Useful tips for beginners in the design for Android
 This post will serve as a kind of beginning of a series of publications on the theme “how I study design under Android”. I never paid enough attention to the guidelines, considering them boring and uninteresting, but everything changed. Now I begin to understand, the platform has reached its maturity and offers a number of interesting solutions.
This post will serve as a kind of beginning of a series of publications on the theme “how I study design under Android”. I never paid enough attention to the guidelines, considering them boring and uninteresting, but everything changed. Now I begin to understand, the platform has reached its maturity and offers a number of interesting solutions. 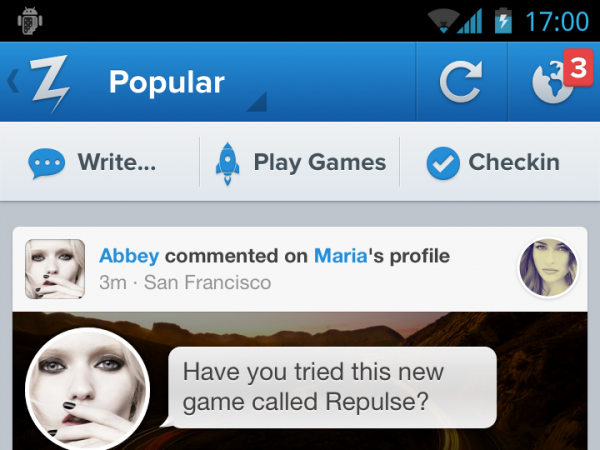
The Back Button
For a long time, back was a hardware button for Android devices, there was no point in adding a software equivalent to the user interface. Now it is fashionable to use the back button to navigate inside applications. If we talk about the “back” button of the user interface (it is called the “up button”), then there is a slight difference between the hardware back and up. Up makes a transition to one screen, within the application, while back to any application or content.
')
Resolution
The resolution settings for Android are a bit confused - xhdpi (2x), hdpi (1.5x) and mdpi (1x).
It sounds very technical. When I started working a year ago, no one could really explain to me what is the ratio of the sides between them. After many inquiries and searches, it was 720 × 1280, 540 × 960 and 360 × 640. When designing a layout design, do not forget to take into account hardkey buttons and the status bar.
From the translator: Actually, what is described in this paragraph is not quite right. Under the link and in the table you will find a more accurate description.
Table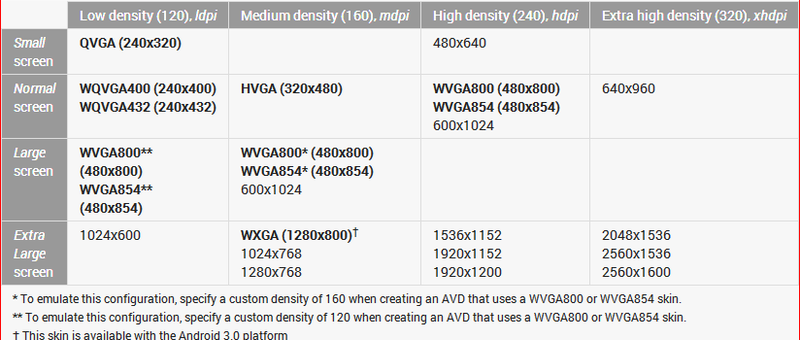

