Curiosity exceeds creator expectations
The United States is currently hosting a scientific conference of the Moon and Planets (44th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference), where new results of Mars research conducted by MSL Curiosity will be released. Scientists from the United States talked about the fact that they were pleasantly surprised by the capabilities of their MastCam cameras, who were able to see what was not supposed to be, and scientists from Russia showed that they were surprised by the surface of Mars, which turned out to be saturated with water in the way that no model promised. .
(Immediately I warn you: there is a lot of science and graphs inside).
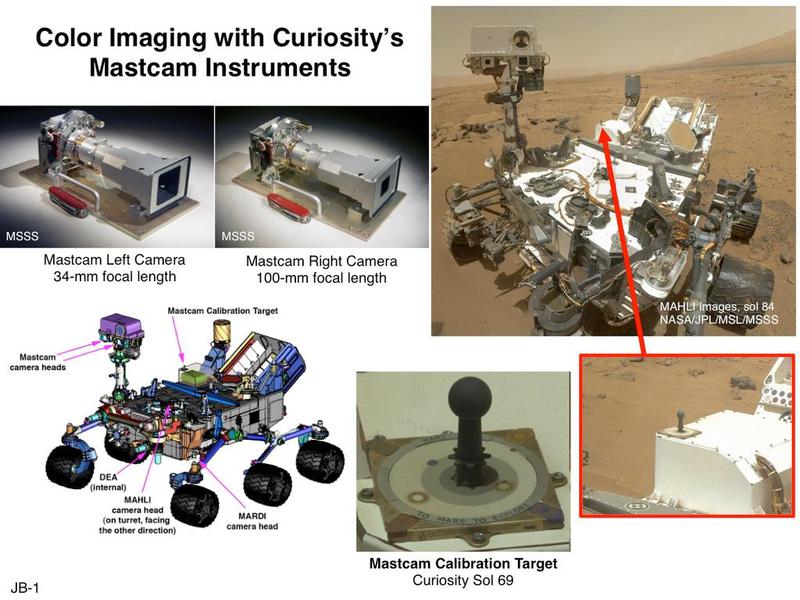
MastCams are two color two megapixel cameras that are located on the mast of the rover. They have a fixed focal length: right 100 mm, and left 34 mm. Due to this, the right “eye” is used for detailed shooting, and the left one - for overview. When Curiosity was just being designed, a fan of 3D movies, director James Cameron, put a lot of effort into flying two identical cameras with a variable focal length. They were made, but did not have time to pass the tests, so Curiosity in one eye is far-sighted, on the other - short-sighted. (A detailed technical description of these cameras and some other Curiosity devices can be found: here )
However, this does not prevent the creation of high-quality stereo-panoramas. (Available on VKontakte tag #MarsAnaglyph ).
')
The cameras have a 1600x1200 CCD matrix Kodak KAI-2020 with a standard Bayer filter , which means they take color photos without processing, which was necessary for his Martian predecessors. In addition to the non-removable filter, each camera is equipped with a set of additional ones that only allow waves of a certain length to pass through. They are located on the wheel between the lens and the matrix.

The combination of Bayer and optional filters provides up to 12 different spectral ranges in which Curiosity can shoot. Moreover, only half of the filters captures the visible range, the rest allow analysis in the out-of-reach infrared range.

All this allows us to explore the surface in more detail, as far as even the experienced eyes of a human geologist would not have provided. Scientists compared the survey with MastCam cameras and compared them with spectral data obtained by other instruments. Thanks to this, we managed to find out that multispectral photography is able to reveal hydrated materials, that is, those in the formation of which water was involved and contained in them.

On the left, the graph shows the degree of reflection of light of different wavelengths in the Knorr region, recorded by mast cameras through different filters, on the right, the degree of reflection characteristic of different materials. Characterized by a dip in infrared light for hydrated materials. The clay in which the bright veins are visible, although formed under the action of water, but does not include it at the molecular level, therefore the difference is determined when shooting MastCam.
NASA uses color coding, which reflects the "signal of hydration" of various strengths:

Pebble Tintina, which broke off the wheel, showed a white fracture:

And his hydration signal turned out to be very strong:

But the comparison of the four surface areas in the place of John Klein did not show any hydrated materials, although the difference in the characteristics of the soil is visible:

They told at the conference about what the difference between “raw” (“raw”), “natural” (natural) and “balanced” (white balanced) color images. As much as anyone would like, but the real Mars is "redder" even what the rover cameras are showing. And the colors close to our vision are obtained by additional processing “as if we were seen on Earth.”

