Biometrics 2013: it's time to abandon bank cards. Dream?
It sounds loud, but the reality is that this technology is already in beta testing on one of the branches of a large Russian bank.
I managed to pull the network, here, quite interesting information with the consent of the developers. I want to talk about current developments in this area from hardware to algorithms. I emphasize that this is a Russian development, the company's staff is not so big, but enough to wipe the nose in international tests for many competitors.

On Habré there were already articles on biometrics, but with rather outdated information, so I tried to collect all the hot questions from them and ask the founder of the Sonda company, Anatoly Bokov.
')
Two of our habrayusers gave their expert opinion on the results of tests of the basis of this technology: A good result for fingers.
Write your questions in the comments, because they have already decided on the second post.
There was a head. The Chair of Automatics at the CPP, defended a thesis on pattern recognition, and that is why in 1989 I was offered to start creating a fingerprint identification system. The topic was too serious, and in 1991 I left the institute and fully engaged in a new topic - the creation of an AFIS for criminologists. And only 10 years ago we began to look at the possibility of civilian application of identification systems.

This is a very serious problem in our country - there is no one to do science. Despite the fact that we have formally one doctor of science and four candidates, only two are seriously engaged in research:
Each one has two assistants, each a mathematician and programmer. To keep pure mathematics ineffective, all experiments are performed immediately on the program. Young people do not want to do science, they need a lot of money at once. Only in the last five years, 7 of our students have gone abroad. And this is not only our problem - common to the country. Already programmers will soon be impossible to find.
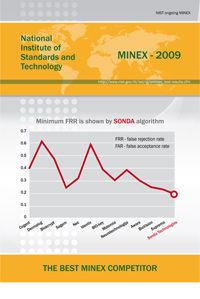 Tests are carried out by two organizations - the National Institute of Standards of the USA (NIST) and the International Biometric Association (these are a number of universities in the USA, Canada, and Europe). The orientation of the NIST tests is more for criminologists (the tests themselves are prepared by the FBI), and the association tests are more for civilian use. Now NIST carries out the most difficult test on the database of 10 million dactycards .
Tests are carried out by two organizations - the National Institute of Standards of the USA (NIST) and the International Biometric Association (these are a number of universities in the USA, Canada, and Europe). The orientation of the NIST tests is more for criminologists (the tests themselves are prepared by the FBI), and the association tests are more for civilian use. Now NIST carries out the most difficult test on the database of 10 million dactycards .
For the first time, not only the probability of errors will be taken into account, but also the search speed. According to the test results, there will be a visible tangible redistribution of the biometrics market by fingerprints. A total of 22 companies showed up, but some have already disappeared, even at the intermediate trial testing. I have 13 companies left. Our task is to get into the top five.
Why such attention is paid to this test? Life challenged - it's time to implement identification systems on databases of hundreds of millions of citizens. Old technologies do not pass - too expensive systems turn out. To implement such systems, it was necessary to algorithmically increase the search speed hundreds of times. And this is a chance for new teams, since at the present time three monsters have practically divided the national level systems market, these are NEC (Japan), Sagem / Morfo (France), 3M / Cogent (USA).
There is no complete project with banks yet, work has begun only at Leto Bank (VTB24 subsidiary), and negotiations are underway with several banks, both large ones such as Sberbank and Gazprombank, and regional ones. Most likely this year we are implementing a full project with several regional banks, there is less bureaucracy.
Banks are very interested, cards create a lot of problems for them. But it takes time. Let's start working with virtual cards, since for this you do not need to change the legislation. And to work directly with customer accounts - there are problems in the legislation.
With dummies actually more noise than problems. First, there are scanners that most dummies detect. Although of course this struggle is eternal. Secondly, there are organizational ways to fight - install scanners in public places whenever possible. We use double finger insertion, and the second time the scanner tells you exactly which finger to attach. To do dummies on all 10 fingers - it is improbable. There is also a “disturbing finger” - it must be applied under duress, the account will be blocked and the alarm signal will go to the law enforcement authorities. We for payment systems make a special scanner, where all this is provided.
