Effective online store. How to create marketable content for a large online store? PART 2
In the last article we wrote about the standard and alternative approach to creating content. Today we will show how we implemented an alternative approach and what results we have achieved.
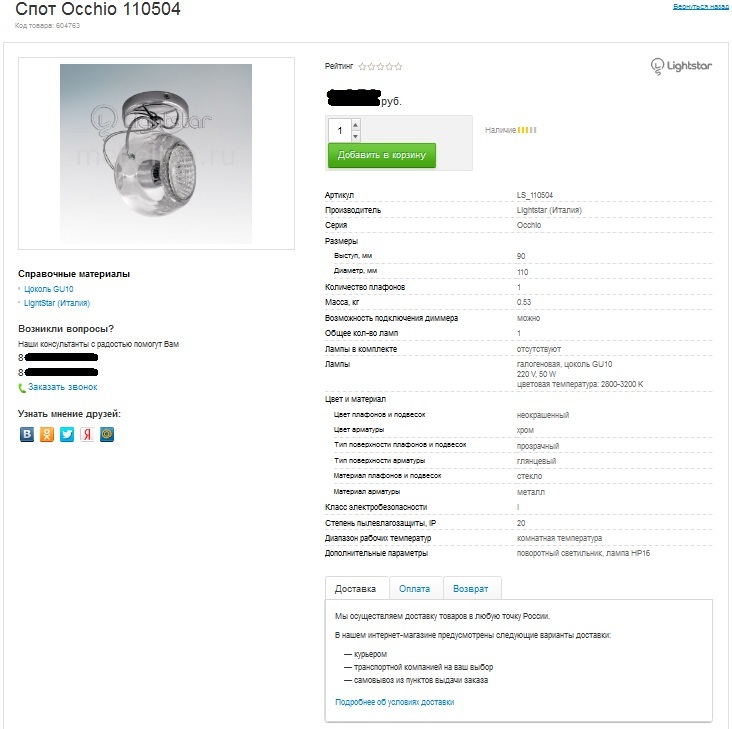
')
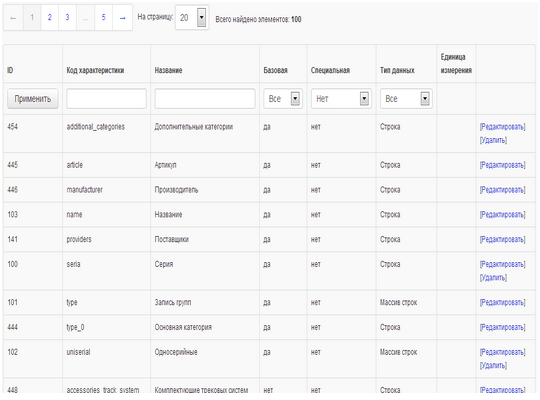
Each characteristic has basic properties that are specified when it is created.
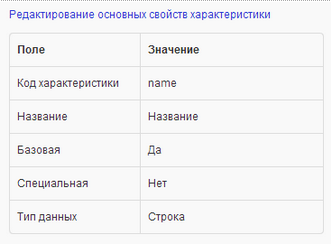
Below is a list of the basic properties of the “Name” feature.
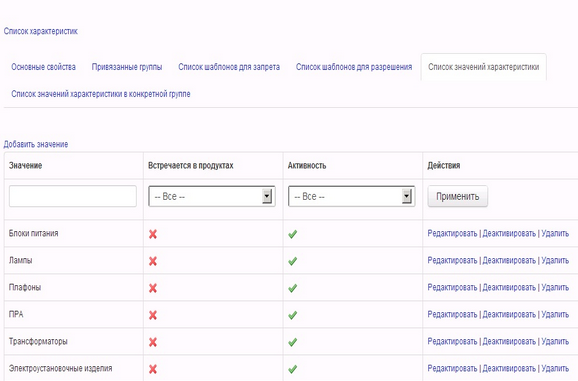
The editing window for the characteristic “Accessories for luminaires” with the tab “List of characteristic values” open:
The window for editing numerical characteristics contains the same tabs as for text characteristics, except for the tab “List of characteristic values”, because ranges of values or specific values for numerical characteristics are set at the level of each specific group from the list of product groups associated with this characteristic, that is, such product groups for which this characteristic is relevant.
