Microsoft released another set of updates, June 2013
Microsoft announced the release of a series of patches aimed at eliminating vulnerabilities in their products. Previously announced in the pre-release (June 6), security fixes cover a total of 23 unique vulnerabilities (one fix with Critical status and 4 with Important status). A detailed report (including correlation fixes with CVE ID) can be found here .
Critical update MS13-047 is aimed at eliminating vulnerabilities like Remote Code Execution that are present in all versions of Internet Explorer, starting with version 6 and ending with the latest IE 10 (for all Windows XP operating systems - 8 - RT, x32 and x64, for OS server versions like Moderate). Reboot is required to apply fix In addition to Internet Explorer, OS components of various versions and the latest version of Microsoft Office 2011 for Mac have been updated.
The company releases security fixes for its products every second Tuesday of the month announcing in two stages. A few days before the updates themselves, the minimum information is laid out, which includes information about the products being updated, a list of the updates that will be delivered, and the types of vulnerabilities to be fixed. The actual release of the updates themselves is accompanied by the publication of extended information, such as, the vulnerability identifiers ( Exploitability Index ), the product components to be fixed, the exploitation technique.
')
Last month was marked by a debate between Google and Microsoft about the timing of the disclosure of information about 0day vulnerabilities.

Artyom Baranov , ESET analyst in Russia comments on:
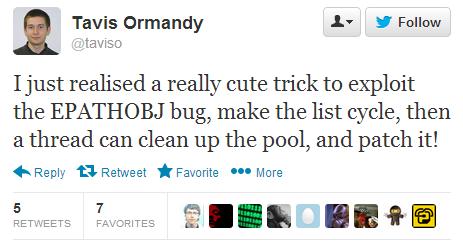

Note that the disclosure of the way of exploitation of the 0day vulnerability, with the publication of the working code, caused controversy in the security-community. In particular, Google in its blog published their position on the period of disclosure of information 0day vulnerability, which has the status of is-being-exploited-in-the-wild:
Exploit demonstration [ Xylit0l Personal Video ] www.youtube.com/watch?v=z99Flb9WguU .

General list of updates and products.
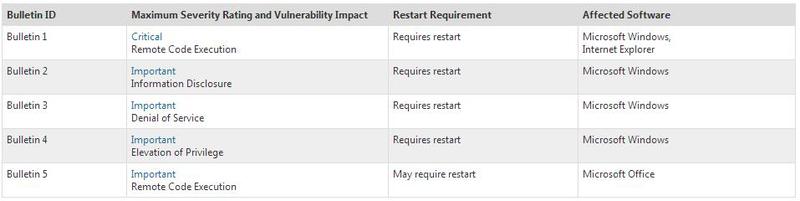
The other four updates marked Important are aimed at fixing vulnerabilities in the OS and Microsoft Office.
The MS13-048 update addresses the vulnerability of CVE-2013-3136 in 32-bit OS versions, starting with Windows XP SP3 and ending with Windows 8. The vulnerability that can be resolved is Information Disclosure and belongs to the OS kernel. As a result of successful exploitation, an attacker can gain read access to memory accessible from kernel mode. Exploit code unlikely.
Update MS13-049 fixes a CVE-2013-3138 type Denial of Service vulnerability on Windows 8, Server 2012, RT systems, and also for Windows Vista, Seven as Moderate. The TCP / IP protocol driver tcpip.sys, which may incorrectly process packets during a TCP connection, is subject to correction, which can cause the entire system to hang. Exploit code unlikely.
The MS13-050 update eliminates the CVE-2013-1339 vulnerability of the Elevation of Privilege type in the OS, starting with Windows Vista and higher, and belongs to the Print Spooler service. Exploit code likely.
The MS13-051 update is aimed at eliminating the vulnerability of CVE-2013-1331 in Microsoft Office (Remote Code Execution). The old Office 2003 version and the newest Mac version for Microsoft Office for Mac 2011 are subject to correction. The vulnerability is related to a buffer overflow when opening a specially formed file. Has the status of is-being-exploited-in-the-wild. Exploit code likely.
The following is a breakdown of the exploitation levels used by MS in the definition of the Microsoft Exploitability Index.