NASA obtained such data through the use of color markers placed on the Curiosity “sundial”:

To identify more subtle color details, processing is performed under false colors (false color), moreover, their falsity will appear if you look in the same mode at the "sundial":

The dull orange-brown color of Mars is due to its dustiness, while fresh fractures expose unexpected colors like this white-blue Sutton_Inlier stone.

From news from California we will move to news from Moscow.
At the same lunar and planetary conference, Russian representatives shared the results of the operation of the DAN instrument.
Let me remind you - this is a device that registers with what energy neutrons fly out of the surface of Mars. This happens when it is bombarded by cosmic charged particles, or from a DAN neutron source. Depending on whether the device catches cosmic neutrons or produces their own modes of operation, it is called passive or active.

Hydrogen in the ground inhibits neutrons, so you can determine how much it is under the device by estimating the percentage of “fast” and “inhibited” particles. In the bulk, hydrogen means either water or hydroxyl (OH). Detector to a depth of 60 cm determines confidently, but is able to catch signals up to 1 m.
Even when Curiosity overcame the first hundred meters, scientists noted that the data from DAN were generally in line with expectations: the ground was very dry and only at the maximum achievable depth the water reached 5%, and did not exceed 1% above. It was quite predictable, because at the Martian equator, in summer, temperatures can rise above 30 degrees Celsius, and low pressure causes the water to evaporate immediately. Such conditions leave no chance to find ice within half a meter from the surface.
When Curiosity descended into Yellowknifle Bay, which is considered the bottom of an ancient lake, the data from the device began to amaze. He began to show that, in some places, the top layer of the surface is wet - up to 3%, and under it begins the "desert" with a 1% water content. That is, DAN revealed the “layering” of Mars even at shallow depths, and these data will allow scientists to more fully present the picture of changes on the planet that led to the situation that is observed now.

The difference in testimony was determined not only on significant segments of the path:

But in a few "steps" of the rover:

Scientists are not in a hurry to interpret the information received and will continue to work further. Although in the coming weeks, the movement of the rover is not expected, so we will not see updates from DAN soon. It remains to hope that the revenge will be when Curiosity goes on a long journey to the mountain.
At the conference, Canadians also shared their results.
They work with the Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) device, which is located on the manipulator:

It allows you to determine the chemical content of the surface that is being investigated. In order to improve the quality of analysis, Curiosity is equipped with a brush that removes dust:

APXS has already conducted many analyzes, but published the results of one, from the Portage site. The graph in a schematic form displays the content of various elements in three types of surface: uncleaned, cleaned, cleaned and rich in white veins. The latter is distinguished by a high content of sulfur and calcium, which generally corresponds to gypsum.

The conference is still ongoing, and the results will be replenished in the next couple of days. Expected at least materials on the operation of the ChemSam laser.
This weekend, the Curiosity computer again gave an error, but this time the problem was quickly identified and eliminated - the culprit was an erroneous file that was deleted. The rover should return to work in the coming days, but on April 4 the connection with it will be interrupted for 4 weeks while the Sun will pass between Mars and Earth. I think at this time I will finish the story that there was an interesting told at today's conference.
(Immediately I warn you: there is a lot of science and graphs inside).

MastCams are two color two megapixel cameras that are located on the mast of the rover. They have a fixed focal length: right 100 mm, and left 34 mm. Due to this, the right “eye” is used for detailed shooting, and the left one - for overview. When Curiosity was just being designed, a fan of 3D movies, director James Cameron, put a lot of effort into flying two identical cameras with a variable focal length. They were made, but did not have time to pass the tests, so Curiosity in one eye is far-sighted, on the other - short-sighted. (A detailed technical description of these cameras and some other Curiosity devices can be found: here )
However, this does not prevent the creation of high-quality stereo-panoramas. (Available on VKontakte tag #MarsAnaglyph ).
')
The cameras have a 1600x1200 CCD matrix Kodak KAI-2020 with a standard Bayer filter , which means they take color photos without processing, which was necessary for his Martian predecessors. In addition to the non-removable filter, each camera is equipped with a set of additional ones that only allow waves of a certain length to pass through. They are located on the wheel between the lens and the matrix.

The combination of Bayer and optional filters provides up to 12 different spectral ranges in which Curiosity can shoot. Moreover, only half of the filters captures the visible range, the rest allow analysis in the out-of-reach infrared range.