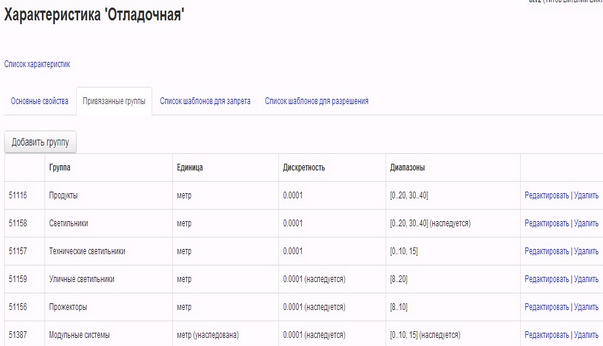
Below is the editing window for the numeric “Debugging” feature with the “Bound Groups” tab open. It is in this tab that you can adjust the ranges, units, and resolution of this characteristic separately for each associated group.
“Units” window:
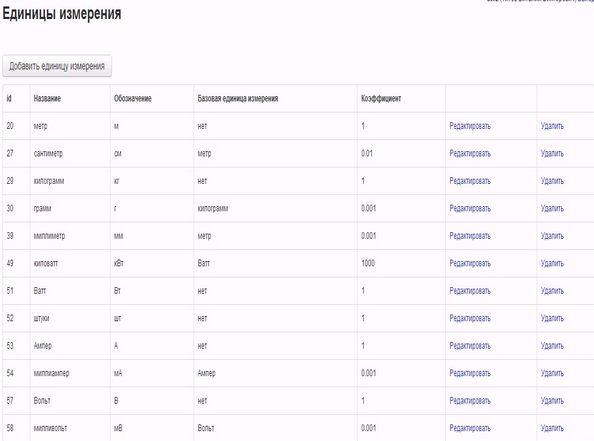
The system allows you to set the base and derived from them units. For example, the unit of measure “Meter” is the base unit, and the unit of measure “Centimeter” and “Millimeter” are derived.
In the same tab “Characteristics” the field “Characteristics” is located.
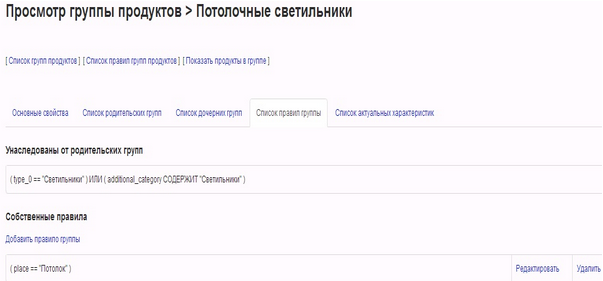
Below is the “View Product Group> Ceiling Lights” window, opened on the “Group Rules List” tab.
Example of the “Feature Sets” window for the “Chandeliers” Product Group
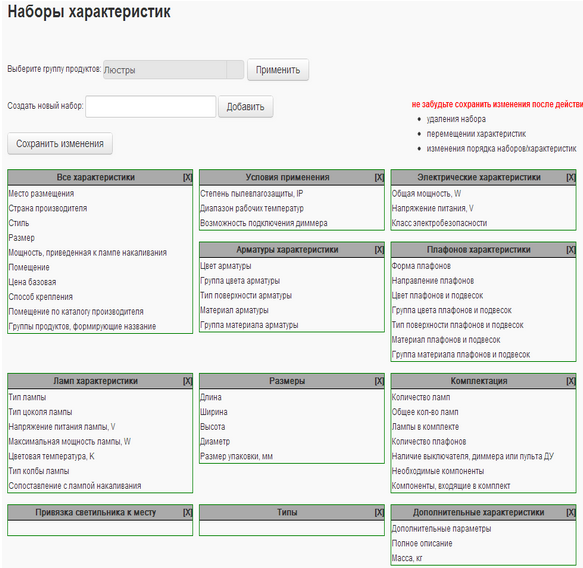
In order not to confuse the groups of characteristics with the groups of products for the former, the name “sets of characteristics” is used. Feature sets serve as a convenient means of structuring and presenting a list of features in a product card.
List of manufacturers.

