Configuring EMC VNX 5100 Storage
Good day to everyone reading these lines. Recently I had a chance to configure the EMC VNX 5100 disk shelf as a storage for a cluster. As it turned out, there is nothing particularly complicated about it, but in the process there are some features that distract time and attention. If you want to use this storage system, but do not want to spend too much time walking the rake, I ask for cat.
The VNX 5100 disk shelf is an entry-level storage system, structurally consisting of the actual disk array and the SPS (Stanby Power Supply) module. The array occupies 3 units, and can contain 15 3.5-inch disks (my version), or 25 2.5-inch disks. The first four disks are occupied by the operating system, and it is not recommended to use them in their work. The SPS module occupies 1 unit, contains built-in batteries, can hold two disk arrays. Its main task - when you turn off the shelf correctly complete all disk operations and write the contents of the cache to disk. Nothing else. In this lie not just a rake - but a rake for children. With the corresponding consequences in the event of an attack. Despite its own battery, the system does not make the slightest attempt to pretend to be a UPS, and when there is a power failure, it lies quietly. So this battery must be included in the external bespereboynik, although the experience actively protests.
The system is packed with a soul, the weight in the package is a little more than 90 kg, so that it is better to invite muscular friends to the "body skid". And if on the way to the server there are steep stairs and narrow doors, then friends will be especially grateful for the pleasure delivered.
The device can be sold with or without bundled software. However, if you don’t find any installation CDs in the box, do not be discouraged. This is normal.
On the installation in the rack will not stop, everything is going without problems. The only thing - pay attention to the power cords that come in the kit. Maybe I was so lucky with the shelves, maybe with rack-top bespereboynikami, but the cords from the kit sit in the UPS connectors quite freely. Of my three shelves, one set of cords had to be almost completely replaced with cords from the UPS, otherwise they just fell out.
')
Before setting up, we register on the manufacturer's website emc.com and download the necessary software. The networks recommend downloading the installation package VNX Installation Toolbox , which contains almost everything you need, but I would advise you to take the necessary utilities in bulk. Firstly, the toolbox does not include all the necessary utilities, and secondly, they are created by the InstallAnywere installer, which does not work correctly under Windows Server 2012. You will need the latest versions of the following utilities (they are already compressed by the InstallAware installer, which works fine):
