Data Transmission Technology in the ERA-GLONASS Emergency Response System
The following year, the launch of an emergency response system with the “ERA-GLONASS” system, which is the Russian equivalent of the pan-European eCall system (should work throughout the EU in 2015), is scheduled.
Both of these systems are designed to automatically call emergency services in case of an accident and are aimed at reducing the level of death and injury on the roads.
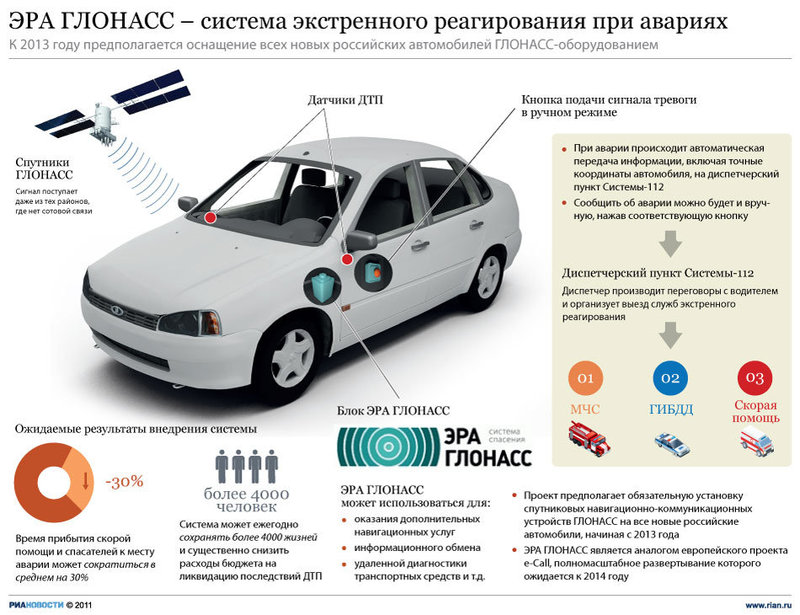
ERA-GLONASS will be used throughout the country and will become the basis for the integration of all navigation systems in transport. The main components of an ERA are a navigation and telecommunications terminal in a vehicle plus the infrastructure of mobile operators and emergency services. Read about the data transfer technology in this system under habrakat.
')
ERA and eCall correspond to each other in basic functionality: they use a tone modem as the main data transmission mechanism, a unified composition and format of mandatory data, uniform voice connection rules with a car driver, etc. "ERA-GLONASS" is fully compatible with eCall, equipment interchangeability Russian and European systems has been validated in a series of field tests.
An emergency phone call can be made manually by pressing a button. In an emergency, the signal will be sent automatically, because the system will record the operation of the airbags or determine the accident using the accelerometer.
ERA-GLONASS will establish a voice connection with the emergency control center, which during the call will be able to send information about the incident: geographical coordinates, VIN-code, etc. (the so-called minimum data set).
Below is a simplified block diagram of ERA-GLONASS and eCall , it shows the components of the data transfer subsystem:
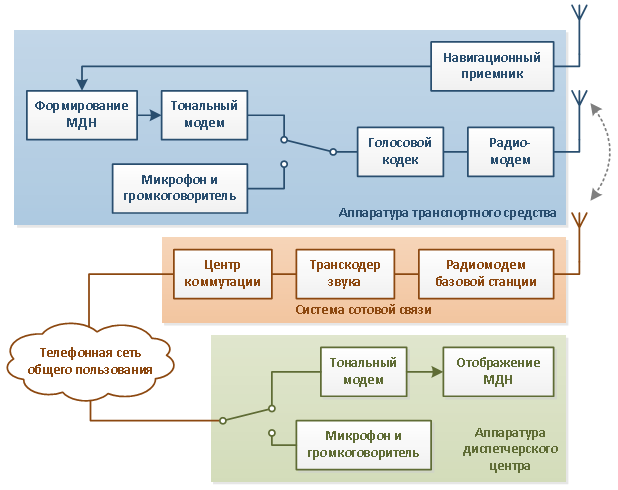
As can be seen from the figure, the voice path is used to transfer the minimum set of data from the vehicle to the control center. The fact is that this method of message delivery has the highest priority and guaranteed delays. Accordingly, this is the optimal technology compared to the short message service or packet data.
