The price of skeletons in the closet
Since the end of the 70s, dozens of films have told us how to use the Internet to easily change a person's fate - one rewritten line in your file - and in an instant you become a criminal marginal from a law-abiding taxpayer. And today, our files stored in the special services are waiting in the wings. But don’t worry if you don’t trade arms or plan a coup d'état - your file will never be used up. Although it is a question! Maybe your file does not wait, and is already used differently?
Of course, the CIA, the FBI, and others. The special services monitor the citizens, but they are not the only ones who make up our file today. Following the spread of computers and access to private information of users, a huge number of corporations have appeared, who want to learn everything about us! Not for any particular purpose, but just to deeply understand and satisfy the consumer.

I wonder how this happens? Then let's see how the files are compiled, what is in them, and how you can independently restrict access to most of the information.
Today, the Networks are used to form our comprehensive files: mobile communications, bank accounts, and the most common network, the Internet. Networks can tell a lot about us!
')
Using any computer to access the Internet, we all reserve the “information footprint” in several ways:
1. An IP address or simply a number assigned to an Internet connection channel. Websites use it so that the information we ask for comes to us, it is logical that this allows localizing the computer. Some ISPs assign IP addresses to computers dynamically changing each time they connect to the Internet. Based on the dynamic IP address, you can only set the approximate location of the user. Similar data about IP-addresses and the exact location of users also exist, but they are stored by the provider who actually controls your Internet access.
2. The file cookies - only a few hear about it for the first time. In essence, this is a file created by a web browser and representing a specific sequence of numbers, letters, and other characters. Using cookies, online stores remember the contents of your shopping carts, advertisers, analyzing previously performed actions, decide which ads that might interest you, etc.
Of course, the creation and storage of these files is consistent with the user. Browsers allow erasing or not creating cookies at all, however they are necessary for the proper operation of many sites. If you delete or block the ability to create cookies, some sections of such sites will stop working and you will not be able to use these sections.
3. Logs of visits.
Most websites use browsing logs and store in them: search queries, time and date of visits, your computer’s IP address and cookies stored on it, type of browser and operating system. The formation of the journal occurs in a split second. Today, some companies are introducing a time limit for storing data in journals. It looks like this - after 9 months from the IP-addresses are removed, data that uniquely identify computers. After 18 months, the identifier of the cookies is replaced with a new sequence of characters and it becomes even harder to link the file to you. But 9 months is a decent time, and older data might just be uninteresting, don't you think?
4. A personal account is another reliable way to get your personal data. Whether it is a social network page or a resume on the site of work - here we reveal ourselves in detail to “all the winds”. A personal account of the online store saves the delivery address, of course, so that you do not have to specify it again and again, it keeps the history of your purchases, so you can find out where, when and what you buy.
How it works.
This entire array of information, daily reported by most of us, is “personal data”. Data is accumulated with a single global goal - to make life easier for those who provide them and those who use them.
Your personal data and data of other users work as a legislative assembly. The majority votes “for”, and the world around is changing. Analysis of the general statistics of the actions of millions of users allows you to constantly make relevant offers, create new products, ensure the safety of states and even control the spread of diseases. How? Brilliantly simple!
Imagine that yesterday you returned from the overseas resort of X. In the morning you had a fever and you did not go to work. Referring to acclimatization, you wrote to friends and colleagues via e-mail that you have a fever and stay at home. Other travelers returning from the same resort, X, also had a fever, and entering search queries into the search engines, they began to search the Internet for ways to reduce it. If similar letters and requests began to arrive from those who rested on resort X with increased frequency, then analyzing the footprint created by “sick” users one can see the general picture: the focus of the virus, the symptoms and the incubation period of the virus.
This applies to everything that happens in the world. It is possible to predict sales volumes, the value of lending rates and the average temperature in the hospital. This is not a joke, you can see the incidence in the world right now on Google Flu Trends , which reports virus activity statistics based on user search queries.
This is not the only Google open source tool that shows the results of our activity on the Internet - the Google Correlate service shows the patterns of the influence of world events on US search queries. Here is an example of graphics for the query: “ go to Russia “. Today, the residents of Georgia want to go to Russia most of all, tomorrow this schedule may change.
In the next section, you will learn how companies make money from your online data.