All this allows us to explore the surface in more detail, as far as even the experienced eyes of a human geologist would not have provided. Scientists compared the survey with MastCam cameras and compared them with spectral data obtained by other instruments. Thanks to this, we managed to find out that multispectral photography is able to reveal hydrated materials, that is, those in the formation of which water was involved and contained in them.

On the left, the graph shows the degree of reflection of light of different wavelengths in the Knorr region, recorded by mast cameras through different filters, on the right, the degree of reflection characteristic of different materials. Characterized by a dip in infrared light for hydrated materials. The clay in which the bright veins are visible, although formed under the action of water, but does not include it at the molecular level, therefore the difference is determined when shooting MastCam.
NASA uses color coding, which reflects the "signal of hydration" of various strengths:

Pebble Tintina, which broke off the wheel, showed a white fracture:

And his hydration signal turned out to be very strong:

But the comparison of the four surface areas in the place of John Klein did not show any hydrated materials, although the difference in the characteristics of the soil is visible:

They told at the conference about what the difference between “raw” (“raw”), “natural” (natural) and “balanced” (white balanced) color images. As much as anyone would like, but the real Mars is "redder" even what the rover cameras are showing. And the colors close to our vision are obtained by additional processing “as if we were seen on Earth.”

NASA obtained such data through the use of color markers placed on the Curiosity “sundial”:

To identify more subtle color details, processing is performed under false colors (false color), moreover, their falsity will appear if you look in the same mode at the "sundial":

The dull orange-brown color of Mars is due to its dustiness, while fresh fractures expose unexpected colors like this white-blue Sutton_Inlier stone.

From news from California we will move to news from Moscow.
At the same lunar and planetary conference, Russian representatives shared the results of the operation of the DAN instrument.
Let me remind you - this is a device that registers with what energy neutrons fly out of the surface of Mars. This happens when it is bombarded by cosmic charged particles, or from a DAN neutron source. Depending on whether the device catches cosmic neutrons or produces their own modes of operation, it is called passive or active.

Hydrogen in the ground inhibits neutrons, so you can determine how much it is under the device by estimating the percentage of “fast” and “inhibited” particles. In the bulk, hydrogen means either water or hydroxyl (OH). Detector to a depth of 60 cm determines confidently, but is able to catch signals up to 1 m.
Even when Curiosity overcame the first hundred meters, scientists noted that the data from DAN were generally in line with expectations: the ground was very dry and only at the maximum achievable depth the water reached 5%, and did not exceed 1% above. It was quite predictable, because at the Martian equator, in summer, temperatures can rise above 30 degrees Celsius, and low pressure causes the water to evaporate immediately. Such conditions leave no chance to find ice within half a meter from the surface.
When Curiosity descended into Yellowknifle Bay, which is considered the bottom of an ancient lake, the data from the device began to amaze. He began to show that, in some places, the top layer of the surface is wet - up to 3%, and under it begins the "desert" with a 1% water content. That is, DAN revealed the “layering” of Mars even at shallow depths, and these data will allow scientists to more fully present the picture of changes on the planet that led to the situation that is observed now.

The difference in testimony was determined not only on significant segments of the path:

But in a few "steps" of the rover:

Scientists are not in a hurry to interpret the information received and will continue to work further. Although in the coming weeks, the movement of the rover is not expected, so we will not see updates from DAN soon. It remains to hope that the revenge will be when Curiosity goes on a long journey to the mountain.
At the conference, Canadians also shared their results.
They work with the Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) device, which is located on the manipulator:

It allows you to determine the chemical content of the surface that is being investigated. In order to improve the quality of analysis, Curiosity is equipped with a brush that removes dust:

APXS has already conducted many analyzes, but published the results of one, from the Portage site. The graph in a schematic form displays the content of various elements in three types of surface: uncleaned, cleaned, cleaned and rich in white veins. The latter is distinguished by a high content of sulfur and calcium, which generally corresponds to gypsum.

The conference is still ongoing, and the results will be replenished in the next couple of days. Expected at least materials on the operation of the ChemSam laser.
This weekend, the Curiosity computer again gave an error, but this time the problem was quickly identified and eliminated - the culprit was an erroneous file that was deleted. The rover should return to work in the coming days, but on April 4 the connection with it will be interrupted for 4 weeks while the Sun will pass between Mars and Earth. I think at this time I will finish the story that there was an interesting told at today's conference.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/173387/
All Articles