NASA has developed a navigation system for interstellar flights

About two hundred years (before the invention of radio navigation), navigators measured the height of the Sun and the Moon using a sextant. Information from two objects is enough to calculate the exact coordinates in space. Now NASA experts have applied the same principle for the development of a global positioning system in space . Instead of the Sun and the Moon, the NICER / SEXTANT space module will determine the direction to neutron stars whose coordinates and trajectories are known rather accurately. Each of the 2000 known pulsars has its own rotation frequency and magnetic field strength, which allows us to create a space analogue of the GPS system.

Using sextant in practice , author: Joaquim Alves Gaspar
A regular sextant is manually guided to the Sun / Moon, and the angle of elevation of the light is displayed on a special scale. After that, the navigator must manually find two suitable position lines in the directory - and their points of intersection.
')

NASA’s NICER / SEXTANT space module will of course work fully automatically.
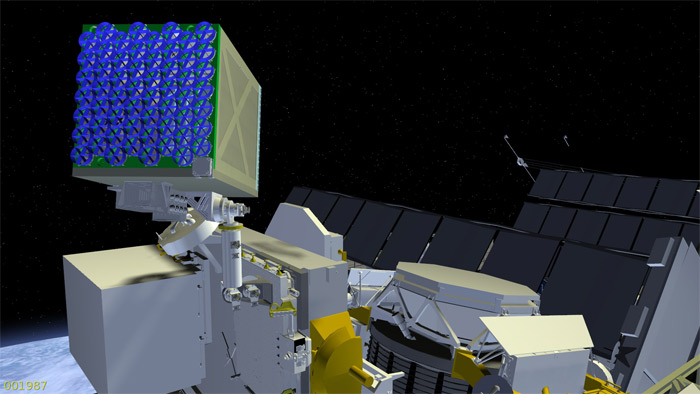
The system determines the sources of x-ray radiation (pulsars), and with the help of special reflectors determines the exact direction to them. NASA specialists want to make an autonomous built-in navigation system on the module that can work without help from the Earth.

Reflective inserts NICER / SEXTANT
The NICER / SEXTANT module contains 56 radio telescopes and detectors, which should record the emission of pulsars with high accuracy. This device, the size of a little more than a refrigerator, is planned to be launched to the International Space Station in 2017. The project cost is about $ 55 million.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/176649/
All Articles