Educational Data Mining: Introduction
Nelson Mandela said: “Education is the most powerful weapon
which you can use to change the world. ”
By the will of fate, we were lucky to become one of the participants in the course on Data Mining ( GameChangers program, St. Petersburg ). The goal of the course is to study data processing methods and technologies in various areas of the IT industry. We give lectures to experts from the largest IT companies, and students work on real-world tasks and projects.
And so it turned out that in the framework of this course, our working group is developing a project in the field of Educational Data Mining.
In Russia, for now, only a few know about the existence of this direction, so for a start we will tell in general about EDM: common goals, who can use and why.
Educational Data Mining

According to the article "Educational Data Mining: A Review of the State of the Art" , EDM is developing methods for researching educational data for educational decision-making.
// for example, to understand students and the “attitudes” they learn from.
It is clear that both DM and EDM are engaged in finding hidden patterns in the data. But what distinguishes EDM from other subdivisions of Data Mining?
Well, first of all, these are goals. EDM is trying with all its might to improve the educational process, to direct students in the right direction, to give recommendations to teachers and moreover to penetrate into the very essence of the phenomenon of education - to understand how we still learn information, acquire skills and abilities.
')
Secondly, the data. The ones used by EDM have rather complex internal semantics. There are several significant levels of hierarchy and relationships between different types of data.
Online systems for EDM most often use log files that contain all the information about the user's work on the site (clicks, transitions, ratings, and much more). It is worth noting that EDM can be used not only in online systems, but also in traditional schools and universities. Another thing is that in this case we have very fragmented and insufficient information. While in the online course, everything is already in a single electronic format and the scale of the audience on such resources as Coursera many times exceeds the standard class. It is for the data of such dimensions that it makes sense to use machine learning algorithms common in DM.
And thirdly, these are the methods themselves. In addition to standard Data Mining methods: clustering, classification, regression, correlation, visualization, statistics, association rule search (eng. Rule mining) ..., - in the EDM some specific ones are used, for example, from the field of psychometrics. According to Wikipedia, psychometry studies the theory and methodology of psychological measurements and is part of statistics. In the EDM, methods from this discipline help to divide students into groups according to information perception (see the MBTI typology), which in turn allows us to adapt the educational process to the student: select the appropriate type of content and organize it in a certain way.
| Preferences | Explanation (what accents) |
|---|---|
| Extraversion - Introversion | Orientation of consciousness |
| Feeling - Intuition | Way of orientation in a situation |
| Thinking - Feeling | Basis of decision making |
| Judgment - Perception | Method of preparing solutions |
And now, perhaps, a few words about who and why EDM is used for.
"The target audience"
There are several main groups of users of Educational Data Mining, consider them on the example of the well-known portal Coursera.

So, we have a student who wants to understand how to program compilers.
A student enters Coursera and enrolls for a Compilers course from Alex Aiken, a teacher at Stanford University.
Let's see what the EDM can offer him, based on information about the training and his personal data, which he fills in the profile or from the answers to the questionnaires of the courses.