1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend that our users install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (this option is enabled by default).

be secure.
Critical update MS13-047 is aimed at eliminating vulnerabilities like Remote Code Execution that are present in all versions of Internet Explorer, starting with version 6 and ending with the latest IE 10 (for all Windows XP operating systems - 8 - RT, x32 and x64, for OS server versions like Moderate). Reboot is required to apply fix In addition to Internet Explorer, OS components of various versions and the latest version of Microsoft Office 2011 for Mac have been updated.
The company releases security fixes for its products every second Tuesday of the month announcing in two stages. A few days before the updates themselves, the minimum information is laid out, which includes information about the products being updated, a list of the updates that will be delivered, and the types of vulnerabilities to be fixed. The actual release of the updates themselves is accompanied by the publication of extended information, such as, the vulnerability identifiers ( Exploitability Index ), the product components to be fixed, the exploitation technique.
')
Last month was marked by a debate between Google and Microsoft about the timing of the disclosure of information about 0day vulnerabilities.

Artyom Baranov , ESET analyst in Russia comments on:
It should be noted that this set of updates contains the least number of patches than all the others that the company has released this year. At the same time, we again see an update that eliminates a cross-IE vulnerability, i.e., a vulnerability that is present in all versions of the browser and has the type Remote Code Execution. Last month, the company closed a similar vulnerability (use-after-free) in IE8, which was used to install Poison Ivy RAT on computers of US civil servants.
This month we did not see a fix for CVE-2013-3660, a vulnerability such as Elevation Of Privelege, which allows elevating user privileges to the system level on all versions of the OS, starting from NT and ending with Windows 8. Details of this vulnerability with exploitation code were published in last month, researcher Tavis Ormandy ( @taviso ) from the Google Security Team. Vulnerability allows you to load arbitrary code into the system address space with its subsequent execution, bypassing the restrictions imposed by the OS.


Note that the disclosure of the way of exploitation of the 0day vulnerability, with the publication of the working code, caused controversy in the security-community. In particular, Google in its blog published their position on the period of disclosure of information 0day vulnerability, which has the status of is-being-exploited-in-the-wild:
It is not necessary to make a decision to ensure that it is not possible. If you want to get a patch, you’ll see it. Based on our experience, however, we’ve taken action for a period of 7 days. Designed for each day, he actively researched the vulnerability of the computer and more computers will be compromised.
... As a result, after all, we can support researchers.
Our recommendation [ regarding the timing of fixing vulnerabilities ] to companies is that they should fix critical vulnerabilities within 60 days, otherwise companies should be notified of emerging risks to the public and suggest workarounds for solving the problem. We recommend that the supervisors publish the results of their research, if the release of the patch takes longer than this. However, based on our experience, we believe that in the case of critical vulnerabilities that are already at the stage of active operation, this repair period should not exceed 7 days. The reason for such a special measure is the fact that the vulnerability that is not disclosed to the public 0day, which is exploited every day, leads to the compromise of a large number of systems.
... As a result, if after 7 days the vulnerability is not closed, we will support researchers who intend to publish details to the public, allowing so on. users to take their own steps to protect their systems.
Exploit demonstration [ Xylit0l Personal Video ] www.youtube.com/watch?v=z99Flb9WguU .

General list of updates and products.

The other four updates marked Important are aimed at fixing vulnerabilities in the OS and Microsoft Office.
The MS13-048 update addresses the vulnerability of CVE-2013-3136 in 32-bit OS versions, starting with Windows XP SP3 and ending with Windows 8. The vulnerability that can be resolved is Information Disclosure and belongs to the OS kernel. As a result of successful exploitation, an attacker can gain read access to memory accessible from kernel mode. Exploit code unlikely.
Update MS13-049 fixes a CVE-2013-3138 type Denial of Service vulnerability on Windows 8, Server 2012, RT systems, and also for Windows Vista, Seven as Moderate. The TCP / IP protocol driver tcpip.sys, which may incorrectly process packets during a TCP connection, is subject to correction, which can cause the entire system to hang. Exploit code unlikely.
The MS13-050 update eliminates the CVE-2013-1339 vulnerability of the Elevation of Privilege type in the OS, starting with Windows Vista and higher, and belongs to the Print Spooler service. Exploit code likely.
The MS13-051 update is aimed at eliminating the vulnerability of CVE-2013-1331 in Microsoft Office (Remote Code Execution). The old Office 2003 version and the newest Mac version for Microsoft Office for Mac 2011 are subject to correction. The vulnerability is related to a buffer overflow when opening a specially formed file. Has the status of is-being-exploited-in-the-wild. Exploit code likely.
The following is a breakdown of the exploitation levels used by MS in the definition of the Microsoft Exploitability Index.

1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend that our users install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (this option is enabled by default).

be secure.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/182494/
All Articles