The diagram also shows the components of a cellular network (a radio modem of a base station, a sound transcoder, a switching center), and a public telephone network - all of which are involved in voice stream transmission.
The main components of the modem from the vehicle are shown in the following diagram:
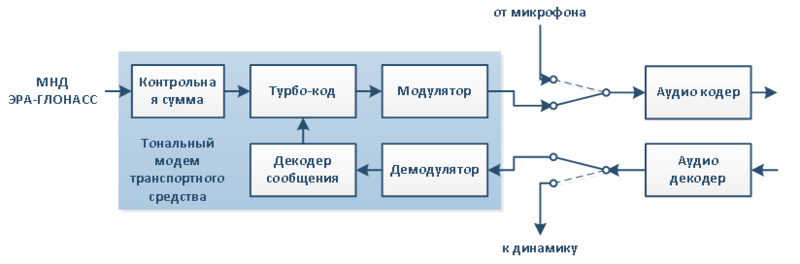
The minimum data set with a length of 140 bytes (1120 bits), which arrived at the transmitter, is supplemented with control information with a length of 28 bits, calculated using the cyclic redundancy code (CRC) algorithm. The received message with a length of 1148 bits is scrambled, robust coding, and interleaved to reduce the sensitivity to data transmission errors. For encoding, the turbo code is used, which is a parallel cascade convolutional code with a rate of 1/3.
This coding scheme gives a stream of different redundancy (the maximum speed is equal to 0.83), which allows to increase the redundancy with each repeated attempt to transfer data. Next, the data stream is combined into three bits of characters, which are converted into a form using bipolar phase-pulse modulation, which is suitable for transmission using voice codecs in cellular communication systems, including GSM Full-Rate and various AMR codec modes.
The sending time of the minimum data set is 1.32 seconds or 2.32 seconds when using the high-speed (1500 bps) and low-speed (750 bps) modes, respectively. Before sending over the air, the signal is supplemented with a synchronization frame with a duration of 260 ms.
The car's receiver can receive messages from the modem of the control center, such as a request for a minimum set of data, an error / acknowledgment. If, during data transmission, an error message in the checksum comes in, the vehicle retransmits the data, simultaneously increasing the redundancy of the error-correcting coding, until a sufficient number of confirmations of successful reception of information is received, or until the dispatch center interrupts the operation. After transferring the data, the modems of the vehicle and the dispatcher go into standby mode, and the audio path is switched to voice transmission.
The main components of the modem from the control center are presented below:
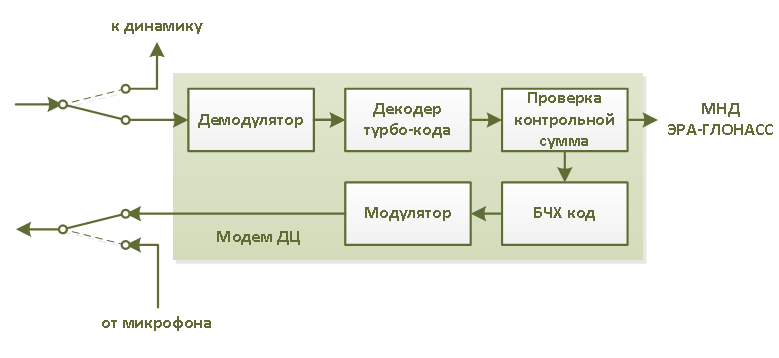
The transmitter of the control center allows you to send up to 16 different types of messages to the vehicle (minimum data set request, checksum error, acknowledgment, other values are reserved).
