The romance of the north: satellite posts at base stations, a shovel and an incredible amount of snow
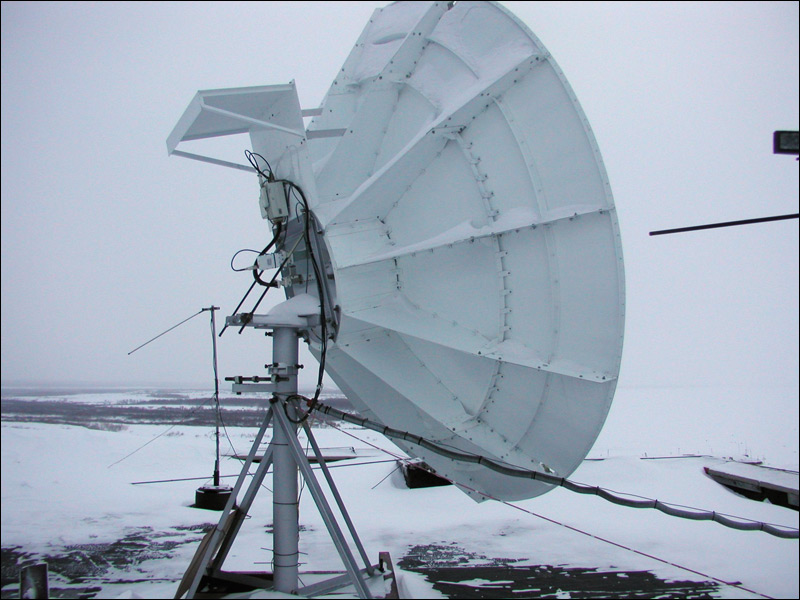

Satellite post, P. Dickson
Krasnoyarsk Territory is the largest by area in the Russian Federation. The territory is huge, and the lived-in part is quite small. Part of the settlements, especially in the northern regions of the region, become difficult to access after the termination of navigation on the Yenisei - that is, about 7 months a year there is only air transport or a winter road.
Many settlements were founded as early as the 17th century, and still exist. Such villages mainly serve as supporting bases for geologists, oilmen, gold miners and other people whose work is closely intertwined with the north.
')
In all these villages, cellular communication is the only way to communicate with the mainland, as well as the opportunity to access the Internet. The first GSM base station "Beeline", working through the "satellite", was put into operation in 2003 in the village of Tura.

Local "all-terrain vehicle", p. Sentry, Taimyr
General situation
In the Krasnoyarsk Territory, Beeline cellular base stations are installed in virtually every large remote village. For example, settlements along the Yenisei River: Bor, Turukhansk are located to the Arctic Circle, and Igarka, Dudinka, Dickson are located beyond the Arctic Circle in the zone of permafrost, you can get here relatively easily. But in Baikit, Khatanga or Tura can be reached in most cases only by air.
Base stations are also installed in oil and gas fields. For example, there is the Vankor oil and gas field: not only GSM base stations are installed there, but also 3G, because the need for communication is more than high. The base station in the port of Dickson is the most northern station "Beeline", located far beyond the Arctic Circle.
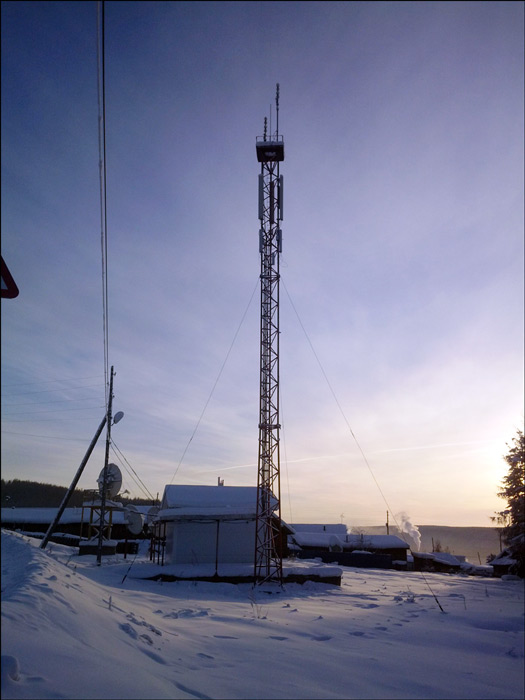