How much do they earn on your data?
To begin with, let's see that all the “free” web services and programs we use are in fact completely non-free.
In recent years, the world of software has changed, we are not in a hurry to pay for high-quality programs, but prefer to receive software “for free”. Why are software developers interested in giving us their products, after all, to make them quite expensive?
The obvious answer is only one: to get user data.
The creators of “free” browsers, social networks, search engines earn money on each user not only by advertising, but also by secretly collecting information. They give us software to get our information in return - it also has a price.
At the same time, program developers deliberately design “barriers of difficulty” on the way to installing more secure configurations of their products, and users are lost in intricate settings. For example, interfaces for managing cookies that are critical for blocking user surveillance by websites are in hard-to-reach places in the browser, and manufacturers often do not improve their usability in this part. Most of the default settings made by companies are not private and are not secure, because users rarely change the default settings. Want to know how quickly you can change your key privacy settings? The following describes the easy way for users of Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox browsers.
Some of the privacy settings in the sites we often use are well hidden, so for a quick search we will use the “Privacyfix” resource or “Privacy Repair” in Russian. The resource groups all the settings into sections and decrypts in detail the value of each setting, so we will use it for information. The final result of the adjustments can be seen immediately and this is also convenient. As soon as you set the settings that block access to your private data, the approximate earnings on your accounts decrease (according to Trefis ). The site interface is divided into 4 sections: Facebook, Google, All websites you visit, All websites that track you.
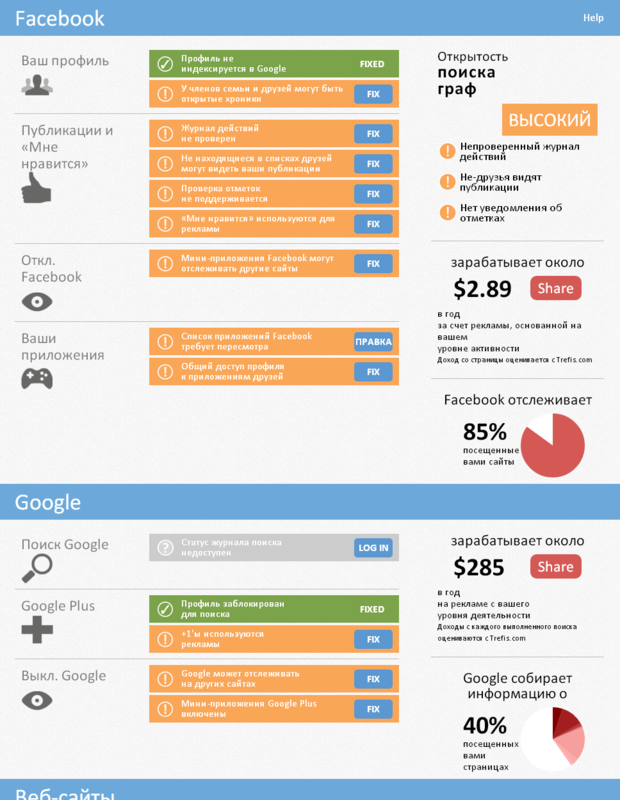
In the “Facebook” section, the availability of your activity on the pages of the site and the estimated annual $ earnings of Facebook on your account are assessed. It usually ranges from a few cents to tens of dollars a year. The amount of earnings affects the region of your stay and activity in the social network. The “Google” section is organized similarly to the previous one, only search queries are evaluated here. According to analysts, Google earns an average of up to $ 14.70 for each 1000 search queries.
The “Websites” provides a detailed list of Internet resources that share your data, and resources that have various problems with the preservation of privacy. In “Tracking” you can see the sites that track you “in the current time” for commercial purposes. Some of these sites may also use your email contact addresses to collect additional information about you.
Privacy settings sections are divided by items. The background color, checkmarks and exclamation mark on the left indicate “state of affairs”. By clicking on the “Fix” buttons corresponding to the items being changed, you will quickly go to the settings sections of your account to correct them.

