DCDIAG - health diagnostics AD single utility
Author's note: The article is primarily written for novice system administrators, experienced ones are unlikely to learn something new and useful for themselves. Inspired by an article about GPUPDATE / force (thanks to mrHobbY ) .
Active Directory is a large and complex organism (even if it consists of two domain controllers and one site), and it is very important for the system administrator to make a diagnosis at any time to analyze the operation of this organism.
Well, and since it is inefficient to use the snap-ins to go and watch, the system’s logs also do not always understand what is happening, so various utilities come to the rescue. One of them is Microsoft's dcdiag.
Let's look at it carefully - because the utility of this utility is difficult to overestimate. I will not give the numerous keys of this command - you can read about it in help if you wish - and I’ll dwell only on those - which I use myself in the diagnosis in practice.
')
The first thing you need to do to work with this utility is to install it on your workstation or on the server itself (everyone is free to choose himself, but in the latest versions of dcdiag, it is written that the checks need to be run on the servers themselves domain controllers, with the exception of the dcPromo and RegisterInDNS tests. For Windows 2003, you need to install the Support Tools package from the operating system distribution kit; for Windows 7 and 8, you need to install the Remote System Administration Tools package (they are different for win7, win7sp1, and win8 - be careful when you download). By the way, RSAT is in itself a useful product - there are many utilities inside that are simply necessary in the daily life of a domain administrator.
After installing the package, the command is already available from the command line.
But do not rush to run it right away; nothing will work on the workstation without specifying the domain controller to which you need to connect. The utility will issue a warning:
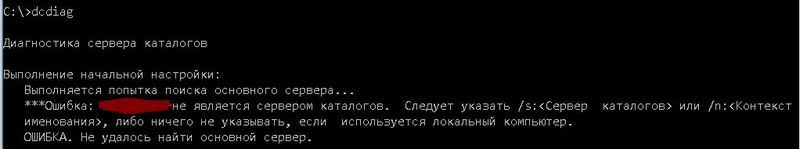
Note: Starting with Windows 7, dcdiag messages are translated into Russian. Before that - everything is only in English. Maybe it will be useful to someone. Although the old versions are very simple and understandable English.
It's great - we found out that it is desirable to specify a domain controller using the / s: key or the naming context is / n:. It is clear which server to specify - the domain controller you want to check - but if you specify the domain naming context - (the domain name in other words - you can specify in Netbios, DNS or DN formats.), The nearest controller (within the site) will be found domain (further CD).
Let's do the simplest check: dcdiag / s: dc01-local
And again, the trouble, although something is already visible:
As we can see, part of the tests passed - but parts were denied access. This is due to the fact that I ran dcdiag from under a normal domain account, without administrator rights. It is clear - that part of the checks to pass under it is simply impossible. Therefore, in order to get the correct diagnostics, you need to run the utility with administrative privileges — either run the command prompt as an administrator, or use the / u keys : domain name \ username and / p: password . Let's try:
dcdiag / s: dc01-local / u: local \ user19 / p: Password
As you can see, the checks passed almost everything except for the Services check. But here I have a completely logical explanation - I am using a new utility (from a package for windows 7) trying to check a domain controller based on win2003 - and it is quite possible that the name of the service may differ.
Lyrical digression number 1. When preparing the article, I encountered anepic fail funny phenomenon, can we discuss it in the comments? :) In general, launching dcdiag from under the normal account of another domain (linked by trust with the local domain under investigation) and setting the parameters / u and / p - (username and password of the administrative account of the local domain) - the utility generated errors in terms of checks - for example, sysvolchek (in the dcdiag 2003 version, frssysvol). If you go to the workstation under an account with administrative authority in the local domain, the checks are fine. So - maybe, all the same, it will not be superfluous to check on the server itself. To the man of lyrical digression number 1 .
Fully describe the results of the team, I do not see the point. It is beautifully described in utility help ( dcdiag / h ). The main thing is clear - there are no problems with this domain controller and all tests have been passed. But from checking one server - it does not follow the fact that AD is now in a healthy state ofchocolate . And here we come to the aid of the key to check all the servers of the enterprise.
This is the key / e . This key forces the utility to bypass all CDs in the domain with the launch of all tests on each server. It is useful to apply with this / v - output extended information for each test. Well, to analyze all this - it is useful to output the data to a file - and the log separately, error messages - separately. The / f: log_file_name and ferr: / err_of_file_name_log files help (the / ferr key is removed in new versions). If you want to check the wrong domain you are in now, add a key to specify the context name / n:.
The whole team looks like this:
dcdiag / n: local / e / v /f:c:\logs\adtest.log /ferr:c:\logs\aderrors.log / u: local \ user19 / p: Password
Attention! In dcdiag versions, starting with windows 2008, the / ferr key : removed from supported (specially repeated :)).