Before installing on the hosts, we perform all the necessary actions - connecting the FC, setting up the network, plant to the domain, etc. Java needs some utilities to work, so we install it too. At the time of setup, I advise you to extinguish the internal interfaces on all nodes of the future cluster, otherwise the regiment may pick them up when registering, and not external ones. Not that it was critical, it will work this way and that, but suddenly, sometime in the future, the regiment will want to communicate on the network with its hosts. Further I will describe each utility, specifying its version. This is not necessarily the latest version at the moment, but this version is guaranteed to work for me.
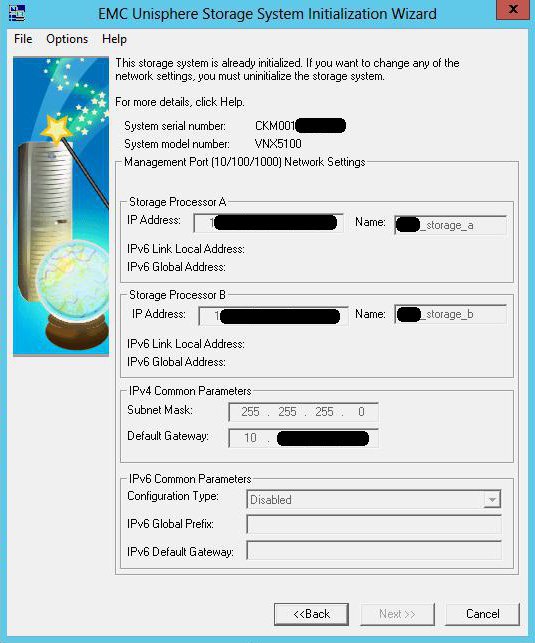
EMC Unisphere Storage System Initialization
(UnisphereInitTool-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0163-1.exe)
This utility initializes your shelf. Before installing it, connect the host interface and disk shelf control interfaces to the same subnet, on the same physical switch. Turn on the shelf. It starts slowly enough, so there is time for a cup of coffee. Install, run the utility, it searches the subnet and shows all found storage systems with their serial number. Please note that at the time the utility runs, you need to turn off the firewall, otherwise the search will fail. By the number we define the necessary, initialize, and set the ip-addresses on the control interfaces. Unfortunately, on this point, my knowledge is only theoretical, from manuals, since my pieces of iron came from the supplier already initialized, with addresses on interfaces of the form 1.1.1.1. So I just made sure that the device is initialized, and determined its ip. If anyone has practical experience of this operation, I will be grateful for clarification.
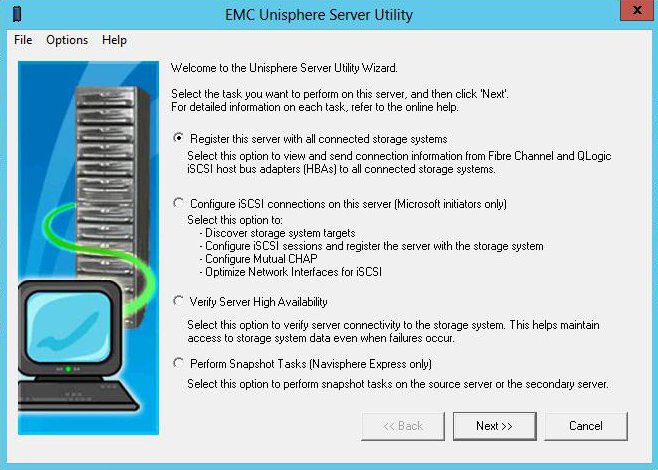
EMC Unisphere Server Utility
(UnisphereServerUtil-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0163-1.exe)
The utility registers a host on a disk shelf, allowing you to assign logical disks to it in the future. If the iSCSI initiator is not running, then it starts. If necessary, registration can be done by hand, from the web interface it will work. But it is more correct to do it automatically. After launch, select the option Register this server with all connected storage system.
EMC Unisphere Server
(UnisphereServer-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0156-1.exe)
EMC Unisphere VNX Client
(UnisphereClient-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0156-1.exe)
Provides access to the web-based shelf management interface. The client part asks to enter the address of the shelf, and connects to it, the server provides the same on the host ip-address. Powered by java. For correct operation of the server part, configure the firewall permissions. You can connect to the same shelf interface by simply entering the shelf ip-address in the browser. Please note that the first time you connect, you need to create an administrator account.