In addition, Privacyfix offers to install the browser plugin of the same name, which will allow you to edit the settings on linkedln, pinterest, twitter, stumbleupon and other sites on the Internet. When installed, the plug-in automatically fixes a part of the system settings and shows where the rest are hidden - they will have to be fixed by yourself. If you do not delete the plugin after changing the privacy settings, it will signal attempts to track on other sites and allow you to erase the tracking Cookes with a single click. But let's not forget that Privacyfix is also a free product!
To limit or not the earnings of corporations on your data, everyone decides for himself. Studying us, most companies aim to improve their products and services. As consumers, we will not lose out by getting the very best. In turn, companies wishing to control sales, are forced to systematically study consumer behavior and cannot abandon this marketing tool. Be sure that the more private information is collected in our dossier, the more will be willing to get it, and who knows what is known about us today. So do not forget, your data and even your “skeletons in the closet” have their value.
Of course, the CIA, the FBI, and others. The special services monitor the citizens, but they are not the only ones who make up our file today. Following the spread of computers and access to private information of users, a huge number of corporations have appeared, who want to learn everything about us! Not for any particular purpose, but just to deeply understand and satisfy the consumer.

I wonder how this happens? Then let's see how the files are compiled, what is in them, and how you can independently restrict access to most of the information.
Today, the Networks are used to form our comprehensive files: mobile communications, bank accounts, and the most common network, the Internet. Networks can tell a lot about us!
')
Dug up everything, found out his old story. God knows where all this came from and knew. There was only evidence even in such cases, about which, Chichikov thought, except for him and the four walls, no one knew.
N.V. Gogol. "Dead Souls"
Using any computer to access the Internet, we all reserve the “information footprint” in several ways:
1. An IP address or simply a number assigned to an Internet connection channel. Websites use it so that the information we ask for comes to us, it is logical that this allows localizing the computer. Some ISPs assign IP addresses to computers dynamically changing each time they connect to the Internet. Based on the dynamic IP address, you can only set the approximate location of the user. Similar data about IP-addresses and the exact location of users also exist, but they are stored by the provider who actually controls your Internet access.
“Moreover, it was whispered that there were such requests at Google, to which the United States responded with an immediate ballistic strike on any part of the globe. It is this that allegedly explains the frequent collapse of the suburban five-story building ”
V. Pelevin. “Pineapple. Water for a beautiful lady ”
2. The file cookies - only a few hear about it for the first time. In essence, this is a file created by a web browser and representing a specific sequence of numbers, letters, and other characters. Using cookies, online stores remember the contents of your shopping carts, advertisers, analyzing previously performed actions, decide which ads that might interest you, etc.
Of course, the creation and storage of these files is consistent with the user. Browsers allow erasing or not creating cookies at all, however they are necessary for the proper operation of many sites. If you delete or block the ability to create cookies, some sections of such sites will stop working and you will not be able to use these sections.
3. Logs of visits.
Most websites use browsing logs and store in them: search queries, time and date of visits, your computer’s IP address and cookies stored on it, type of browser and operating system. The formation of the journal occurs in a split second. Today, some companies are introducing a time limit for storing data in journals. It looks like this - after 9 months from the IP-addresses are removed, data that uniquely identify computers. After 18 months, the identifier of the cookies is replaced with a new sequence of characters and it becomes even harder to link the file to you. But 9 months is a decent time, and older data might just be uninteresting, don't you think?
4. A personal account is another reliable way to get your personal data. Whether it is a social network page or a resume on the site of work - here we reveal ourselves in detail to “all the winds”. A personal account of the online store saves the delivery address, of course, so that you do not have to specify it again and again, it keeps the history of your purchases, so you can find out where, when and what you buy.
How it works.
This entire array of information, daily reported by most of us, is “personal data”. Data is accumulated with a single global goal - to make life easier for those who provide them and those who use them.
Your personal data and data of other users work as a legislative assembly. The majority votes “for”, and the world around is changing. Analysis of the general statistics of the actions of millions of users allows you to constantly make relevant offers, create new products, ensure the safety of states and even control the spread of diseases. How? Brilliantly simple!
Imagine that yesterday you returned from the overseas resort of X. In the morning you had a fever and you did not go to work. Referring to acclimatization, you wrote to friends and colleagues via e-mail that you have a fever and stay at home. Other travelers returning from the same resort, X, also had a fever, and entering search queries into the search engines, they began to search the Internet for ways to reduce it. If similar letters and requests began to arrive from those who rested on resort X with increased frequency, then analyzing the footprint created by “sick” users one can see the general picture: the focus of the virus, the symptoms and the incubation period of the virus.