Base station and satellite post, Baikit
Construction and maintenance
The biggest problem in the construction of such base stations is the delivery of equipment, equipment and components. The easiest case is to load equipment into standard 20-ton containers during navigation, put them on ships and send them to the desired point along the Yenisei. Ships go to Dixon. In Khatanga to deliver the necessary equipment will work only by air, since the navigation period is very short.
Base stations are installed standard (previously installed Ericsson 2206, now Ericsson 6601), the main units are the same as throughout the network (we are not talking about cooling and power). To any base station should be suitable transport channel that connects it to the network operator. For the most distant base stations, a double-sided satellite channel acts as such a channel: a satellite dish installed next to the base station and a satellite modem.
Large satellite hubs have been installed in large cities to provide a large band: several base stations are connected with them at once. For example, if the call goes from Dixon to Norilsk, then the scheme would be:
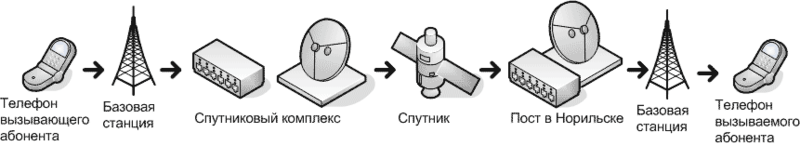
At the same time, the satellite is located at an altitude of 36 thousand kilometers above the ground in the geostationary orbit, and the total delay in signal transmission can reach 0.5-1.5 seconds. These delays are valid for both voice and data transmission.
Large satellite nodes can operate with several satellites in different modes. Small satellite posts near remote stations, as a rule, are guided by a pre-selected satellite where satellite capacity is leased. There are several satellites that can be used for work: it is estimated that both the technical capability to serve this region (not every satellite serves the regions of the far north) and the cost of renting onboard capacity. Each time a new base station is launched, the network development department selects the most suitable satellite.
Satellite nodes in large cities are usually placed on the roof of buildings or on a special platform outside the city, at remote sites - on special metal frames or suitable for building a building so that there is no antenna shift due to ground movements.
In servicing such remote satellite posts there is a major problem - snow. He is able to fall asleep plate "with a slide", which can lead to a deterioration of the signal, and to its complete disappearance. Therefore, one of the main service tools is a shovel and a broom, which, like a brush, with archaeological accuracy, it is necessary to dig out a plate without hitting the converter and not changing its azimuth.
Mid-May in Norilsk:
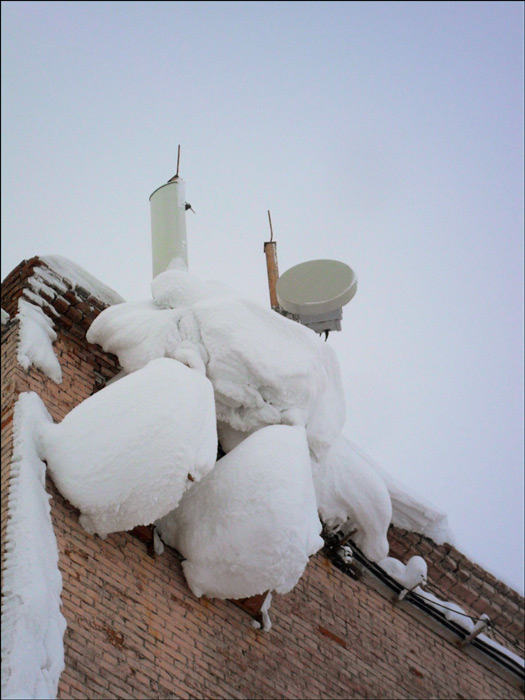