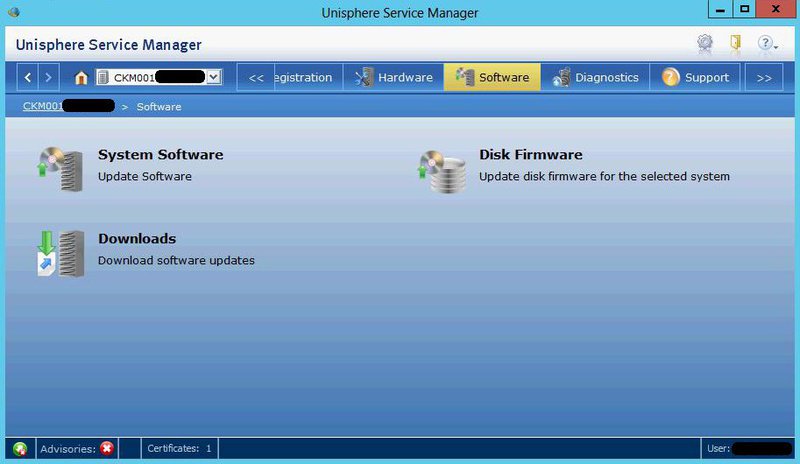
EMC Unisphere Service Manager
(UnisphereServiceManager-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.26.1.0068-1.exe)
The service utility used to change the firmware, OS, hardware upgrades, diagnostics collection, etc. Not used in normal work.
EMC PowerPath
(EMCPower.X64.signed.5.5.b289.exe)
The PowerPath utility is a separate load balancing product between different FCs, can be used with storage systems from different manufacturers, and generally speaking - a thing licensed and paid. However, for connections to EMC Clarion and EMC VNX systems, the manufacturer allows using it without a license. To do this, when installing, we specify that “Yes”, we have Only Clarion arrays connected to this host. I used version 5.5 without a patch. The site has a patch, and in the documentation there are references to version 5.7. Structurally, the shelf contains two blocks, each of which sends information about the assigned logical drives to the host. Thus, in Computer Manager you will see two sets of storage disks, one of which is connected, and the second one knocks out an error (and no wonder, because the disks are already taken). PowerPath automatically processes all FCs and hides an extra set of disks. Everything will work without it, but it is better to do it beautifully and correctly.