The most effective dummy resistant scanners from Lumidigm (USA) and NEC (Japan). The first scanner uses multi-spectral radiation that penetrates the skin. And the second scanner uses not only the image of a print, but also a pattern of veins. Even if you make a dummy pattern on the print, then the pattern of the veins can not be replaced. We actively cooperate with both companies, there are samples of their scanners. Into your payment terminal, we insert either one of these scanners, or, most likely, our own protection system, over which we have been working for a long time.
 We in our scanners have two types of highlights. One traditional - from the bottom through the prism, and the second - through the finger on each side of the finger. We made this illumination in order to ensure uniform illumination over the entire surface of the cylindrical indentation, but unexpectedly got a second effect - the dependence of the image quality of the imprint on the skin condition (dry, wet) decreased. Also, there was a protection against dummies - you can measure the pulse and the illumination is sharply reduced when dummy films are applied to your finger. We also increased the resolution, which is important for kids and old people (they have many folds on the skin of their fingers).
We in our scanners have two types of highlights. One traditional - from the bottom through the prism, and the second - through the finger on each side of the finger. We made this illumination in order to ensure uniform illumination over the entire surface of the cylindrical indentation, but unexpectedly got a second effect - the dependence of the image quality of the imprint on the skin condition (dry, wet) decreased. Also, there was a protection against dummies - you can measure the pulse and the illumination is sharply reduced when dummy films are applied to your finger. We also increased the resolution, which is important for kids and old people (they have many folds on the skin of their fingers).

A serious problem is that in Russia it is impossible to organize competitive devices, there is no high-tech infrastructure at normal market prices. All production is designed for military commissary, where prices do not look. We work more with Hong Kong than with China. Moreover, in Hong Kong, found companies that are either fully founded by Russian, or with the participation of Russian. Therefore, there are no problems, we go through the usual cycles: prototypes, corrections, and the release of a serial batch.
In China, we work only with an optical company. I must say that we found a good company, located near the border with Hong Kong, and export-oriented. They react to comments normally, ours are often worse. And the quality - we were amazed that the quality is better than in Yekaterinburg at the famous optical-mechanical plant and three times cheaper.
To adapt to the customs, the Urals - this is not Moscow, do without bribes.
To reduce the cost - you need to change the design, make it more technological with a smaller number of components and with a decrease in manual labor. Consider the possibility of manufacturing parts of plastic optics. Also, cost of production significantly decreases when ordering large quantities.
The feature of the fingerprint identification task is the inability to index the database. Virtually complete enumeration of the base, the meaning of search accelerators is to learn how to immediately discard other people's prints. Our model of the description of a print is based on the description of the topology; therefore, independence from the deformations of the prints and from the scale appears. Small cuts are not terrible, as the description is redundant. For severe injuries, use other fingers. We always register several fingers in the database. In the access control system and in the payment system, a person is interested in being correctly identified and special measures are not required.
We set a goal - several million citizens . True for reliability and for dealing with false positives - be sure to use two fingers. On international tests, where prints were obtained using optical scanners, we recorded the probability of false positives at about one error per thousand cases. When using two fingers, there will be a product of probabilities — one error per million cases.
I see this problem as the main one in the payment project, but we calmly treat it. There are several options for reducing such errors. As we work, we will apply certain measures.
We already have an implementation of a system with a database of 6 million (this is in Guinea), and now it will expand to 10 million ... National level systems, including migrant control systems, use 10-finger registration and there is no reliability problems (almost 100% reliability). We, and all other biometric companies, use classical calculators - servers with multi-core processors. We have the usual integer arithmetic and many reboring problems. Algorithmic acceleration is much more efficient than hardware. At the moment, almost all companies have abandoned the use of special processors, the algorithms are changing very quickly.
Thanks for attention.
Ps. if anyone has questions, leave in the comments. We will do with you if you have the desire.
I managed to pull the network, here, quite interesting information with the consent of the developers. I want to talk about current developments in this area from hardware to algorithms. I emphasize that this is a Russian development, the company's staff is not so big, but enough to wipe the nose in international tests for many competitors.

