ASP.NET MVC Lesson 6. Authorization
The purpose of the lesson : To study the method of authorization through cookies, the use of standard attributes of access to the controller and the method of the controller. Using IPrincipal. Creating your own module (IHttpModule) and your own IActionFilter filter.
A small digression: In fact, in asp.net mvc all textbooks recommend using the already invented authorization system called AspNetMembershipProvider, it was described in the article http://habrahabr.ru/post/142711/ (access is now closed), but explained This is from the point of view of “press and do not understand what is inside”. When I first met asp.net mvc, it confused me. Further, in this article http://habrahabr.ru/post/143024/ - it is said that it is impossible to use this provider. And I agree with that. Here, we are deep enough to learn all sorts of tricky asp.net mvc standard tricks, so this is one of the main lessons.
A cookie is a piece of information sent by the server to the browser, which the browser returns to the server along with every (almost every) request.
')
The server in the response header writes:
For example:
Browser (if the cookie has not expired) with each request:
Set a cookie (/Areas/Default/Controllers/HomeController.cs):
In Chrome, we check the installation:

For cookies:
Make a breakpoint and check:
Note: you can learn more about cookies at the following link:
http://www.nczonline.net/blog/2009/05/05/http-cookies-explained/
In our case, the authorization will be based on the use of cookies. To do this, we study the following provisions:
Let's get started
Create an IAuthentication interface and its implementation of CustomAuthentication (/Global/Auth/IAuthentication.cs):
Implementation (/Global/Auth/CustomAuthentication.cs):
The essence comes down to the following, when we initialize the request, we access the
A new IRepository.Login method has been added for authorization in IRepository. Implementation in SqlRepository:
UserProvider, in fact, implements the IPrincipal interface (which has role checking and access to IIdentity).
Consider the UserProvider class (/Global/Auth/UserProvider.cs):
Our
In the
Consider the UserIdentity class (/Global/Auth/UserIdentity.cs):
In the
Almost everything is ready. Print CurrentUser in BaseController:
Yes, this is not very correct, as strong binding is present here. Therefore, let's do this, we introduce another interface
And now we will try to initialize it all.
First we add our IAuthentication + CustomAuthentication to the registration to Ninject (/App_Start/NinjectWebCommon.cs):
Then we will create a module that will perform an authorization action on the AuthenticateRequest event:
All salt in lines:
We connect the module to Web.config:
The plan is:
Go. Add
_Layout.cshtml (/Areas/Default/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml):
UserLogin.cshtml (/Areas/Default/Views/Home/UserLogin.cshtml):
LoginController exit controller (/Areas/Default/Controllers/LoginController.cs):
LoginView.cs (/Models/ViewModels/LoginView.cs):
Index.cshtml login page (/Areas/Default/Views/Index.cshtml):
We start and check:

After authorization:
All sources are located at https://bitbucket.org/chernikov/lessons
A small digression: In fact, in asp.net mvc all textbooks recommend using the already invented authorization system called AspNetMembershipProvider, it was described in the article http://habrahabr.ru/post/142711/ (access is now closed), but explained This is from the point of view of “press and do not understand what is inside”. When I first met asp.net mvc, it confused me. Further, in this article http://habrahabr.ru/post/143024/ - it is said that it is impossible to use this provider. And I agree with that. Here, we are deep enough to learn all sorts of tricky asp.net mvc standard tricks, so this is one of the main lessons.
Cookies
A cookie is a piece of information sent by the server to the browser, which the browser returns to the server along with every (almost every) request.
')
The server in the response header writes:
Set-Cookie: value[; expires=date][; domain=domain][; path=path][; secure] For example:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-type: text/html Set-Cookie: name=value Set-Cookie: name2=value2; Expires=Wed, 09-Jun-2021 10:18:14 GMT Browser (if the cookie has not expired) with each request:
GET /spec.html HTTP/1.1 Host: www.example.org Cookie: name=value; name2=value2 Accept: */* Set a cookie (/Areas/Default/Controllers/HomeController.cs):
public ActionResult Index() { var cookie = new HttpCookie() { Name ="test_cookie", Value = DateTime.Now.ToString("dd.MM.yyyy"), Expires = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(10), }; Response.SetCookie(cookie); return View(); } In Chrome, we check the installation:

For cookies:
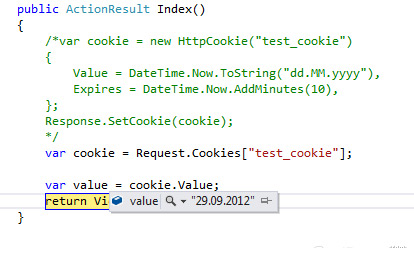
var cookie = Request.Cookies["test_cookie"]; Make a breakpoint and check:

Note: you can learn more about cookies at the following link:
http://www.nczonline.net/blog/2009/05/05/http-cookies-explained/
Authorization
In our case, the authorization will be based on the use of cookies. To do this, we study the following provisions:
- FormsAuthenticationTicket - we will use this class to store authorization data in encrypted form
- You need to implement the IPrincipal interface and set it in
HttpContext.Userto verify the roles andIIdentityinterface. - For interface IIdentity make implementation
- Print in BaseController property CurrentUser the value of the user who is currently logged in.
Let's get started
Create an IAuthentication interface and its implementation of CustomAuthentication (/Global/Auth/IAuthentication.cs):
public interface IAuthentication { /// <summary> /// ( ) /// </summary> HttpContext HttpContext { get; set; } User Login(string login, string password, bool isPersistent); User Login(string login); void LogOut(); IPrincipal CurrentUser { get; } } Implementation (/Global/Auth/CustomAuthentication.cs):
public class CustomAuthentication : IAuthentication { private static NLog.Logger logger = NLog.LogManager.GetCurrentClassLogger(); private const string cookieName = "__AUTH_COOKIE"; public HttpContext HttpContext { get; set; } [Inject] public IRepository Repository { get; set; } #region IAuthentication Members public User Login(string userName, string Password, bool isPersistent) { User retUser = Repository.Login(userName, Password); if (retUser != null) { CreateCookie(userName, isPersistent); } return retUser; } public User Login(string userName) { User retUser = Repository.Users.FirstOrDefault(p => string.Compare(p.Email, userName, true) == 0); if (retUser != null) { CreateCookie(userName); } return retUser; } private void CreateCookie(string userName, bool isPersistent = false) { var ticket = new FormsAuthenticationTicket( 1, userName, DateTime.Now, DateTime.Now.Add(FormsAuthentication.Timeout), isPersistent, string.Empty, FormsAuthentication.FormsCookiePath); // Encrypt the ticket. var encTicket = FormsAuthentication.Encrypt(ticket); // Create the cookie. var AuthCookie = new HttpCookie(cookieName) { Value = encTicket, Expires = DateTime.Now.Add(FormsAuthentication.Timeout) }; HttpContext.Response.Cookies.Set(AuthCookie); } public void LogOut() { var httpCookie = HttpContext.Response.Cookies[cookieName]; if (httpCookie != null) { httpCookie.Value = string.Empty; } } private IPrincipal _currentUser; public IPrincipal CurrentUser { get { if (_currentUser == null) { try { HttpCookie authCookie = HttpContext.Request.Cookies.Get(cookieName); if (authCookie != null && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(authCookie.Value)) { var ticket = FormsAuthentication.Decrypt(authCookie.Value); _currentUser = new UserProvider(ticket.Name, Repository); } else { _currentUser = new UserProvider(null, null); } } catch (Exception ex) { logger.Error("Failed authentication: " + ex.Message); _currentUser = new UserProvider(null, null); } } return _currentUser; } } #endregion } The essence comes down to the following, when we initialize the request, we access the
HttpContext.Request.Cookies and initialize the UserProvider : var ticket = FormsAuthentication.Decrypt(authCookie.Value); _currentUser = new UserProvider(ticket.Name, Repository); A new IRepository.Login method has been added for authorization in IRepository. Implementation in SqlRepository:
public User Login(string email, string password) { return Db.Users.FirstOrDefault(p => string.Compare(p.Email, email, true) == 0 && p.Password == password); } UserProvider, in fact, implements the IPrincipal interface (which has role checking and access to IIdentity).
Consider the UserProvider class (/Global/Auth/UserProvider.cs):
public class UserProvider : IPrincipal { private UserIndentity userIdentity { get; set; } #region IPrincipal Members public IIdentity Identity { get { return userIdentity; } } public bool IsInRole(string role) { if (userIdentity.User == null) { return false; } return userIdentity.User.InRoles(role); } #endregion public UserProvider(string name, IRepository repository) { userIdentity = new UserIndentity(); userIdentity.Init(name, repository); } public override string ToString() { return userIdentity.Name; } Our
UserProvider knows that its IIdentity class is UserIdentity , and therefore it knows about the User class, inside which we implement the InRoles(role) method: public bool InRoles(string roles) { if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(roles)) { return false; } var rolesArray = roles.Split(new[] { "," }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); foreach (var role in rolesArray) { var hasRole = UserRoles.Any(p => string.Compare(p.Role.Code, role, true) == 0); if (hasRole) { return true; } } return false; } In the
InRoles method InRoles we expect to InRoles query about the roles that are allowed to the resource, separated by commas. Ie, for example, “admin, moderator, editor”, if at least one of the roles is in our User - then we return the value “true” (access is available). We compare the field Role.Code, and not Role.Name.Consider the UserIdentity class (/Global/Auth/UserIdentity.cs):
public class UserIndentity : IIdentity { public User User { get; set; } public string AuthenticationType { get { return typeof(User).ToString(); } } public bool IsAuthenticated { get { return User != null; } } public string Name { get { if (User != null) { return User.Email; } // return "anonym"; } } public void Init(string email, IRepository repository) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(email)) { User = repository.GetUser(email); } } } In the
