UX / UI. Foreign design experience VS Russia
It's no secret that designing an interface is not just creating a site layout or application mockup. This is a whole set of factors depending on how a person acts, because most of our life consists of interaction with the environment. According to Western colleagues, when designing site layouts, it is imperative to pay attention to a number of factors that influence the interaction between the user and the interface. This is confirmed by a huge number of translations of English-language articles on Habré. And every designer, programmer, or person who is at the beginning of the site's design, inevitably tries to apply such knowledge and techniques in practice, everywhere bumping into misunderstanding and the words: "Yes, this is all theory ...".
The position of the UX-designer appeared on the labor market relatively recently and most often, especially in young companies, does not have an established design culture. In a large company, however, an expert turns into a “draftsman” of interfaces, guided by such arguments as “the button should be on the left, because the person is reading from left to right and will definitely notice it”. Or in the ux-statistician, continuously writing reports based on data from analytics systems [infographics on the topic: Don't Be A UX statistic http://vitamintalent.com/ux-statistic/#Development ].
If you are a fan of your business and work primarily for yourself, then this article will tell you how to apply the works of Garrett, Cooper, Koshik, Raskin and many other authors in practice, in conditions of insufficient time and resources.
Competitive analysis
Any site, first of all, must solve the user's tasks. And your project is no exception. Useful, in this case, will be given to the audience of competitors, because this is your potential visitors.
')
Find out the demographic data users help resource alexa.com. Since the data is provided by the statistics panel, which is not installed by the browser in the entire audience, using the alexa.com panel data is only the first step, so to speak, food for thought.

We are designing a user interaction scheme, not an interface, so information about where the visitor came from, and where this visitor most often goes, may give rise to a worthwhile thought. For example, big traffic from the social network VKontakte speaks of a relatively young age of the audience.
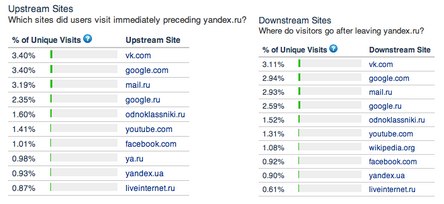
In the case of an installed analytics tool for your site, you should pay attention to the conversion and failure metrics. If the percentage of clicks to search engine sites or competitors' sites goes off-line, it's time to think about changing the solution. Avinash Koshik often mentions this in his book Web Analytics 2.0, a blog and podcasts http://www.kaushik.net/avinash/ .
Along the way, you should look at the geographical location of the target audience and the heat map of Yandex.
If you are attracted by various behavioral (behavioral) studies, then you should pay attention to the Feng-GUI resource, which will help to carry out eye-tracking (eye movement analysis) using artificial intelligence algorithms, without interacting with people.
Characters and Scripts as Tasks
1. Select the main use cases, for this we include ingenuity and rules of logic. In addition, you can ask a question directly to the site user (for example, through his profile in social networks): “Why do you go to site X?”. The answer will be simple and logical: “Read news, download a movie, buy goods, chat with friends” - this will be our main case study.
2. We communicate with interested parties to get answers to the questions:
- Is our audience divided into segments?
- Is it possible to put down the ranks?
3. You can try to get information through those. support of a competitor (if any), namely, try to talk to them in an informal setting. Do you think they will have stories about customers for a “mug” of tea?
For the first time a similar idea was proposed by R. Unger and K. Chandler in their book “UX-design. Designing experience interaction.
Now there is everything to find the right person in the social. network, you can even make friends. The result is a handy list of characters with detailed information.
[photo] Vasya Gennadyevich
Demographics: ...
Psychography: ...
Uses resources: ...
Scenario:…
Tasks (shortened use case):
A, B, C.
For more details on character creation, see A. Cooper's book, Basics of Interaction Design, or R. Unger and K. Chandler, UX Design.
Requirements collection
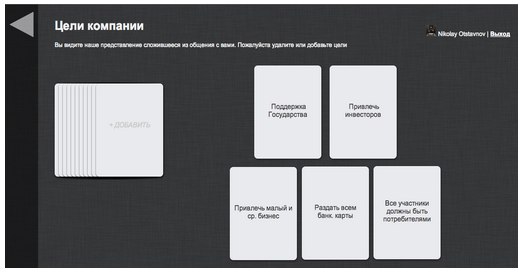
There are a huge number of methods for collecting requirements, but each of them requires waste of temporary resources and high-quality study with interested parties. But we remember that our resources are limited: you need to make a design, typeset and start programming.
Therefore, we take any available card sorting tool:
- http://www.optimalworkshop.com/optimalsort.htm ,
- http://uxpunk.com/websort ,
- http://www.userzoom.com/ ,
- An example of its free (without specified groups) card sorting . If uncomfortable, then MindMap will do.
Then we ask stakeholders to see whether the requirements are true, whether priorities are correctly defined. To save your nerves and time, it is better to intentionally make a set of cards or MindMap is bad, without wasting time on predicting business goals.
You can view and work with goals in the kit remotely, so we ask the managers to comment on the work done, ask the question: “Do these goals correspond to reality?”. Then we have three options for further action:
1. Managers independently form new goals => WIN.
2. Condemn the work done, criticize, put forward arguments, why it is bad - the arguments are precisely the goals => WIN.
3. They do not look and say that everything is fine.
So, two of the three chances that targets will be obtained.
Using card sorting allows you to fully implement the methodology: “KJ Method”, proposed by Ivan Mikhailov at the conference UX Russia 2011.
Features
There are a huge number of functional specification options - in my opinion, the BEM methodology is very good. In addition, we need an information architecture and content requirements. At best, a thoughtful navigation chain in terms of SEO and the mental model of our target audience. But time and resources are limited, so we will use a beautiful object-oriented philosophy, which allows you to start thinking through the information architecture. To do this, absolutely everything must be represented as objects. You can start with the objects "sections", which consist of one field - "name".
Layouts
By this stage, we have already formed ideas about the target audience and its possible needs. In addition, we understand the purpose of the business. Thanks to a simple information architecture, we have an idea of what kind of data we use. And to solve the same type of problems, taking into account our data, it is worth looking at the patterns:
- 40+ Helpful Resources On User Interface Design Patterns .