On Habré there were already articles on biometrics, but with rather outdated information, so I tried to collect all the hot questions from them and ask the founder of the Sonda company, Anatoly Bokov.
')
Two of our habrayusers gave their expert opinion on the results of tests of the basis of this technology: A good result for fingers.
Write your questions in the comments, because they have already decided on the second post.
Tell us a little about how you got into this area. How did it all start?
There was a head. The Chair of Automatics at the CPP, defended a thesis on pattern recognition, and that is why in 1989 I was offered to start creating a fingerprint identification system. The topic was too serious, and in 1991 I left the institute and fully engaged in a new topic - the creation of an AFIS for criminologists. And only 10 years ago we began to look at the possibility of civilian application of identification systems.

How many people do you have in the scientific field? All maths and programmers or is there someone else?
This is a very serious problem in our country - there is no one to do science. Despite the fact that we have formally one doctor of science and four candidates, only two are seriously engaged in research:
- Gudkov - processing of prints and the formation of templates
- Mosunov - a comparison of patterns and most importantly - search accelerators.
Each one has two assistants, each a mathematician and programmer. To keep pure mathematics ineffective, all experiments are performed immediately on the program. Young people do not want to do science, they need a lot of money at once. Only in the last five years, 7 of our students have gone abroad. And this is not only our problem - common to the country. Already programmers will soon be impossible to find.
I know that according to international tests you took no further than 5th place, but where is the first. Tell us in more detail how tests are carried out, by whom and by what criteria does the comparison take place? How good are the competitors and what do they have your hands on?
 Tests are carried out by two organizations - the National Institute of Standards of the USA (NIST) and the International Biometric Association (these are a number of universities in the USA, Canada, and Europe). The orientation of the NIST tests is more for criminologists (the tests themselves are prepared by the FBI), and the association tests are more for civilian use. Now NIST carries out the most difficult test on the database of 10 million dactycards .
Tests are carried out by two organizations - the National Institute of Standards of the USA (NIST) and the International Biometric Association (these are a number of universities in the USA, Canada, and Europe). The orientation of the NIST tests is more for criminologists (the tests themselves are prepared by the FBI), and the association tests are more for civilian use. Now NIST carries out the most difficult test on the database of 10 million dactycards .For the first time, not only the probability of errors will be taken into account, but also the search speed. According to the test results, there will be a visible tangible redistribution of the biometrics market by fingerprints. A total of 22 companies showed up, but some have already disappeared, even at the intermediate trial testing. I have 13 companies left. Our task is to get into the top five.
Why such attention is paid to this test? Life challenged - it's time to implement identification systems on databases of hundreds of millions of citizens. Old technologies do not pass - too expensive systems turn out. To implement such systems, it was necessary to algorithmically increase the search speed hundreds of times. And this is a chance for new teams, since at the present time three monsters have practically divided the national level systems market, these are NEC (Japan), Sagem / Morfo (France), 3M / Cogent (USA).
You are aiming at the banking sector, and you are raising the question of refusing credit cards. Do you already have projects running in this technology?
There is no complete project with banks yet, work has begun only at Leto Bank (VTB24 subsidiary), and negotiations are underway with several banks, both large ones such as Sberbank and Gazprombank, and regional ones. Most likely this year we are implementing a full project with several regional banks, there is less bureaucracy.
Banks are very interested, cards create a lot of problems for them. But it takes time. Let's start working with virtual cards, since for this you do not need to change the legislation. And to work directly with customer accounts - there are problems in the legislation.
How does the scanner guess the dummy? Today there are 3D printers printing gram plates. Is this the war of the future? Printers and scanners?
With dummies actually more noise than problems. First, there are scanners that most dummies detect. Although of course this struggle is eternal. Secondly, there are organizational ways to fight - install scanners in public places whenever possible. We use double finger insertion, and the second time the scanner tells you exactly which finger to attach. To do dummies on all 10 fingers - it is improbable. There is also a “disturbing finger” - it must be applied under duress, the account will be blocked and the alarm signal will go to the law enforcement authorities. We for payment systems make a special scanner, where all this is provided.