If you have a complex forest structure, and even with slow communication channels, be prepared to wait. Yes, even if it is simple - let's say I have in one real forest - 10 KD, 5 sites and 256 kbit / s channels. The execution of this command takes on average up to 20 minutes.
The performance result is highly recommended to carefully review for problems. Well, it is very desirable to run this utility regularly to diagnose AD health.
For hardcore, you can also add the / fix key - making secure fixes, but you shouldn't do this without a thought.
That's all that I wanted to tell today. And how often do you have to use this utility at work? What alternatives do you know?
update 1 : I remembered something, again from personal experience: if you have a large domain connected by slow (for example, satellite) communication channels, the utility will produce a lot of errors if it is not available - most often, RPC is unavailable. This is normal, and you need to know about it. If the majority of tests end with a similar message, then there is no connection, it is necessary to apply measures to eliminate the failure. The second is often a common problem - errors in DNS - but this topic is for a separate article.
ps to update 1 -dcdiag / fix - including registering a new record in the dns of the netlogon service - it is also useful to know!
Active Directory is a large and complex organism (even if it consists of two domain controllers and one site), and it is very important for the system administrator to make a diagnosis at any time to analyze the operation of this organism.
Well, and since it is inefficient to use the snap-ins to go and watch, the system’s logs also do not always understand what is happening, so various utilities come to the rescue. One of them is Microsoft's dcdiag.
Let's look at it carefully - because the utility of this utility is difficult to overestimate. I will not give the numerous keys of this command - you can read about it in help if you wish - and I’ll dwell only on those - which I use myself in the diagnosis in practice.
')
The first thing you need to do to work with this utility is to install it on your workstation or on the server itself (everyone is free to choose himself, but in the latest versions of dcdiag, it is written that the checks need to be run on the servers themselves domain controllers, with the exception of the dcPromo and RegisterInDNS tests. For Windows 2003, you need to install the Support Tools package from the operating system distribution kit; for Windows 7 and 8, you need to install the Remote System Administration Tools package (they are different for win7, win7sp1, and win8 - be careful when you download). By the way, RSAT is in itself a useful product - there are many utilities inside that are simply necessary in the daily life of a domain administrator.
After installing the package, the command is already available from the command line.
But do not rush to run it right away; nothing will work on the workstation without specifying the domain controller to which you need to connect. The utility will issue a warning:

Note: Starting with Windows 7, dcdiag messages are translated into Russian. Before that - everything is only in English. Maybe it will be useful to someone. Although the old versions are very simple and understandable English.
It's great - we found out that it is desirable to specify a domain controller using the / s: key or the naming context is / n:. It is clear which server to specify - the domain controller you want to check - but if you specify the domain naming context - (the domain name in other words - you can specify in Netbios, DNS or DN formats.), The nearest controller (within the site) will be found domain (further CD).
Let's do the simplest check: dcdiag / s: dc01-local
And again, the trouble, although something is already visible:
Work result
dcdiag /s:dc01-local.local : * AD. . : Local\dc01-local : Connectivity ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Connectivity : Local\dc01-local : Advertising ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Advertising : FrsEvent 5 File Replication Service \\DC01-LOCAL:File Replication Service: . ......................... DC01-LOCAL - FrsEvent : DFSREvent ......................... DC01-LOCAL - DFSREvent : SysVolCheck ......................... DC01-LOCAL - SysVolCheck : KccEvent 5 Directory Service \\DC01-LOCAL:Directory Service: . ......................... DC01-LOCAL - KccEvent : KnowsOfRoleHolders ......................... DC01-LOCAL - KnowsOfRoleHolders : MachineAccount ......................... DC01-LOCAL - MachineAccount : NCSecDesc ......................... DC01-LOCAL - NCSecDesc : NetLogons [DC01-LOCAL] . , , . ......................... DC01-LOCAL - NetLogons : ObjectsReplicated ......................... DC01-LOCAL - ObjectsReplicated : Replications [ ,DC01-LOCAL] DsReplicaGetInfo(PENDING_OPS, NULL), 0x2105 " ." ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Replications : RidManager ......................... DC01-LOCAL - RidManager : Services dc01-local.local, 0x5 " ." ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Services : SystemLog 5 System \\DC01-LOCAL:System: . ......................... DC01-LOCAL - SystemLog : VerifyReferences ......................... DC01-LOCAL - VerifyReferences : Schema : CheckSDRefDom ......................... Schema - CheckSDRefDom : CrossRefValidation ......................... Schema - CrossRefValidation : Configuration : CheckSDRefDom ......................... Configuration - CheckSDRefDom : CrossRefValidation ......................... Configuration - CrossRefValidation : LOCAL : CheckSDRefDom ......................... LOCAL - CheckSDRefDom : CrossRefValidation ......................... LOCAL - CrossRefValidation : LOCAL.local : LocatorCheck ......................... LOCAL.local - LocatorCheck : Intersite ......................... LOCAL.local - Intersite As we can see, part of the tests passed - but parts were denied access. This is due to the fact that I ran dcdiag from under a normal domain account, without administrator rights. It is clear - that part of the checks to pass under it is simply impossible. Therefore, in order to get the correct diagnostics, you need to run the utility with administrative privileges — either run the command prompt as an administrator, or use the / u keys : domain name \ username and / p: password . Let's try:
dcdiag / s: dc01-local / u: local \ user19 / p: Password
Work result
: * AD. . : Magadan\DC01-LOCAL : Connectivity ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Connectivity : Magadan\DC01-LOCAL : Advertising ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Advertising : FrsEvent ......................... DC01-LOCAL - FrsEvent : DFSREvent ......................... DC01-LOCAL - DFSREvent : SysVolCheck ......................... DC01-LOCAL - SysVolCheck : KccEvent ......................... DC01-LOCAL - KccEvent : KnowsOfRoleHolders ......................... DC01-LOCAL - KnowsOfRoleHolders : MachineAccount ......................... DC01-LOCAL - MachineAccount : NCSecDesc ......................... DC01-LOCAL - NCSecDesc : NetLogons ......................... DC01-LOCAL - NetLogons : ObjectsReplicated ......................... DC01-LOCAL - ObjectsReplicated : Replications ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Replications : RidManager ......................... DC01-LOCAL - RidManager : Services : RpcSs DC01-LOCAL, - WIN32_OWN_PROCESS, - WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS ......................... DC01-LOCAL - Services : SystemLog ......................... DC01-LOCAL - SystemLog : VerifyReferences ......................... DC01-LOCAL - VerifyReferences : Schema : CheckSDRefDom ......................... Schema - CheckSDRefDom : CrossRefValidation ......................... Schema - CrossRefValidation : Configuration : CheckSDRefDom ......................... Configuration - CheckSDRefDom : CrossRefValidation ......................... Configuration - CrossRefValidation : LOCAL : CheckSDRefDom ......................... LOCAL - CheckSDRefDom : CrossRefValidation ......................... LOCAL - CrossRefValidation : LOCAL.Local : LocatorCheck ......................... LOCAL.Local - LocatorCheck : Intersite ......................... LOCAL.Local - Intersite As you can see, the checks passed almost everything except for the Services check. But here I have a completely logical explanation - I am using a new utility (from a package for windows 7) trying to check a domain controller based on win2003 - and it is quite possible that the name of the service may differ.
Lyrical digression number 1. When preparing the article, I encountered an
Fully describe the results of the team, I do not see the point. It is beautifully described in utility help ( dcdiag / h ). The main thing is clear - there are no problems with this domain controller and all tests have been passed. But from checking one server - it does not follow the fact that AD is now in a healthy state of
This is the key / e . This key forces the utility to bypass all CDs in the domain with the launch of all tests on each server. It is useful to apply with this / v - output extended information for each test. Well, to analyze all this - it is useful to output the data to a file - and the log separately, error messages - separately. The / f: log_file_name and ferr: / err_of_file_name_log files help (the / ferr key is removed in new versions). If you want to check the wrong domain you are in now, add a key to specify the context name / n:.
The whole team looks like this:
dcdiag / n: local / e / v /f:c:\logs\adtest.log /ferr:c:\logs\aderrors.log / u: local \ user19 / p: Password
Attention! In dcdiag versions, starting with windows 2008, the / ferr key : removed from supported (specially repeated :)).
If you have a complex forest structure, and even with slow communication channels, be prepared to wait. Yes, even if it is simple - let's say I have in one real forest - 10 KD, 5 sites and 256 kbit / s channels. The execution of this command takes on average up to 20 minutes.
The performance result is highly recommended to carefully review for problems. Well, it is very desirable to run this utility regularly to diagnose AD health.
For hardcore, you can also add the / fix key - making secure fixes, but you shouldn't do this without a thought.
That's all that I wanted to tell today. And how often do you have to use this utility at work? What alternatives do you know?
update 1 : I remembered something, again from personal experience: if you have a large domain connected by slow (for example, satellite) communication channels, the utility will produce a lot of errors if it is not available - most often, RPC is unavailable. This is normal, and you need to know about it. If the majority of tests end with a similar message, then there is no connection, it is necessary to apply measures to eliminate the failure. The second is often a common problem - errors in DNS - but this topic is for a separate article.
ps to update 1 -dcdiag / fix - including registering a new record in the dns of the netlogon service - it is also useful to know!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/174379/
All Articles