List of suppliers.
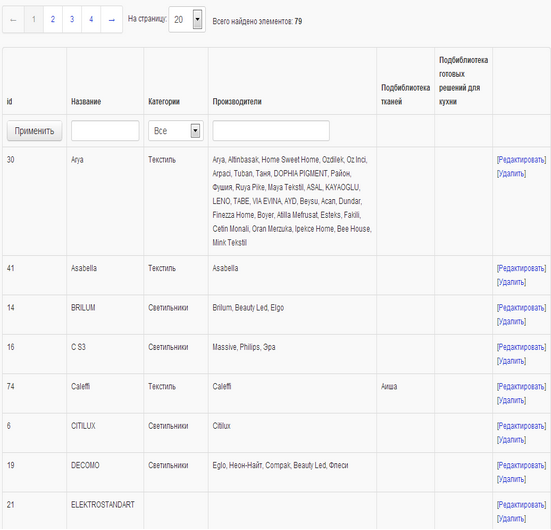
List of sites on which content will be downloaded.
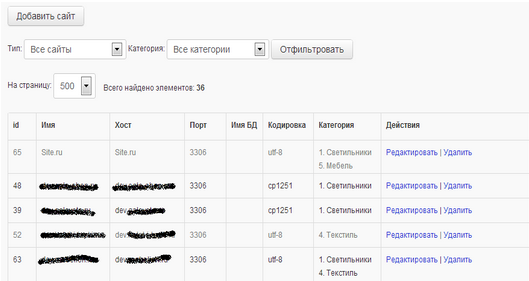
At the next stage of setting up the base for this product category, the administrator must create rules for checking the content, more precisely, the rules for linking the values of various characteristics to each other.
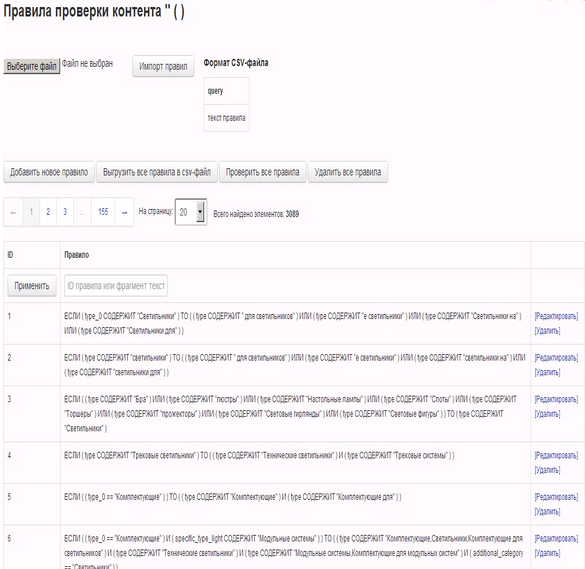
The relationship between characteristics can be hard, when one characteristic value rigidly determines the value or range of values of another characteristic. Or the rule is a ban on the relationship between the values of the considered characteristics. In the first case, if on the basis of such values of characteristics groups of products are formed, then between them there will be a parent-child (nested) relationship. In the second case, product groups created on the basis of the values in question can never be connected in one product - in one Record of groups. If the rules do not regulate the connection or the prohibition of the connection between the values of the characteristics, then the groups formed on the basis of such values can be combined or not combined in the Groups Record.
Next, the administrator creates templates for adding products belonging to different groups within the same category. Without the creation of characteristics, product groups and content verification rules, the creation of such templates is impossible. After the formation of templates, content managers can begin to establish commodity items.
Example of entering a new Product using the “Add Product” template
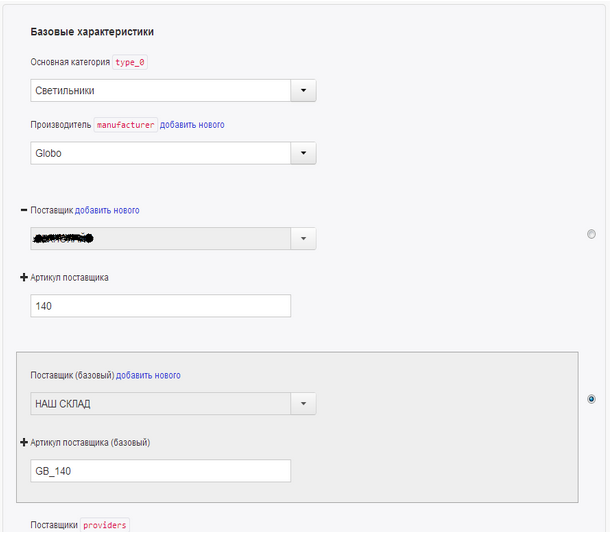
Managers under their accounts:
When the required number of commodity items is entered into the system, the rules for uploading products to the site are created. Each online store contains a catalog with sections and subsections (several levels of nesting). To download products to a specific section of the site, the administrator creates section generation rules — product selections based on characteristic values that allow you to select products from the system base according to the described conditions.
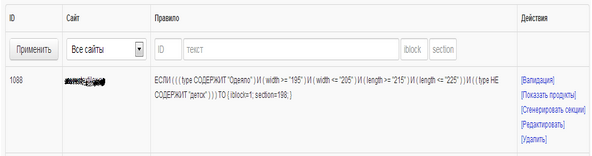
Example conditions for uploading to the site products for the category “Bed linen”
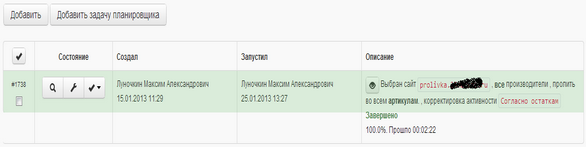
The administrator creates a scheduled task in the system. Which performs the loading of goods on the site according to the selected rules.
Sample job uploading goods to the site.
Creation of commodity content using such a system requires high-quality input of source data and a qualified administrator who is familiar with the product categories for which he will customize the database. He must correctly record the characteristics of the products and structure the product groups. Formalize basic concepts and describe basic terminology so that content managers understand the differences between one product and another.
An example of the definition of “Chandelier”:
A chandelier is a ceiling lamp with 3 or more lamps, with 3 or more lampshades or without lampshades, with any fixing to the ceiling, except for embedding, and a non-linear arrangement of lampshades or lamps.
Key advantages of this model of formation of commercial content:
The use of simple, but at the same time not obvious rules for the formation of marketable content, allows you to make the process fairly easy to manage, controllable and scalable, reducing the percentage of errors to no more than 0.5%.