The most effective dummy resistant scanners from Lumidigm (USA) and NEC (Japan). The first scanner uses multi-spectral radiation that penetrates the skin. And the second scanner uses not only the image of a print, but also a pattern of veins. Even if you make a dummy pattern on the print, then the pattern of the veins can not be replaced. We actively cooperate with both companies, there are samples of their scanners. Into your payment terminal, we insert either one of these scanners, or, most likely, our own protection system, over which we have been working for a long time.
Optical multispectral fingerprint sensor lumidigm
Lumidigm has developed a multi-spectral imaging device that is able to collect additional information from the bottom layer of the skin of a finger. Unlike traditional technologies, multispectral technology does not depend on the quality and authenticity of fingerprints. Lumidigm sensor can see the image through the top layer of the skin of the finger, to check its authenticity and increase the identifying image. If a person with a worn fingerprint pattern (for example, a carpenter) applies a finger for comparison, the Lumidigm sensor reads a unique, unaffected, internal fingerprint pattern under the skin of the finger and enlarges the image for comparison. Also, if the finger is wet or dirty, or not fully placed on the reader, the multi-spectral reading technology is able to recognize a unique pattern of the lower layer of the skin of the finger. The Lumidigm sensor is a unique device for detecting fake fingers. Multispectral technology makes it easy to detect a false finger, knowing the characteristics of "live" skin. The technology makes it possible to compare the subsurface and the surface layer in order to ascertain their identity.
Lumidigm has developed a multi-spectral imaging technology that allows you to collect additional information from the bottom layer of the surface of the skin of the finger. The multispectral sensor has 2 main components: a light source, an imaging system. Unlike the TIR sensor, these components are designed specifically to avoid the phenomenon of total internal reflection. The multispectral system uses multiple wavelengths of light rather than quasi-monochrome, as is commonly used in TIR sensors. Linear polarization illumination allows multi-spectral light to penetrate the surface of the skin. Multispectral sensor allows you to collect more information from a finger than optical TIR sensors.
TIR sensors are precise devices when quality and genuine fingers are presented to them. However, this situation is not as common as you may think. When a finger is not completely placed on the sensor, or is dry, the image from the TIR sensor will be incomplete. At the same time, multispectral sensors are able to use information from the bottom layer of a finger in order to enlarge the image later. TIR sensors reflect any finger crests, even if they are fake, the Lumidigm sensor is able to see below to reject a fake finger. Multispectral sensors are also effective in high humidity and bright light, with dry fingers.
A multispectral sensor is able to detect a living finger from a false one. The figure shows the difference in the spectral characteristics of the subsurface and surface layer for a live and false finger. Knowing this data, the Lumidigm sensor will easily detect a fake finger. Since the internal structure of the skin layer of the finger depends on the external, which will determine the real finger. When the finger is located on the sensor, blood is faded. Since the sensor sees the inner layer of the skin of the finger, it can detect this fact.

Traditional optical sensors work in limited environmental conditions. Lumidigm sensors are ideal for working in extreme environmental conditions.
Water (rain or sweat, for example), ambient light, dryness, dirty finger will not interfere with the multispectral technology Lumidigm, since direct contact of the finger with the sensor is not required. This allows the sensor to work with dry and covered with "urban" dirt with your fingers.
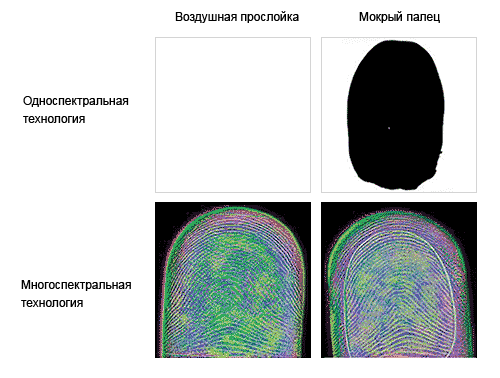
The picture shows two extreme situations: the finger does not touch the sensor, and the wet finger. In both cases, the ability of multispectral technology to recognize the finger is visible.