Do not forget about the cognetics and works for which the whole life was spent - the study of Jeff Raskin. It is enough to remember only one golden rule:
“Whenever there are no significant arguments against, the pattern is justified: an object is an action (for example: make a text bold).”
The design phase and the subsequent steps of the continuous cycle remain. Perhaps, by the time when for the first time you decide to find time in the project for all tasks, the layouts will already be drawn. This means that it is possible to assess how well your work corresponds to the goals you are going to achieve. In any case, information for reflection will be more than enough. This will bring you closer to the balance of logic and emotions of Captain Spock from the Star Trek series.
And if you have the strength, the desire and the enthusiasm to design a terrific interaction experience, the doors of REG.RU are always open for you.
The position of the UX-designer appeared on the labor market relatively recently and most often, especially in young companies, does not have an established design culture. In a large company, however, an expert turns into a “draftsman” of interfaces, guided by such arguments as “the button should be on the left, because the person is reading from left to right and will definitely notice it”. Or in the ux-statistician, continuously writing reports based on data from analytics systems [infographics on the topic: Don't Be A UX statistic http://vitamintalent.com/ux-statistic/#Development ].
If you are a fan of your business and work primarily for yourself, then this article will tell you how to apply the works of Garrett, Cooper, Koshik, Raskin and many other authors in practice, in conditions of insufficient time and resources.
Competitive analysis
Any site, first of all, must solve the user's tasks. And your project is no exception. Useful, in this case, will be given to the audience of competitors, because this is your potential visitors.
')
Find out the demographic data users help resource alexa.com. Since the data is provided by the statistics panel, which is not installed by the browser in the entire audience, using the alexa.com panel data is only the first step, so to speak, food for thought.

We are designing a user interaction scheme, not an interface, so information about where the visitor came from, and where this visitor most often goes, may give rise to a worthwhile thought. For example, big traffic from the social network VKontakte speaks of a relatively young age of the audience.