IRepository add a new method GetUser(email) . Implementation for SqlRepository.GetUser() (LessonProject.Model: /SqlRepository/User.cs): public User GetUser(string email) { return Db.Users.FirstOrDefault(p => string.Compare(p.Email, email, true) == 0); } Almost everything is ready. Print CurrentUser in BaseController:
[Inject] public IAuthentication Auth { get; set; } public User CurrentUser { get { return ((UserIndentity)Auth.CurrentUser.Identity).User; } } Yes, this is not very correct, as strong binding is present here. Therefore, let's do this, we introduce another interface
IUserProvider , from which we will demand to return us an authorized User : public interface IUserProvider { User User { get; set; } } … public class UserIndentity : IIdentity, IUserProvider { /// <summary> /// /// </summary> public User User { get; set; } … [Inject] public IAuthentication Auth { get; set; } public User CurrentUser { get { return ((IUserProvider)Auth.CurrentUser.Identity).User; } } And now we will try to initialize it all.
First we add our IAuthentication + CustomAuthentication to the registration to Ninject (/App_Start/NinjectWebCommon.cs):
kernel.Bind<IAuthentication>().To<CustomAuthentication>().InRequestScope(); Then we will create a module that will perform an authorization action on the AuthenticateRequest event:
public class AuthHttpModule : IHttpModule { public void Init(HttpApplication context) { context.AuthenticateRequest += new EventHandler(this.Authenticate); } private void Authenticate(Object source, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication app = (HttpApplication)source; HttpContext context = app.Context; var auth = DependencyResolver.Current.GetService<IAuthentication>(); auth.HttpContext = context; context.User = auth.CurrentUser; } public void Dispose() { } } All salt in lines:
auth.HttpContext = context context.User = auth.CurrentUser . As soon as our authorization module learns about the context and the cookies it contains, the same instantly gets access to the name, it receives the user data in the repository and returns it to the BaseController. But not all at once, but on demand.We connect the module to Web.config:
<system.web> … <httpModules> <add name="AuthHttpModule" type="LessonProject.Global.Auth.AuthHttpModule"/> </httpModules> </system.web> The plan is:
- Upstairs we show whether the user is authorized or not. If authorized, then his email and link to exit, if not, then links to login and registration
- Create a login form
- If the user has entered the data correctly, then we will authorize it and send it to the main page.
- If the user logs out, then we kill his authorization.
Go. Add
Html.Action(“UserLogin”, “Home”) - this is a partial view (ie, a piece of code that does not have a Layout) - that is, it is displayed where it is registered, and not in RenderBody ()._Layout.cshtml (/Areas/Default/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml):
<body> <div class="navbar navbar-fixed-top"> <div class="navbar-inner"> <div class="container"> <ul class="nav nav-pills pull-right"> @Html.Action("UserLogin", "Home") </ul> </div> </div> </div> @RenderBody() HomeController.cs: public ActionResult UserLogin() { return View(CurrentUser); } UserLogin.cshtml (/Areas/Default/Views/Home/UserLogin.cshtml):
@model LessonProject.Model.User @if (Model != null) { <li>@Model.Email</li> <li>@Html.ActionLink("", "Logout", "Login")</li> } else { <li>@Html.ActionLink("", "Index", "Login")</li> <li>@Html.ActionLink("", "Register", "User")</li> } LoginController exit controller (/Areas/Default/Controllers/LoginController.cs):
public class LoginController : DefaultController { [HttpGet] public ActionResult Index() { return View(new LoginView()); } [HttpPost] public ActionResult Index(LoginView loginView) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { var user = Auth.Login(loginView.Email, loginView.Password, loginView.IsPersistent); if (user != null) { return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } ModelState["Password"].Errors.Add(" "); } return View(loginView); } public ActionResult Logout() { Auth.LogOut(); return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } } LoginView.cs (/Models/ViewModels/LoginView.cs):
public class LoginView { [Required(ErrorMessage = " email")] public string Email { get; set; } [Required(ErrorMessage = " ")] public string Password { get; set; } public bool IsPersistent { get; set; } } Index.cshtml login page (/Areas/Default/Views/Index.cshtml):
@model LessonProject.Models.ViewModels.LoginView @{ ViewBag.Title = ""; Layout = "~/Areas/Default/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml"; } <h2></h2> @using (Html.BeginForm("Index", "Login", FormMethod.Post, new { @class = "form-horizontal" })) { <fieldset> <legend></legend> <div class="control-group"> <label class="control-label" for="Email"> Email</label> <div class="controls"> @Html.TextBox("Email", Model.Email, new { @class = "input-xlarge" }) <p class="help-block"> Email</p> @Html.ValidationMessage("Email") </div> </div> <div class="control-group"> <label class="control-label" for="Password"> </label> <div class="controls"> @Html.Password("Password", Model.Password, new { @class = "input-xlarge" }) @Html.ValidationMessage("Password") </div> </div> <div class="form-actions"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary"> </button> </div> </fieldset> } We start and check:

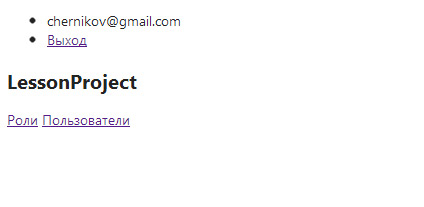
After authorization:

All sources are located at https://bitbucket.org/chernikov/lessons
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/176043/
All Articles