System scenario
- There are two types of users in the system - the “content manager” and the “administrator”. Each user has a separate account.
- The administrator configures and checks the system - enters into it static data that must be entered once and subsequently used to form commodity items in the system: Article, Name, Color, Weight, etc. Also, it records possible values for textual characteristics or ranges of values, discreteness and dimensionality for numerical characteristics.
')

Each characteristic has basic properties that are specified when it is created.
Below is a list of the basic properties of the “Name” feature.

The editing window for the characteristic “Accessories for luminaires” with the tab “List of characteristic values” open:

The window for editing numerical characteristics contains the same tabs as for text characteristics, except for the tab “List of characteristic values”, because ranges of values or specific values for numerical characteristics are set at the level of each specific group from the list of product groups associated with this characteristic, that is, such product groups for which this characteristic is relevant.
Below is the editing window for the numeric “Debugging” feature with the “Bound Groups” tab open. It is in this tab that you can adjust the ranges, units, and resolution of this characteristic separately for each associated group.

“Units” window:

The system allows you to set the base and derived from them units. For example, the unit of measure “Meter” is the base unit, and the unit of measure “Centimeter” and “Millimeter” are derived.
In the same tab “Characteristics” the field “Characteristics” is located.
Below is the “View Product Group> Ceiling Lights” window, opened on the “Group Rules List” tab.

Example of the “Feature Sets” window for the “Chandeliers” Product Group

In order not to confuse the groups of characteristics with the groups of products for the former, the name “sets of characteristics” is used. Feature sets serve as a convenient means of structuring and presenting a list of features in a product card.
List of manufacturers.

List of suppliers.

List of sites on which content will be downloaded.

At the next stage of setting up the base for this product category, the administrator must create rules for checking the content, more precisely, the rules for linking the values of various characteristics to each other.

The relationship between characteristics can be hard, when one characteristic value rigidly determines the value or range of values of another characteristic. Or the rule is a ban on the relationship between the values of the considered characteristics. In the first case, if on the basis of such values of characteristics groups of products are formed, then between them there will be a parent-child (nested) relationship. In the second case, product groups created on the basis of the values in question can never be connected in one product - in one Record of groups. If the rules do not regulate the connection or the prohibition of the connection between the values of the characteristics, then the groups formed on the basis of such values can be combined or not combined in the Groups Record.
Next, the administrator creates templates for adding products belonging to different groups within the same category. Without the creation of characteristics, product groups and content verification rules, the creation of such templates is impossible. After the formation of templates, content managers can begin to establish commodity items.
Example of entering a new Product using the “Add Product” template

Managers under their accounts:
- Create products directly from the database (the “Add product” window) or load externally the product characteristics (the “Download CSV with products window”), which are automatically checked and recorded in the database.
- Upload to the database of product photos.
- If necessary, edit the content directly in the product card.
When the required number of commodity items is entered into the system, the rules for uploading products to the site are created. Each online store contains a catalog with sections and subsections (several levels of nesting). To download products to a specific section of the site, the administrator creates section generation rules — product selections based on characteristic values that allow you to select products from the system base according to the described conditions.
Example conditions for uploading to the site products for the category “Bed linen”

The administrator creates a scheduled task in the system. Which performs the loading of goods on the site according to the selected rules.
Sample job uploading goods to the site.

Conclusions and statistics
Creation of commodity content using such a system requires high-quality input of source data and a qualified administrator who is familiar with the product categories for which he will customize the database. He must correctly record the characteristics of the products and structure the product groups. Formalize basic concepts and describe basic terminology so that content managers understand the differences between one product and another.
An example of the definition of “Chandelier”:
A chandelier is a ceiling lamp with 3 or more lamps, with 3 or more lampshades or without lampshades, with any fixing to the ceiling, except for embedding, and a non-linear arrangement of lampshades or lamps.
Key advantages of this model of formation of commercial content:
- The use of templates and standard definitions, pre-prepared lists of characteristic values and product groups, as well as rules for checking content and generating sections for sites, reduces the number of errors in the formation and loading of content by no less than an order of magnitude.
- Standardization significantly reduces the ceiling requirements for the level of personnel for the preparation and editing of content.
- Standardization and automation reduce the time to prepare and update the content several times.
- Routine tasks for uploading content to sites allow you to update products at any time, for a large number of product categories and sites.
The use of simple, but at the same time not obvious rules for the formation of marketable content, allows you to make the process fairly easy to manage, controllable and scalable, reducing the percentage of errors to no more than 0.5%.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/173267/
All Articles