Launch VMmanager virtual machine management platform
We are pleased to present a new software for managing virtual machines called VMmanager.
Like all our products of the fifth version, it is based on the new software “core” COREmanager 5, which provides a universal interface for both developers and users of our software.
QEMU / KVM is used as the hypervisor, and the libvirt library performs all the operations for managing the hypervisor. We chose KVM as the most dynamically developing and stable solution.
')
Now software installation is carried out through the convenient web-based management interface COREmanager, through which it will also be possible to install our other software products.
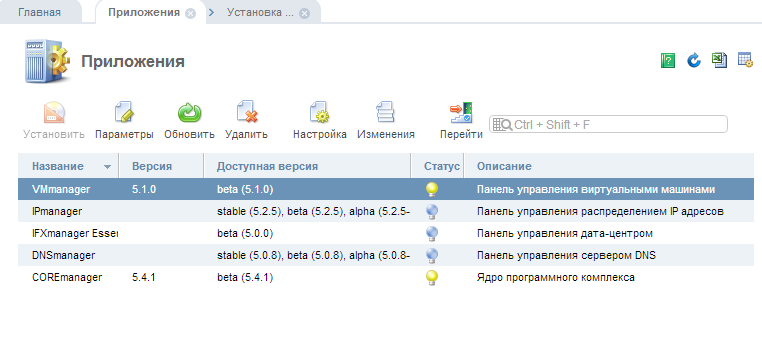
We have developed a new web interface (in the fifth version, the design theme has been changed) codenamed orion, which has more features compared to the old interface, for example, the ability to quickly search the menu, support for tabs.
The screenshots of the control panel show the ability to search the main menu by the first letters of the module name, all links open in tabs and you can always switch between them.
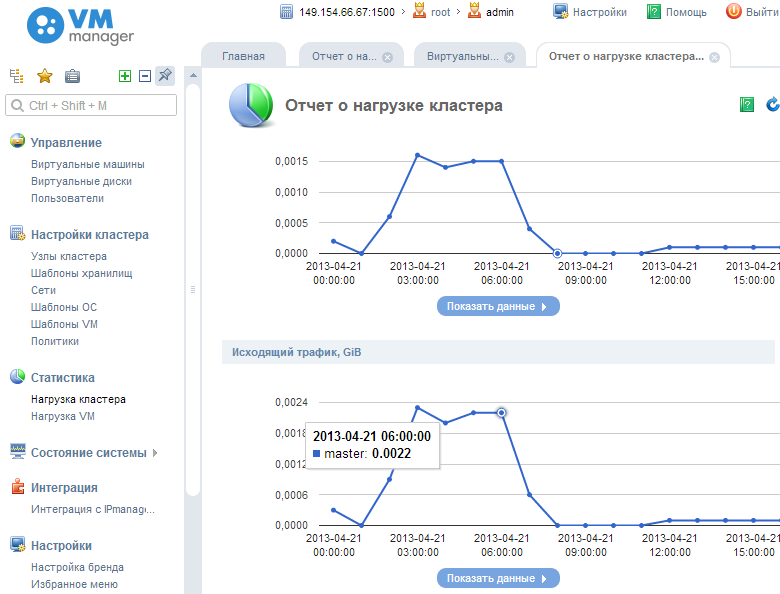
Various statistics information is available, such as load and traffic of the main system, load of virtual machines, you can choose any arbitrary time interval.
When you click on the bend points of the graph, you can see detailed information in the places of its change.
Distinctive features of VMmanager from previous versions of our software for managing virtual machines are enhanced scalability - the management module can be installed on one of the servers, and the remaining servers running virtual machines will be under its control.
Processing requests to the control panel is carried out in multi-threaded mode — requests to several virtual machines can be processed simultaneously.
The web interface now uses its own built-in HTTP server.
VMmanager stores all configuration data of virtual machines in the MySQL database, perhaps both local and remote data storage.
The installation of virtual machines is made from templates that are connected from a shared network drive via the NFS protocol.
It is supported by both the administrator level of virtual dedicated servers and the user. Administrators can create, delete, virtual dedicated servers, manage network settings and server settings. Users can reboot, reinstall the operating system, monitor the status and characteristics of the virtual machine.
VMmanager provides a variety of analytical information on the load of virtual servers and the use of server resources in the form of graphs and tables
An HTML5 VNC client has been added to the VMmanager pane, which can be used to connect to the “local” console of the virtual machine using a standard web browser.
Both local and network data storages, live migration of virtual machines without stopping them, and the rest of the functionality supported by this library are supported.
It is necessary to allocate a server that will be the main cluster machine on which the panel and virtual server templates (NFS storage) will be installed, and servers on which virtual machines will run.
The same operating system and the same virtualization technology are installed on all servers, the cluster nodes are managed via SSH from the main node, using the utilities of the libvirt virtualization management library
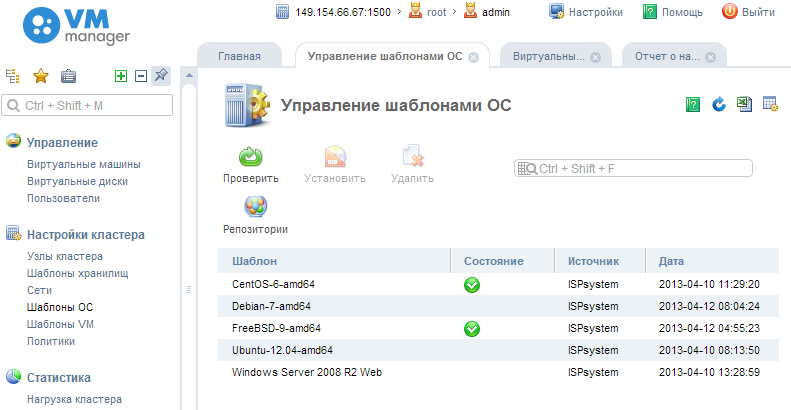
After VMmanager is installed, the templates of the operating systems used are specified, one or several cluster nodes are connected on which virtual machines will be created.