Direct sunlight has a negative effect on fingerprint scanning in most optical sensors, the multi-spectral Lumidigm sensor is specifically designed for reliable use in outdoor conditions in direct sunlight.

Revolutionary fingerprint recognition technology
Lumidigm has developed a multi-spectral imaging device that is able to collect additional information from the bottom layer of the skin of a finger. Unlike traditional technologies, multispectral technology does not depend on the quality and authenticity of fingerprints. Lumidigm sensor can see the image through the top layer of the skin of the finger, to check its authenticity and increase the identifying image. If a person with a worn fingerprint pattern (for example, a carpenter) applies a finger for comparison, the Lumidigm sensor reads a unique, unaffected, internal fingerprint pattern under the skin of the finger and enlarges the image for comparison. Also, if the finger is wet or dirty, or not fully placed on the reader, the multi-spectral reading technology is able to recognize a unique pattern of the lower layer of the skin of the finger. The Lumidigm sensor is a unique device for detecting fake fingers. Multispectral technology makes it easy to detect a false finger, knowing the characteristics of "live" skin. The technology makes it possible to compare the subsurface and the surface layer in order to ascertain their identity.
Multispectral fingerprint recognition technology
Lumidigm has developed a multi-spectral imaging technology that allows you to collect additional information from the bottom layer of the surface of the skin of the finger. The multispectral sensor has 2 main components: a light source, an imaging system. Unlike the TIR sensor, these components are designed specifically to avoid the phenomenon of total internal reflection. The multispectral system uses multiple wavelengths of light rather than quasi-monochrome, as is commonly used in TIR sensors. Linear polarization illumination allows multi-spectral light to penetrate the surface of the skin. Multispectral sensor allows you to collect more information from a finger than optical TIR sensors.
Is subsurface information really necessary?
TIR sensors are precise devices when quality and genuine fingers are presented to them. However, this situation is not as common as you may think. When a finger is not completely placed on the sensor, or is dry, the image from the TIR sensor will be incomplete. At the same time, multispectral sensors are able to use information from the bottom layer of a finger in order to enlarge the image later. TIR sensors reflect any finger crests, even if they are fake, the Lumidigm sensor is able to see below to reject a fake finger. Multispectral sensors are also effective in high humidity and bright light, with dry fingers.
Fake finger protection
A multispectral sensor is able to detect a living finger from a false one. The figure shows the difference in the spectral characteristics of the subsurface and surface layer for a live and false finger. Knowing this data, the Lumidigm sensor will easily detect a fake finger. Since the internal structure of the skin layer of the finger depends on the external, which will determine the real finger. When the finger is located on the sensor, blood is faded. Since the sensor sees the inner layer of the skin of the finger, it can detect this fact.

Work in extreme conditions
Traditional optical sensors work in limited environmental conditions. Lumidigm sensors are ideal for working in extreme environmental conditions.
Wet conditions
Water (rain or sweat, for example), ambient light, dryness, dirty finger will not interfere with the multispectral technology Lumidigm, since direct contact of the finger with the sensor is not required. This allows the sensor to work with dry and covered with "urban" dirt with your fingers.

The picture shows two extreme situations: the finger does not touch the sensor, and the wet finger. In both cases, the ability of multispectral technology to recognize the finger is visible.
Direct sunlight
Direct sunlight has a negative effect on fingerprint scanning in most optical sensors, the multi-spectral Lumidigm sensor is specifically designed for reliable use in outdoor conditions in direct sunlight.
In addition to the prism of a 120-degree finger, your scanners are scanned in infrared light to avoid unnecessary information getting in the form of dirt on the sensor surface. What else do they have?
 We in our scanners have two types of highlights. One traditional - from the bottom through the prism, and the second - through the finger on each side of the finger. We made this illumination in order to ensure uniform illumination over the entire surface of the cylindrical indentation, but unexpectedly got a second effect - the dependence of the image quality of the imprint on the skin condition (dry, wet) decreased. Also, there was a protection against dummies - you can measure the pulse and the illumination is sharply reduced when dummy films are applied to your finger. We also increased the resolution, which is important for kids and old people (they have many folds on the skin of their fingers).