This applies to everything that happens in the world. It is possible to predict sales volumes, the value of lending rates and the average temperature in the hospital. This is not a joke, you can see the incidence in the world right now on Google Flu Trends , which reports virus activity statistics based on user search queries.
This is not the only Google open source tool that shows the results of our activity on the Internet - the Google Correlate service shows the patterns of the influence of world events on US search queries. Here is an example of graphics for the query: “ go to Russia “. Today, the residents of Georgia want to go to Russia most of all, tomorrow this schedule may change.
In the next section, you will learn how companies make money from your online data.
How much do they earn on your data?
To begin with, let's see that all the “free” web services and programs we use are in fact completely non-free.
In recent years, the world of software has changed, we are not in a hurry to pay for high-quality programs, but prefer to receive software “for free”. Why are software developers interested in giving us their products, after all, to make them quite expensive?
The obvious answer is only one: to get user data.
“I give so that you give me as well” (latin do ut des).
The formula of Roman law, which establishes one of the relations between two persons.
The creators of “free” browsers, social networks, search engines earn money on each user not only by advertising, but also by secretly collecting information. They give us software to get our information in return - it also has a price.
At the same time, program developers deliberately design “barriers of difficulty” on the way to installing more secure configurations of their products, and users are lost in intricate settings. For example, interfaces for managing cookies that are critical for blocking user surveillance by websites are in hard-to-reach places in the browser, and manufacturers often do not improve their usability in this part. Most of the default settings made by companies are not private and are not secure, because users rarely change the default settings. Want to know how quickly you can change your key privacy settings? The following describes the easy way for users of Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox browsers.
Some of the privacy settings in the sites we often use are well hidden, so for a quick search we will use the “Privacyfix” resource or “Privacy Repair” in Russian. The resource groups all the settings into sections and decrypts in detail the value of each setting, so we will use it for information. The final result of the adjustments can be seen immediately and this is also convenient. As soon as you set the settings that block access to your private data, the approximate earnings on your accounts decrease (according to Trefis ). The site interface is divided into 4 sections: Facebook, Google, All websites you visit, All websites that track you.

In the “Facebook” section, the availability of your activity on the pages of the site and the estimated annual $ earnings of Facebook on your account are assessed. It usually ranges from a few cents to tens of dollars a year. The amount of earnings affects the region of your stay and activity in the social network. The “Google” section is organized similarly to the previous one, only search queries are evaluated here. According to analysts, Google earns an average of up to $ 14.70 for each 1000 search queries.
The “Websites” provides a detailed list of Internet resources that share your data, and resources that have various problems with the preservation of privacy. In “Tracking” you can see the sites that track you “in the current time” for commercial purposes. Some of these sites may also use your email contact addresses to collect additional information about you.
Privacy settings sections are divided by items. The background color, checkmarks and exclamation mark on the left indicate “state of affairs”. By clicking on the “Fix” buttons corresponding to the items being changed, you will quickly go to the settings sections of your account to correct them.

In addition, Privacyfix offers to install the browser plugin of the same name, which will allow you to edit the settings on linkedln, pinterest, twitter, stumbleupon and other sites on the Internet. When installed, the plug-in automatically fixes a part of the system settings and shows where the rest are hidden - they will have to be fixed by yourself. If you do not delete the plugin after changing the privacy settings, it will signal attempts to track on other sites and allow you to erase the tracking Cookes with a single click. But let's not forget that Privacyfix is also a free product!
To limit or not the earnings of corporations on your data, everyone decides for himself. Studying us, most companies aim to improve their products and services. As consumers, we will not lose out by getting the very best. In turn, companies wishing to control sales, are forced to systematically study consumer behavior and cannot abandon this marketing tool. Be sure that the more private information is collected in our dossier, the more will be willing to get it, and who knows what is known about us today. So do not forget, your data and even your “skeletons in the closet” have their value.
“If you do not value your rights, remember that others will not appreciate them”
(lat. non sentis si ius suum non aestimant eos memores alios)
Latin saying
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/173463/
All Articles