1. Students / students
In order for the student to successfully complete the compiler course and return for further study, the Coursera platform can do the following:
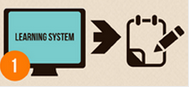 When a student wants to gain knowledge on the Internet - he uses an online educational system. It interacts with the student, providing personalized content and customized help.
When a student wants to gain knowledge on the Internet - he uses an online educational system. It interacts with the student, providing personalized content and customized help. The system collects detailed information about what content the student opens most often (task, video, text), as well as the speed, duration and frequency of its viewing. After it saves to the database.
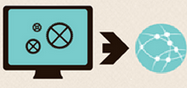
The system collects detailed information about what content the student opens most often (task, video, text), as well as the speed, duration and frequency of its viewing. After it saves to the database.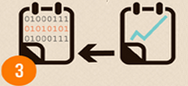 The obtained information is processed and based on the received training models, the system tries to adapt the course to the student in the best way possible.
The obtained information is processed and based on the received training models, the system tries to adapt the course to the student in the best way possible. The system can also give recommendations of other courses. There are a huge number of recommendation algorithms that can be used. Very good about recommender systems algorithms written in snikolenko .
The system can also give recommendations of other courses. There are a huge number of recommendation algorithms that can be used. Very good about recommender systems algorithms written in snikolenko . If the system sees that a student very quickly copes with quizzes and homework, quickly scrolls through the training material, then she can offer him “workaround” (shortened) ways to complete the course - more complex tasks, passing to a more difficult level during the exam, etc.
If the system sees that a student very quickly copes with quizzes and homework, quickly scrolls through the training material, then she can offer him “workaround” (shortened) ways to complete the course - more complex tasks, passing to a more difficult level during the exam, etc. Otherwise, it will help generate an adapted hint. If a student has problems with some part of the course (this can be understood on the basis of errors in quizzes, homework assignments and questions on the forum), the system can advise on additional material or redirect it to the appropriate chapter.
Otherwise, it will help generate an adapted hint. If a student has problems with some part of the course (this can be understood on the basis of errors in quizzes, homework assignments and questions on the forum), the system can advise on additional material or redirect it to the appropriate chapter.2. Instructors / instructors
At the same time, teachers, such as Alex Aiken, also need information and tools to improve the course. The system can give the teacher the following information:
 When creating a course, based on an analysis of existing courses, the teacher will be able to predict in advance the behavior of the student and adapt the material to his needs.
When creating a course, based on an analysis of existing courses, the teacher will be able to predict in advance the behavior of the student and adapt the material to his needs. During the course it is very important to get a fitback (feedback) about the learning process. For example, it may be an integral assessment or the dynamics of students' work on the course (completed quizzes, homework, etc.)
During the course it is very important to get a fitback (feedback) about the learning process. For example, it may be an integral assessment or the dynamics of students' work on the course (completed quizzes, homework, etc.) Also, the teacher has the opportunity to classify students into groups, for example, by academic performance, activity, gender, age, background, etc.
Also, the teacher has the opportunity to classify students into groups, for example, by academic performance, activity, gender, age, background, etc. The system provides tools for the frequency and distribution of errors that students make. Using additional parameters, such as
The system provides tools for the frequency and distribution of errors that students make. Using additional parameters, such asviewed topics, previous ratings, etc., it is possible to understand the causes of errors.
3. Developers / researchers
 Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller, as creators of the platform, are interested in courses being in demand and students acquiring new knowledge, therefore, together with a group of researchers (from computer science), they are developing EDM tools with which they try:
Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller, as creators of the platform, are interested in courses being in demand and students acquiring new knowledge, therefore, together with a group of researchers (from computer science), they are developing EDM tools with which they try: Improve student learning. For example, according to the statistics of selected courses, recommendations can be given to students for further study, a schedule is drawn up + all that is described above.
Improve student learning. For example, according to the statistics of selected courses, recommendations can be given to students for further study, a schedule is drawn up + all that is described above. Evaluate the structure of the course content and its effectiveness in the learning process. Before the eyes of the developers a complete picture of what is happening on the resource. It is in their interest to keep and improve successful courses and select the best way to present information.
Evaluate the structure of the course content and its effectiveness in the learning process. Before the eyes of the developers a complete picture of what is happening on the resource. It is in their interest to keep and improve successful courses and select the best way to present information. Automatically create student and mentor models. Based on the data on teachers and students, psychometrics will help here, you can select the best student-mentor combinations, which should increase the digestibility of the material.
Automatically create student and mentor models. Based on the data on teachers and students, psychometrics will help here, you can select the best student-mentor combinations, which should increase the digestibility of the material.4. Organizations: universities / companies / ... | 5. Educational process administrators / system administrators
For higher education institutions, such as Stanford, implementing EDM will help:
 To offer groups of students certain courses that may be useful, thereby making the content of classes more cost-effective.
To offer groups of students certain courses that may be useful, thereby making the content of classes more cost-effective. Improve the quality of student training. With the help of EDM, the administrator receives new tools for assessing teachers, curricula, and how to better use limited resources (teachers, developers, and materials).
Improve the quality of student training. With the help of EDM, the administrator receives new tools for assessing teachers, curricula, and how to better use limited resources (teachers, developers, and materials). EDM algorithms will prompt system administrators when to expect peak network loads, and how to optimize web services, adapting them to users.
EDM algorithms will prompt system administrators when to expect peak network loads, and how to optimize web services, adapting them to users.In conclusion about the use of EDM.
The main directions in which development is being carried out can be found in the diagram. We draw your attention to the fact that the data were collected on 300 works until 2009.

For more information on the topic I recommend:
- Articles:
- Coursera: coursera.org
- Book times: C. Romero, S. Ventura et al. Handbook of Educational Data Mining. 2010 (amazon)
- Book two: C. Romero & S. Ventura. Data Mining in E-learning. 2006 (amazon)
- TED Online Education: Daphne Koller: What are you learning from online education
If the topic is interesting, then this post may be the first of a series of posts on EDM. Let me know.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/181053/
All Articles