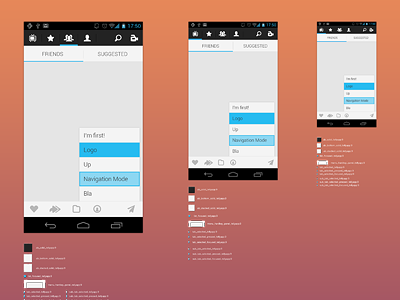
Starter Kit
Jeremy Sally, a designer from Telly , graphically demonstrated the ratio of these three resolutions. You need Android Action Bar Style Generator to work with themes by default. It allows you to set the basic parameters of color, style and save the settings in a Zip file for all three permissions. The best way to experiment to visualize.
9-slice scaling
Android has a peculiar way of scaling graphic resources, which is not similar to CSS. 9-slicing allows you to specify exactly which part of the picture you want to scale. The rest, such as rounded corners, remain fixed in size even when scaling the entire resource. To do this, you need to draw black lines 1px wide in the following areas in the image file:
- Top: An area that can be stretched horizontally.
- Left: Vertically Similar
- Right: The vertical area in which the content will be located. This parameter can be used to set indents.
- Bottom: similar vertical
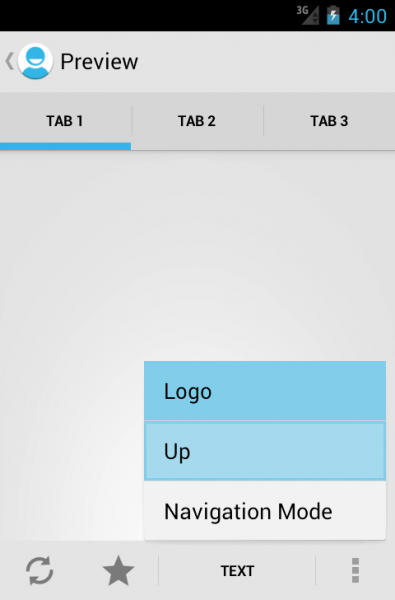
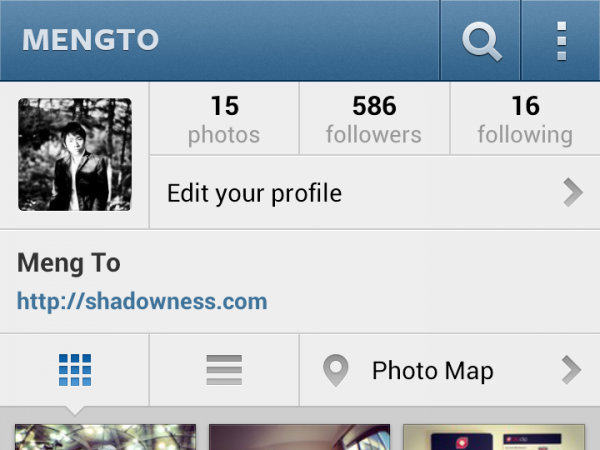
The action bar
Unlike the iPhone, where the name is usually located in the middle of the title, on Android the name is in the upper left corner, next to the application logo. Clicking on the logo usually brings up a side menu or takes you back to the previous screen.

Under the name of the application, sometimes you can see a triangular arrow, thanks to it, navigation inside the application is possible. Just like on the Internet, a very frequent way to display a drop-down menu on Android.

Finally, if you are serious about guidelines, all controls should be in the upper right corner. This applies to the update function (pull to update as on the iPhone, very rarely used in Android), search, and the infamous “action” buttons, which ideally should be in the form of three points. Points are used for those actions that Action Bar could not accommodate.
Fonts
Fonts, unfortunately, depend on the specifics of the device, so be prepared for incidents. Do not be discouraged if you have to test the design on the old device. There were worse days too - remember IE6. The most popular font at the moment is Droid Sans . However, Roboto is gaining popularity, as it is present on new devices.
Dimensions
Starting with Android 2.x, the minimum element size should be: 28px for text, 96px for menu and header, 116px for footer. This is a little more than iOS (24px, 88px and 100px). If we talk about the ratio of 116% of Android to iOS.
View the projected design on your Android device
Roman Nurik from Google has developed a very useful tool Android Design Preview . The tool will help the designer to see how the layout of the application drawn in a graphic editor on a computer will look on a real device.
The Android Design Preview program can be installed on Windows, Mac OS X or almost any of the operating systems of the * nix family. The application is written in Java and is a regular JAR file. Android Design Preview works as follows: the developer connects the smartphone to the computer via USB (ADT must be installed on the PC), launches the Design Preview, clicks “Select Mirror Region” in this program and sees a frame in front of it. He sets this frame on the layout and sees it on the smartphone screen.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/173767/
All Articles