In the case of an installed analytics tool for your site, you should pay attention to the conversion and failure metrics. If the percentage of clicks to search engine sites or competitors' sites goes off-line, it's time to think about changing the solution. Avinash Koshik often mentions this in his book Web Analytics 2.0, a blog and podcasts http://www.kaushik.net/avinash/ .
Along the way, you should look at the geographical location of the target audience and the heat map of Yandex.
If you are attracted by various behavioral (behavioral) studies, then you should pay attention to the Feng-GUI resource, which will help to carry out eye-tracking (eye movement analysis) using artificial intelligence algorithms, without interacting with people.
Characters and Scripts as Tasks
1. Select the main use cases, for this we include ingenuity and rules of logic. In addition, you can ask a question directly to the site user (for example, through his profile in social networks): “Why do you go to site X?”. The answer will be simple and logical: “Read news, download a movie, buy goods, chat with friends” - this will be our main case study.
2. We communicate with interested parties to get answers to the questions:
- Is our audience divided into segments?
- Is it possible to put down the ranks?
3. You can try to get information through those. support of a competitor (if any), namely, try to talk to them in an informal setting. Do you think they will have stories about customers for a “mug” of tea?
For the first time a similar idea was proposed by R. Unger and K. Chandler in their book “UX-design. Designing experience interaction.
Now there is everything to find the right person in the social. network, you can even make friends. The result is a handy list of characters with detailed information.
[photo] Vasya Gennadyevich
Demographics: ...
Psychography: ...
Uses resources: ...
Scenario:…
Tasks (shortened use case):
A, B, C.
For more details on character creation, see A. Cooper's book, Basics of Interaction Design, or R. Unger and K. Chandler, UX Design.
Requirements collection

There are a huge number of methods for collecting requirements, but each of them requires waste of temporary resources and high-quality study with interested parties. But we remember that our resources are limited: you need to make a design, typeset and start programming.
Therefore, we take any available card sorting tool:
- http://www.optimalworkshop.com/optimalsort.htm ,
- http://uxpunk.com/websort ,
- http://www.userzoom.com/ ,
- An example of its free (without specified groups) card sorting . If uncomfortable, then MindMap will do.
Then we ask stakeholders to see whether the requirements are true, whether priorities are correctly defined. To save your nerves and time, it is better to intentionally make a set of cards or MindMap is bad, without wasting time on predicting business goals.
You can view and work with goals in the kit remotely, so we ask the managers to comment on the work done, ask the question: “Do these goals correspond to reality?”. Then we have three options for further action:
1. Managers independently form new goals => WIN.
2. Condemn the work done, criticize, put forward arguments, why it is bad - the arguments are precisely the goals => WIN.
3. They do not look and say that everything is fine.
So, two of the three chances that targets will be obtained.
Using card sorting allows you to fully implement the methodology: “KJ Method”, proposed by Ivan Mikhailov at the conference UX Russia 2011.
Features
There are a huge number of functional specification options - in my opinion, the BEM methodology is very good. In addition, we need an information architecture and content requirements. At best, a thoughtful navigation chain in terms of SEO and the mental model of our target audience. But time and resources are limited, so we will use a beautiful object-oriented philosophy, which allows you to start thinking through the information architecture. To do this, absolutely everything must be represented as objects. You can start with the objects "sections", which consist of one field - "name".
the main
- Catalog
- - Cabinets: [sorting goods;
search: [input; button];
product: [name; a photo; description; button to the trash; link to detailed page]
product: [...]
...
]
- - - Detailed product page [
Product Name;
3 photos;
specifications;
description;
meta tags;
Comments: [date; author; comment]
]
Layouts
By this stage, we have already formed ideas about the target audience and its possible needs. In addition, we understand the purpose of the business. Thanks to a simple information architecture, we have an idea of what kind of data we use. And to solve the same type of problems, taking into account our data, it is worth looking at the patterns:
- 40+ Helpful Resources On User Interface Design Patterns .

Do not forget about the cognetics and works for which the whole life was spent - the study of Jeff Raskin. It is enough to remember only one golden rule:
“Whenever there are no significant arguments against, the pattern is justified: an object is an action (for example: make a text bold).”
The design phase and the subsequent steps of the continuous cycle remain. Perhaps, by the time when for the first time you decide to find time in the project for all tasks, the layouts will already be drawn. This means that it is possible to assess how well your work corresponds to the goals you are going to achieve. In any case, information for reflection will be more than enough. This will bring you closer to the balance of logic and emotions of Captain Spock from the Star Trek series.
And if you have the strength, the desire and the enthusiasm to design a terrific interaction experience, the doors of REG.RU are always open for you.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/176375/
All Articles