At the transport level, messages are protected using a shortened block BCH code (60.4). Further, 4-bit symbols are applied to a bipolar pulse-phase modulator (the duration of transmission of one symbol is 5 ms). Thus, sending a single message takes 60 ms. Each transfer is preceded by a synchronization frame and guard intervals before and after the message.
A communication session begins with the sending of a request for a minimum set of data from the transmitter of the control center, while the receiver of the control center constantly analyzes the incoming signal from the telephone network. As soon as the “ERA-GLONASS” signal is detected and synchronization has occurred, a reception error message is sent and the demodulator decodes the stream of characters.
The automatic retransmission request scheme combines the first received message of the minimum data set followed by the repeated send and decodes the turbo code to determine the information bits and check the checksum of the data set. If the checksum does not converge, the receiver of the control center generates an error message and thus requests a retransmission from the vehicle transmitter with increased redundancy. In the case of successful decoding, the data is transmitted to the operator of the control center, the modem of the car receives a message on successful transmission, and the voice path goes into the mode of a normal voice call.
In the passive mode, the control center expects a signal that the minimum set of data is ready to be transmitted from the vehicle. When this signal is detected, the center sends a request for data transfer as in the active mode and the communication session continues as described above.
It is worth noting that the technology of data transmission using a tone modem is basic, but not the only one. For example, if it is impossible to transfer a minimum set of data over a voice connection, they should be sent using the short message service. Packet data transfer is used to transfer additional data, such as the acceleration profile recorded by the accelerometer, this information is necessary to assess the severity of accidents.
According to media reports, from January 1, 2015, all new car models in the EU and the Russian Federation will be equipped with eCall and ERA-GLONASS, respectively. Both systems will work without a monthly fee for car owners.
As can be seen from the technical description of the system, the developers of eCall and ERA have provided a variety of methods for sending data, laid the possibility of working in automatic and manual mode, significantly accelerated the delivery of messages. However, the system itself will not save anyone, it is just an infrastructure to help rescuers and motorists. The lives of people will still depend on the doctors and firefighters, who will have to arrive on time at the scene of the accident.
[!?] Questions and comments are welcome. They will meet the software engineer of the company Promwad, a specialist in the development of embedded software for GPS / GLONASS electronics.
Both of these systems are designed to automatically call emergency services in case of an accident and are aimed at reducing the level of death and injury on the roads.
ERA-GLONASS will be used throughout the country and will become the basis for the integration of all navigation systems in transport. The main components of an ERA are a navigation and telecommunications terminal in a vehicle plus the infrastructure of mobile operators and emergency services. Read about the data transfer technology in this system under habrakat.
')

ERA and eCall correspond to each other in basic functionality: they use a tone modem as the main data transmission mechanism, a unified composition and format of mandatory data, uniform voice connection rules with a car driver, etc. "ERA-GLONASS" is fully compatible with eCall, equipment interchangeability Russian and European systems has been validated in a series of field tests.
An emergency phone call can be made manually by pressing a button. In an emergency, the signal will be sent automatically, because the system will record the operation of the airbags or determine the accident using the accelerometer.
ERA-GLONASS will establish a voice connection with the emergency control center, which during the call will be able to send information about the incident: geographical coordinates, VIN-code, etc. (the so-called minimum data set).
Below is a simplified block diagram of ERA-GLONASS and eCall , it shows the components of the data transfer subsystem:

As can be seen from the figure, the voice path is used to transfer the minimum set of data from the vehicle to the control center. The fact is that this method of message delivery has the highest priority and guaranteed delays. Accordingly, this is the optimal technology compared to the short message service or packet data.
The diagram also shows the components of a cellular network (a radio modem of a base station, a sound transcoder, a switching center), and a public telephone network - all of which are involved in voice stream transmission.