Actually, the service is carried out as follows: in every village there are specialists who are responsible for local communications (for example, engineers serving television stations in the villages). We make arrangements with them for maintenance, since we cannot keep a special person near each base station. Approximately 80% of situations are solved thanks to them, in the remaining 20%, replacement units and a Beeline specialist are sent by air transport.
Base stations are installed in specially prepared for this room, where there is a mandatory waterproofing, antistatic, and so on, as well as enhanced insulation. A mandatory anti-fire door is installed. There are sensors of fire, flooding and, in general, a full set of monitoring that allows you to remotely understand what is wrong in case of malfunctions.
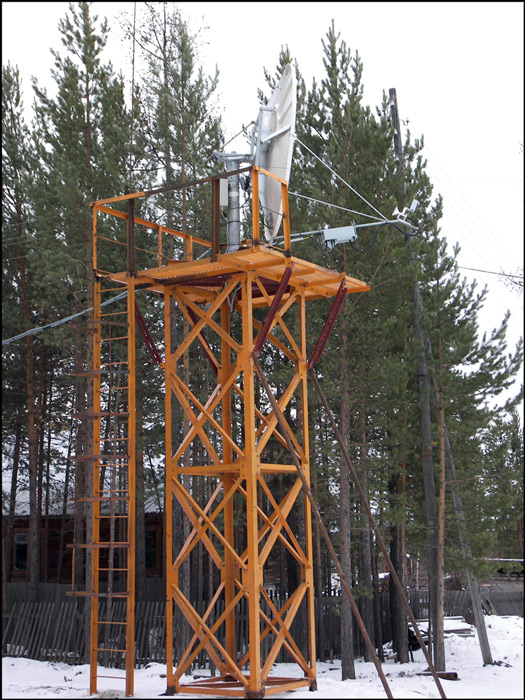

Satellite post, with. Vanavara
Connection
As I said, they use communication very actively. The fact is that at 6 pm there is simply nothing to do in most remote locations, therefore cellular communication and the Internet are highly popular. In recent years, there has been a real explosion in the use of social networks. To this it is worth adding that in the society there is a very high percentage of people under 30, who are happy to accept new technologies. And smartphones are very common. The income of people in the far north is quite high, there is no place to spend money (the villages are cut off from the whole world), so when a person goes to the big land, among other things, he almost always buys a top smartphone.
Where GSM base stations are currently used, there are GPRS / EDGE channels, but the data transfer rate to them is very dependent on the traffic load of the channel with voice traffic. Given that the load is always 100% (even at night there are no breaks at all), the speed is not the highest. Where 3G base stations are installed, we set them up primarily for data transfer, not voice.
In the last measurements of speed in one rotational settlement of oilmen, we received a speed of about 2 Mbit / s on a conventional 3G modem when downloading a long file (this is in a real situation, when there were many active subscribers using mobile Internet in a cell). At the same time, HTML pages can be loaded rather slowly due to a very long ping via satellite (I remind you, from half a second to one and a half, nobody has canceled the speed limit of light).
Why speed can vary within such limits? Because today, there may be, say, 3,000 workers at the field, and tomorrow there will be a shift of duty - and the number of employees will increase to 12,000 people, and at least half of them will communicate with their friends and relatives in other cities, including through Skype
At industrial facilities, M2M is used rather extensively - napimer, near the North-Yenisei gold ore is carried at BelAZ, and each of them has a block, which is continuously monitored.
Development
Since 2003 and the first base station connected via satellite in Tours, we have done very well the construction process and the inclusion of new base stations. In recent years, cellular and Internet consumption in the region has been growing very actively, so we continue to expand. Now we are waiting for the summer to open the navigation, and we could begin to mount several more new base stations at once.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/175069/
All Articles