The utility supports three modes of operation:
Active-active - FC work simultaneously with load balancing.
Active-passive - one FC is active, and the rest are in reserve, and are connected when the active one fails. Only one FC is running at a time.
ALUA is a protocol for choosing the preferred path to data placed on controllers with different priority, for example, one of the two is more preferable as an access path than the other. So, using the ALUA protocol (if the OS can use it), the one that is more advantageous to access this piece of data (for example, LUN) is selected from several paths. If the controller, the priority for this data, is unavailable, then access will go through the controller that has the “second from the top” priority, and so on. Nevertheless, both of them are active, although at this particular point in time, for a particular LUN, one is used predominantly (this is in contrast to the Active Passive). (c) track
It is this mode that supports our device, in contrast to the previous two, which only older models can work with.
So, all the software is installed, and now you can go directly to the shelf.
Connect to the web interface and go to the Hosts> Host List tab. Since we have already registered, we see our servers in this tab. The Hosts> Initiators tab lists the initiators that connect servers to storage units. You can unregister the initiator and manually create a new one instead of it by selecting the server name from the existing ones or specifying a new one. Will work. Now all initiators in the list are presented with yellow warning triangles - because they are not connected anywhere yet. On the Settings> Network> Edit network settings tab, we reconfigure ip-addresses to our network.
Since our system is being prepared for a cluster, we will create two LUNs - a quorum of 1 GB and a LUN of data for the rest of the space. First we prepare the pool for the placement of these LUNs. On the Storage> Storage Pools tab, select the raid type and total pool size. There is also a feature here - the system does not know how to create raids on an arbitrary number of hard drives. Instead, you can choose one of the preset templates.

So, 10 disks in raid5 do not mean a 9 + 1 scheme at all. A means (4 + 1) + (4 + 1), with a corresponding drop in the total capacity. And raid5 on 8 disks means a combination (4 + 1) + (2 + 1). It’s good if the raid simply contains file data, and if it’s application data, we’ll have unpredictable performance problems. Given that initially I can count on 10 disks (15 minus 4 under OSes and minus 1 HotSpare), I have to choose between raid5 for 10 disks, and raid6 for 8 disks plus two in the mirror. For reasons of disk capacity, it was decided to stop at raid5. So - we specify the type of raid, indicate the number of disks allocated for it, the name of the new pool - and OK.
Now Storage> Luns . Specify the name of the pool on which the newly created LUN will be placed, its name and size.
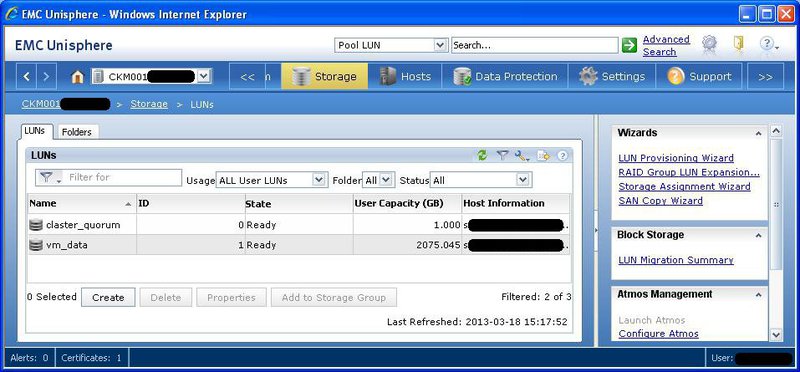
Finally, on the Hosts> Storage Groops tab, we create a new storage group, linking the LUNs and the hosts:
Create , then Connect LUNs , then Connect Hosts . Storage groups, in fact, match one or more LUNs to one or more hosts. Please note - you can connect several hosts to the same LUN only if they are future members of the cluster. Otherwise, the hosts will damage each other's data due to inconsistent disk writes.