We in our scanners have two types of highlights. One traditional - from the bottom through the prism, and the second - through the finger on each side of the finger. We made this illumination in order to ensure uniform illumination over the entire surface of the cylindrical indentation, but unexpectedly got a second effect - the dependence of the image quality of the imprint on the skin condition (dry, wet) decreased. Also, there was a protection against dummies - you can measure the pulse and the illumination is sharply reduced when dummy films are applied to your finger. We also increased the resolution, which is important for kids and old people (they have many folds on the skin of their fingers).Who is in charge of your hardware, who is writing the drivers, and how is the communication with the Chinese at the factory? How do you feel about custom products, the first samples were terrible? How troublesome are you with the problem of importing and clearing your products across the border? What can be done to reduce the cost of scanners?

A serious problem is that in Russia it is impossible to organize competitive devices, there is no high-tech infrastructure at normal market prices. All production is designed for military commissary, where prices do not look. We work more with Hong Kong than with China. Moreover, in Hong Kong, found companies that are either fully founded by Russian, or with the participation of Russian. Therefore, there are no problems, we go through the usual cycles: prototypes, corrections, and the release of a serial batch.
In China, we work only with an optical company. I must say that we found a good company, located near the border with Hong Kong, and export-oriented. They react to comments normally, ours are often worse. And the quality - we were amazed that the quality is better than in Yekaterinburg at the famous optical-mechanical plant and three times cheaper.
To adapt to the customs, the Urals - this is not Moscow, do without bribes.
To reduce the cost - you need to change the design, make it more technological with a smaller number of components and with a decrease in manual labor. Consider the possibility of manufacturing parts of plastic optics. Also, cost of production significantly decreases when ordering large quantities.
How are databases built for storing a fingerprint model mat? Here I have a couple of scratches appeared for a couple of years, what is the reaction of the scanner to cuts and other damage? What to do in this case?
The feature of the fingerprint identification task is the inability to index the database. Virtually complete enumeration of the base, the meaning of search accelerators is to learn how to immediately discard other people's prints. Our model of the description of a print is based on the description of the topology; therefore, independence from the deformations of the prints and from the scale appears. Small cuts are not terrible, as the description is redundant. For severe injuries, use other fingers. We always register several fingers in the database. In the access control system and in the payment system, a person is interested in being correctly identified and special measures are not required.
How much can a shower hang on one fingerprint using your scanners? According to the information in the network, I heard that the bases of more than 2 thousand prints may already give false positives. But if the goal is banks, we are already talking about bases of hundreds of thousands of people.
We set a goal - several million citizens . True for reliability and for dealing with false positives - be sure to use two fingers. On international tests, where prints were obtained using optical scanners, we recorded the probability of false positives at about one error per thousand cases. When using two fingers, there will be a product of probabilities — one error per million cases.
I see this problem as the main one in the payment project, but we calmly treat it. There are several options for reducing such errors. As we work, we will apply certain measures.
And what to do with the databases in the millions of prints? After all, the problem of illegal immigration is already asking for it. This is how long does it take to wait for identification in a million base? What did you manage to implement? You do not use video processors with CUDA technology instead of processors, which today brings tangible effect in mathematical calculations in narrow areas?
We already have an implementation of a system with a database of 6 million (this is in Guinea), and now it will expand to 10 million ... National level systems, including migrant control systems, use 10-finger registration and there is no reliability problems (almost 100% reliability). We, and all other biometric companies, use classical calculators - servers with multi-core processors. We have the usual integer arithmetic and many reboring problems. Algorithmic acceleration is much more efficient than hardware. At the moment, almost all companies have abandoned the use of special processors, the algorithms are changing very quickly.
Thanks for attention.
Ps. if anyone has questions, leave in the comments. We will do with you if you have the desire.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/174397/
All Articles