All necessary software (libvirt library, qemu-kvm, lvm) is installed automatically when creating a cluster node, the necessary network settings are also made (creating a bridge interface).
VMmanager automatically monitors the status of cluster nodes and excludes problem nodes from the list of virtual machines available for creation, checks for states such as the inability to connect to a node using the ssh protocol or the inactivity of the libvirt service used to manage virtualization.
When creating a new virtual machine in the VMmanager control panel, it is created on the cluster node and installed from a template that is located on the network storage.
Operating system templates are a metadata file and a set of files to install. Mechanisms for installing the operating system on virtual machines such as kickstart are supported (supported by installation programs of popular Linux distributions based on the question-answer file), the ability to install an installation disk from a modified image (used when installing FreeBSD systems).
It supports the work through the API, integration with our other software products, such as the billing system (BILLmanager), the IP address allocation system (IPmanager).
VMmanager is conceived in two versions: VMmanager Basic and VMmanager Cloud (expected). The basic version differs from Cloud by the lack of additional features, for example, there are no tools for automatically distributing the load across nodes, means for automatically launching virtual machines when one of the nodes on the neighboring node is unavailable, and other additional tools for building cloud architecture.
Additional information and documentation on VMmanager is available on our official website .
Like all our products of the fifth version, it is based on the new software “core” COREmanager 5, which provides a universal interface for both developers and users of our software.
QEMU / KVM is used as the hypervisor, and the libvirt library performs all the operations for managing the hypervisor. We chose KVM as the most dynamically developing and stable solution.
')
Features of the VMmanager 5 user interface
Now software installation is carried out through the convenient web-based management interface COREmanager, through which it will also be possible to install our other software products.

We have developed a new web interface (in the fifth version, the design theme has been changed) codenamed orion, which has more features compared to the old interface, for example, the ability to quickly search the menu, support for tabs.
The screenshots of the control panel show the ability to search the main menu by the first letters of the module name, all links open in tabs and you can always switch between them.

Various statistics information is available, such as load and traffic of the main system, load of virtual machines, you can choose any arbitrary time interval.
When you click on the bend points of the graph, you can see detailed information in the places of its change.

VMmanager features
Distinctive features of VMmanager from previous versions of our software for managing virtual machines are enhanced scalability - the management module can be installed on one of the servers, and the remaining servers running virtual machines will be under its control.
Processing requests to the control panel is carried out in multi-threaded mode — requests to several virtual machines can be processed simultaneously.
The web interface now uses its own built-in HTTP server.
VMmanager stores all configuration data of virtual machines in the MySQL database, perhaps both local and remote data storage.
The installation of virtual machines is made from templates that are connected from a shared network drive via the NFS protocol.
It is supported by both the administrator level of virtual dedicated servers and the user. Administrators can create, delete, virtual dedicated servers, manage network settings and server settings. Users can reboot, reinstall the operating system, monitor the status and characteristics of the virtual machine.
VMmanager provides a variety of analytical information on the load of virtual servers and the use of server resources in the form of graphs and tables
An HTML5 VNC client has been added to the VMmanager pane, which can be used to connect to the “local” console of the virtual machine using a standard web browser.
Both local and network data storages, live migration of virtual machines without stopping them, and the rest of the functionality supported by this library are supported.
Technical details of the work of VMmanager
It is necessary to allocate a server that will be the main cluster machine on which the panel and virtual server templates (NFS storage) will be installed, and servers on which virtual machines will run.
The same operating system and the same virtualization technology are installed on all servers, the cluster nodes are managed via SSH from the main node, using the utilities of the libvirt virtualization management library
After VMmanager is installed, the templates of the operating systems used are specified, one or several cluster nodes are connected on which virtual machines will be created.

All necessary software (libvirt library, qemu-kvm, lvm) is installed automatically when creating a cluster node, the necessary network settings are also made (creating a bridge interface).
VMmanager automatically monitors the status of cluster nodes and excludes problem nodes from the list of virtual machines available for creation, checks for states such as the inability to connect to a node using the ssh protocol or the inactivity of the libvirt service used to manage virtualization.
When creating a new virtual machine in the VMmanager control panel, it is created on the cluster node and installed from a template that is located on the network storage.
Operating system templates are a metadata file and a set of files to install. Mechanisms for installing the operating system on virtual machines such as kickstart are supported (supported by installation programs of popular Linux distributions based on the question-answer file), the ability to install an installation disk from a modified image (used when installing FreeBSD systems).
It supports the work through the API, integration with our other software products, such as the billing system (BILLmanager), the IP address allocation system (IPmanager).
VMmanager is conceived in two versions: VMmanager Basic and VMmanager Cloud (expected). The basic version differs from Cloud by the lack of additional features, for example, there are no tools for automatically distributing the load across nodes, means for automatically launching virtual machines when one of the nodes on the neighboring node is unavailable, and other additional tools for building cloud architecture.
Additional information and documentation on VMmanager is available on our official website .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/176957/
All Articles