Now you can go to the Hosts> Initiators tab and admire the green checkmarks in front of all initiators, indicating the correct connection.
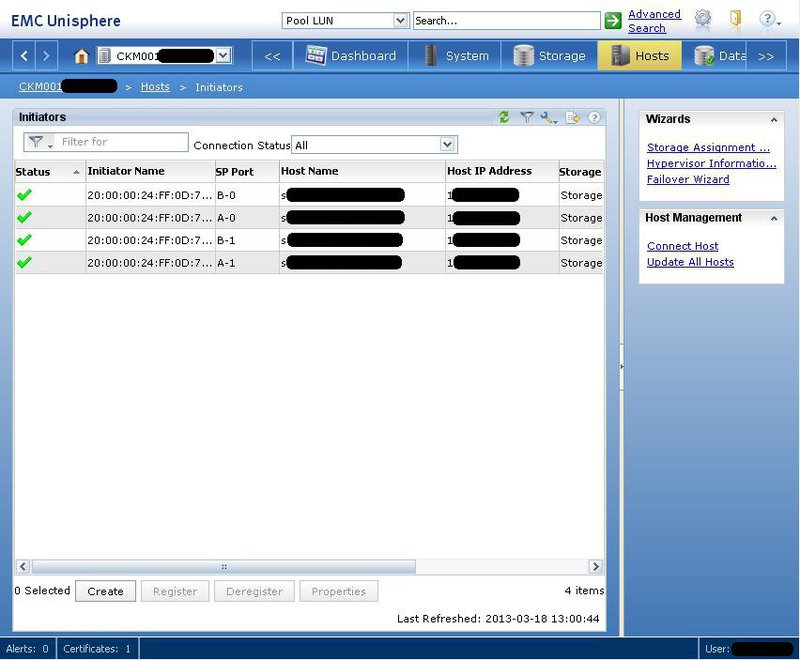
At this setting, the disk shelf can be considered over. On each host we go to Disk Management and translate our new disks online without assigning a letter. We formatted in NTFS, we raise a cluster, and we catch disks to it. You can work. I raised the cluster on Windows Server 2012, the differences in the process from Server 2008 are cosmetic. But, if anyone is interested, I can describe.
Phew That seems to be "everything that I wanted to say about the Vietnam War" (c)
PS Many thanks to habrayumer litweg and track for interesting and useful additions.
The VNX 5100 disk shelf is an entry-level storage system, structurally consisting of the actual disk array and the SPS (Stanby Power Supply) module. The array occupies 3 units, and can contain 15 3.5-inch disks (my version), or 25 2.5-inch disks. The first four disks are occupied by the operating system, and it is not recommended to use them in their work. The SPS module occupies 1 unit, contains built-in batteries, can hold two disk arrays. Its main task - when you turn off the shelf correctly complete all disk operations and write the contents of the cache to disk. Nothing else. In this lie not just a rake - but a rake for children. With the corresponding consequences in the event of an attack. Despite its own battery, the system does not make the slightest attempt to pretend to be a UPS, and when there is a power failure, it lies quietly. So this battery must be included in the external bespereboynik, although the experience actively protests.
The system is packed with a soul, the weight in the package is a little more than 90 kg, so that it is better to invite muscular friends to the "body skid". And if on the way to the server there are steep stairs and narrow doors, then friends will be especially grateful for the pleasure delivered.
The device can be sold with or without bundled software. However, if you don’t find any installation CDs in the box, do not be discouraged. This is normal.
On the installation in the rack will not stop, everything is going without problems. The only thing - pay attention to the power cords that come in the kit. Maybe I was so lucky with the shelves, maybe with rack-top bespereboynikami, but the cords from the kit sit in the UPS connectors quite freely. Of my three shelves, one set of cords had to be almost completely replaced with cords from the UPS, otherwise they just fell out.
')
Before setting up, we register on the manufacturer's website emc.com and download the necessary software. The networks recommend downloading the installation package VNX Installation Toolbox , which contains almost everything you need, but I would advise you to take the necessary utilities in bulk. Firstly, the toolbox does not include all the necessary utilities, and secondly, they are created by the InstallAnywere installer, which does not work correctly under Windows Server 2012. You will need the latest versions of the following utilities (they are already compressed by the InstallAware installer, which works fine):
- EMC PowerPath
- EMC Unisphere Storage System Initialization
- EMC Unisphere Server Utility
- EMC Unisphere VNX Client
- EMC Unisphere Server
- EMC Unisphere Service Manager
Before installing on the hosts, we perform all the necessary actions - connecting the FC, setting up the network, plant to the domain, etc. Java needs some utilities to work, so we install it too. At the time of setup, I advise you to extinguish the internal interfaces on all nodes of the future cluster, otherwise the regiment may pick them up when registering, and not external ones. Not that it was critical, it will work this way and that, but suddenly, sometime in the future, the regiment will want to communicate on the network with its hosts. Further I will describe each utility, specifying its version. This is not necessarily the latest version at the moment, but this version is guaranteed to work for me.
EMC Unisphere Storage System Initialization
(UnisphereInitTool-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0163-1.exe)
This utility initializes your shelf. Before installing it, connect the host interface and disk shelf control interfaces to the same subnet, on the same physical switch. Turn on the shelf. It starts slowly enough, so there is time for a cup of coffee. Install, run the utility, it searches the subnet and shows all found storage systems with their serial number. Please note that at the time the utility runs, you need to turn off the firewall, otherwise the search will fail. By the number we define the necessary, initialize, and set the ip-addresses on the control interfaces. Unfortunately, on this point, my knowledge is only theoretical, from manuals, since my pieces of iron came from the supplier already initialized, with addresses on interfaces of the form 1.1.1.1. So I just made sure that the device is initialized, and determined its ip. If anyone has practical experience of this operation, I will be grateful for clarification.

