modify-write” requests are reduced.

Fig. 4 The principle of the cache 3PAR 7450 write
If the host receives write requests in large blocks (for example, 128KB), then the 3PAR array cache breaks them into smaller blocks and divides the load between the carriers. In this approach, each SSD media wears much less. In addition, the controller can simultaneously handle requests of different types: sequential and random. Each type of request is processed in parallel by ASIC chips, thereby reducing the queue and increasing the speed of the array in mixed loads. In traditional arrays on mixed loads, large queues of requests are characteristic.

Fig. 5 The principle of the 3PAR array cache in mixed loads
What are the advantages of such storage system, along with numerous projects of Flash-arrays that appeared in the near future?
- First, the 3PAR 7450 array provides high performance comparable to flash arrays. This uses SSD drives, which are significantly cheaper than Flash modules. Traditional data storage systems, due to outdated architecture, cannot achieve high levels of performance.
- Secondly, the 3PAR array supports Disaster recovery, which so far manufacturers of Flash arrays cannot offer.
- Third, Flash arrays, like traditional architecture arrays, cannot grow to 4 controllers with automatic load balancing between them.
- Fourthly, the Flash array itself is usually weakly connected to other storage systems, which reduces the area for its use, while 3PAR allows you to store all types of data on the same storage system, with a single management interface and dynamic data movement between levels .
- Fifth, 3PAR arrays can be federated from several systems, with load balancing between arrays, which is currently not available in both Flash solutions and arrays of traditional architecture.
Disaster Recovery Support
In addition to performance improvements, the ability to build fault-tolerant solutions has increased in 3PAR arrays. In particular, the work of Peer Persistence technology, which is aimed at working together with VMware solutions, has improved. Several improvements:
- The load balancing features between the two sites were implemented in conjunction with Storage vMotion. Now, VMware automatic load balancing is possible not only inside the array between all controllers, but also between several arrays.
- A high availability feature has been implemented for virtual machines between multiple data centers.
- Synchronous replication now supports never disappearing LUN presentation technology:
The volume is replicated between arrays and fault-tolerant paths are presented to it, presented to the host. Disk arrays located at different sites will be interconnected by replication implemented using 3PAR Remote Copy. Due to the fact that both sites are active, replication will be two-way. 3PAR Peer Persistence technology provides vMSC cluster nodes with uniform access to two storage systems at data center sites, while each logical drive (LUN) of each 3Par storage system has a synchronous copy on another site (as reflected in the diagram below). This copy is presented to the VMware virtual environment passively to the main LUN, since it has the same WWN identifier (a unique device identifier on SANs). In the event of a failure of the main LUN, its backup remains visible to hosts, thus allowing the hypervisor to migrate virtual machines using conventional vMotion, High-Availability or Fault-Tollerance technologies. Switching between sites is performed by quorum, i.e. This is a fully automatic operation.
Most traditional technologies (such as, for example, the automated solution of VMware Site Recovery Manager) in the event of a storage system failure can transfer the entire virtual environment to a backup site, but this will require a reboot of the virtual machines. Due to the above-described Peer Persistence technology, storage is available for a virtual cluster even when the disk array of one of the sites has failed. At the same time, switching to the backup site occurs without the use of third-party mechanisms, which makes it possible to transfer virtual machines to another platform without stopping them and, at the same time, does not complicate the management of the infrastructure.

Fig. 6 Disaster Recovery Technology in VMware Environment
For physical machines, application clustering software that works in conjunction with 3PAR arrays is still available - HP Cluster Extension for Linux and Windows and MetroCluster for HP-UX.
Data encryption system in 3PAR StoreServ 7000/10000 arrays
Since June, customers have the opportunity to order arrays with the function of data encryption in addition to standard 3PAR 7000/10000 arrays. The difference of these arrays in the presence of special disks SED (Self-Encrypted Disk), each of which has an encryption chip. The AES-128 / RSA-2048 / SHA-256 / RNG FIPS-186 / SP 800-90DRBG encryption protocols are supported. Due to the low latency of the chip, the speed of the SED disk is almost the same as the speed of a regular disk. During the first initialization, the encryption key is recognized by the Local Key Manager, which is part of the array's operating system and runs on each controller. During the first initialization of the array, you will be asked to save a copy of the key. In the event of a power failure on the disks or array, the data is blocked and data access can be resumed by re-entering the encryption key in the Local Key Manager console. If the IT specialist leaves the organization, you can change the key. When migrating to an array without the encryption function, the data will be decrypted; when migrating in the opposite direction, it will be encrypted. There are important nuances:
- Encryption is activated by a license; one license per array is acquired.
- You cannot mix normal and SED disks in an array with the encryption function activated.
- If the encryption function is not activated, then you can mix disks in the array, but the cost of SED disks is about 5% higher.
- After the encryption function is activated - all SED disks must be reinitialized, i.e. the data on the disks will not be available.
Several types of SEDs will be available for encryption - 400GB MLC SSD, 450GB 10k, 900GB 10k, 1TB 7.2k 2.5 ”.

Fig. 7 Scheme of data encryption in 3PAR array
Encryption is enabled very quickly, in several parallel streams, for example, on a 160-disk system, encryption is applied in ~ 30 seconds.
What media is the HP 3PAR 7450 array for?
Firstly, these are the technology OLTP / WEB 2.0, for which the response time and speed of the array is crucial, and for the enterprise it directly affects the profit.
Secondly, these are the VDI technologies that have become widely demanded, which are characterized by the presence of an avalanche-like growth of calls to the array over a very short period of time (boot storm). The use of the 3PAR 7450 fast array will allow you to squeeze the maximum performance out of SSD drives (up to 10,000 IOPS from the carrier), thus reducing their number.

Fig. 9 Pattern of typical array calls for VDI
Thirdly, it is a business analyst. Quick analysis of large amounts of data - quick response to changes and high profits.
Which announcements are still worth mentioning:
- You can order MLC SSDs with 400GB drives - for those cases when large SSD volumes are needed, NL SAS drives 1TB 7.2k 2.5 "- for those who need capacious storage in the 2.5" form factor (for 3PAR 7000), SAS drives 600GB 10k 2.5 ”.
- Technology Priority Assignment for Hosts (QoS).
- Announced support for OpenVMS, Ubuntu.
- Support for OpenStack interfaces and drivers has been announced, the 3PAR array becomes an object data storage and is even easier integrated into the cloud.
- FCoE connectivity is now supported on devices with multiple hopes.
UPD: Appeared test protocol functional 3PAR Peer Persistence on the site VMware . Pay particular attention to the test script table of virtual machines in the cluster.
Bibliography:
- HP 3PAR 7450 Quickspecs
- HP 3PAR 7000 Quickspecs
- HP 3PAR 10000 Quickspecs
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/182724/
All Articles