The main components of the modem from the vehicle are shown in the following diagram:

The minimum data set with a length of 140 bytes (1120 bits), which arrived at the transmitter, is supplemented with control information with a length of 28 bits, calculated using the cyclic redundancy code (CRC) algorithm. The received message with a length of 1148 bits is scrambled, robust coding, and interleaved to reduce the sensitivity to data transmission errors. For encoding, the turbo code is used, which is a parallel cascade convolutional code with a rate of 1/3.
This coding scheme gives a stream of different redundancy (the maximum speed is equal to 0.83), which allows to increase the redundancy with each repeated attempt to transfer data. Next, the data stream is combined into three bits of characters, which are converted into a form using bipolar phase-pulse modulation, which is suitable for transmission using voice codecs in cellular communication systems, including GSM Full-Rate and various AMR codec modes.
The sending time of the minimum data set is 1.32 seconds or 2.32 seconds when using the high-speed (1500 bps) and low-speed (750 bps) modes, respectively. Before sending over the air, the signal is supplemented with a synchronization frame with a duration of 260 ms.
The car's receiver can receive messages from the modem of the control center, such as a request for a minimum set of data, an error / acknowledgment. If, during data transmission, an error message in the checksum comes in, the vehicle retransmits the data, simultaneously increasing the redundancy of the error-correcting coding, until a sufficient number of confirmations of successful reception of information is received, or until the dispatch center interrupts the operation. After transferring the data, the modems of the vehicle and the dispatcher go into standby mode, and the audio path is switched to voice transmission.
The main components of the modem from the control center are presented below:

The transmitter of the control center allows you to send up to 16 different types of messages to the vehicle (minimum data set request, checksum error, acknowledgment, other values are reserved).
At the transport level, messages are protected using a shortened block BCH code (60.4). Further, 4-bit symbols are applied to a bipolar pulse-phase modulator (the duration of transmission of one symbol is 5 ms). Thus, sending a single message takes 60 ms. Each transfer is preceded by a synchronization frame and guard intervals before and after the message.
A communication session begins with the sending of a request for a minimum set of data from the transmitter of the control center, while the receiver of the control center constantly analyzes the incoming signal from the telephone network. As soon as the “ERA-GLONASS” signal is detected and synchronization has occurred, a reception error message is sent and the demodulator decodes the stream of characters.
The automatic retransmission request scheme combines the first received message of the minimum data set followed by the repeated send and decodes the turbo code to determine the information bits and check the checksum of the data set. If the checksum does not converge, the receiver of the control center generates an error message and thus requests a retransmission from the vehicle transmitter with increased redundancy. In the case of successful decoding, the data is transmitted to the operator of the control center, the modem of the car receives a message on successful transmission, and the voice path goes into the mode of a normal voice call.
In the passive mode, the control center expects a signal that the minimum set of data is ready to be transmitted from the vehicle. When this signal is detected, the center sends a request for data transfer as in the active mode and the communication session continues as described above.
It is worth noting that the technology of data transmission using a tone modem is basic, but not the only one. For example, if it is impossible to transfer a minimum set of data over a voice connection, they should be sent using the short message service. Packet data transfer is used to transfer additional data, such as the acceleration profile recorded by the accelerometer, this information is necessary to assess the severity of accidents.
According to media reports, from January 1, 2015, all new car models in the EU and the Russian Federation will be equipped with eCall and ERA-GLONASS, respectively. Both systems will work without a monthly fee for car owners.
As can be seen from the technical description of the system, the developers of eCall and ERA have provided a variety of methods for sending data, laid the possibility of working in automatic and manual mode, significantly accelerated the delivery of messages. However, the system itself will not save anyone, it is just an infrastructure to help rescuers and motorists. The lives of people will still depend on the doctors and firefighters, who will have to arrive on time at the scene of the accident.
[!?] Questions and comments are welcome. They will meet the software engineer of the company Promwad, a specialist in the development of embedded software for GPS / GLONASS electronics.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/180689/
All Articles