EMC Unisphere Server Utility
(UnisphereServerUtil-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0163-1.exe)
The utility registers a host on a disk shelf, allowing you to assign logical disks to it in the future. If the iSCSI initiator is not running, then it starts. If necessary, registration can be done by hand, from the web interface it will work. But it is more correct to do it automatically. After launch, select the option Register this server with all connected storage system.

EMC Unisphere Server
(UnisphereServer-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0156-1.exe)
EMC Unisphere VNX Client
(UnisphereClient-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.25.1.0156-1.exe)
Provides access to the web-based shelf management interface. The client part asks to enter the address of the shelf, and connects to it, the server provides the same on the host ip-address. Powered by java. For correct operation of the server part, configure the firewall permissions. You can connect to the same shelf interface by simply entering the shelf ip-address in the browser. Please note that the first time you connect, you need to create an administrator account.

EMC Unisphere Service Manager
(UnisphereServiceManager-Win-32-x86-en_US-1.2.26.1.0068-1.exe)
The service utility used to change the firmware, OS, hardware upgrades, diagnostics collection, etc. Not used in normal work.

EMC PowerPath
(EMCPower.X64.signed.5.5.b289.exe)
The PowerPath utility is a separate load balancing product between different FCs, can be used with storage systems from different manufacturers, and generally speaking - a thing licensed and paid. However, for connections to EMC Clarion and EMC VNX systems, the manufacturer allows using it without a license. To do this, when installing, we specify that “Yes”, we have Only Clarion arrays connected to this host. I used version 5.5 without a patch. The site has a patch, and in the documentation there are references to version 5.7. Structurally, the shelf contains two blocks, each of which sends information about the assigned logical drives to the host. Thus, in Computer Manager you will see two sets of storage disks, one of which is connected, and the second one knocks out an error (and no wonder, because the disks are already taken). PowerPath automatically processes all FCs and hides an extra set of disks. Everything will work without it, but it is better to do it beautifully and correctly.

The utility supports three modes of operation:
Active-active - FC work simultaneously with load balancing.
Active-passive - one FC is active, and the rest are in reserve, and are connected when the active one fails. Only one FC is running at a time.
ALUA is a protocol for choosing the preferred path to data placed on controllers with different priority, for example, one of the two is more preferable as an access path than the other. So, using the ALUA protocol (if the OS can use it), the one that is more advantageous to access this piece of data (for example, LUN) is selected from several paths. If the controller, the priority for this data, is unavailable, then access will go through the controller that has the “second from the top” priority, and so on. Nevertheless, both of them are active, although at this particular point in time, for a particular LUN, one is used predominantly (this is in contrast to the Active Passive). (c) track
It is this mode that supports our device, in contrast to the previous two, which only older models can work with.
So, all the software is installed, and now you can go directly to the shelf.
Connect to the web interface and go to the Hosts> Host List tab. Since we have already registered, we see our servers in this tab. The Hosts> Initiators tab lists the initiators that connect servers to storage units. You can unregister the initiator and manually create a new one instead of it by selecting the server name from the existing ones or specifying a new one. Will work. Now all initiators in the list are presented with yellow warning triangles - because they are not connected anywhere yet. On the Settings> Network> Edit network settings tab, we reconfigure ip-addresses to our network.
Since our system is being prepared for a cluster, we will create two LUNs - a quorum of 1 GB and a LUN of data for the rest of the space. First we prepare the pool for the placement of these LUNs. On the Storage> Storage Pools tab, select the raid type and total pool size. There is also a feature here - the system does not know how to create raids on an arbitrary number of hard drives. Instead, you can choose one of the preset templates.

So, 10 disks in raid5 do not mean a 9 + 1 scheme at all. A means (4 + 1) + (4 + 1), with a corresponding drop in the total capacity. And raid5 on 8 disks means a combination (4 + 1) + (2 + 1). It’s good if the raid simply contains file data, and if it’s application data, we’ll have unpredictable performance problems. Given that initially I can count on 10 disks (15 minus 4 under OSes and minus 1 HotSpare), I have to choose between raid5 for 10 disks, and raid6 for 8 disks plus two in the mirror. For reasons of disk capacity, it was decided to stop at raid5. So - we specify the type of raid, indicate the number of disks allocated for it, the name of the new pool - and OK.
Now Storage> Luns . Specify the name of the pool on which the newly created LUN will be placed, its name and size.

Finally, on the Hosts> Storage Groops tab, we create a new storage group, linking the LUNs and the hosts:
Create , then Connect LUNs , then Connect Hosts . Storage groups, in fact, match one or more LUNs to one or more hosts. Please note - you can connect several hosts to the same LUN only if they are future members of the cluster. Otherwise, the hosts will damage each other's data due to inconsistent disk writes.

Now you can go to the Hosts> Initiators tab and admire the green checkmarks in front of all initiators, indicating the correct connection.

At this setting, the disk shelf can be considered over. On each host we go to Disk Management and translate our new disks online without assigning a letter. We formatted in NTFS, we raise a cluster, and we catch disks to it. You can work. I raised the cluster on Windows Server 2012, the differences in the process from Server 2008 are cosmetic. But, if anyone is interested, I can describe.
Phew That seems to be "everything that I wanted to say about the Vietnam War" (c)
PS Many thanks to habrayumer litweg and track for interesting and useful additions.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/173513/
All Articles