Making a VoIP GSM gateway from Tp-link mr-3020 and Huawei E-171 - part two - add Siemens Gigaset c470IP and SMS
There is such a standard ETSI 201 912 SMS for “land lines” (landline sms zap. Sources) as it turned out it is supported by Gigaset c470IP and sms can be sent using VoIP, having learned it wanted to do “shifting sms” i. All that comes to the dongle is sent to the Gigaset C470 IP, and vice versa - in order to be able to send sms from the C470IP to the outside world via the dongle, all of this will happen as in the first part on tp-link mr-3020 under openwrt, the final will also be shown configuration and some pictures.
For those who missed the first part , I talked about the basic installation of openwrt and asterisk on tp-link 3020 using pivotroot on an external flash memory card reader dongle huawei E-171.
The essence of the solution is quite simple, there is a special application for asterisk app_sms and with it the smsq binary to send “landline” sms, for the dongle to work with sms, in addition to the chan-dongle, we will need the function BASE64_DECODE.
But unfortunately, neither the binary nor the function, which in fact the asterisk module is not installed in openwrt, in order to assemble and install them, will have to be compiled from the source codes, in this case it is easier to build the entire system (c) droidman right away. For convenience, I collected everything I needed right away and made my repository, later correcting opkg.conf, IMHO it’s better to collect more than not to complete. I will give the list of packages and important options in my opinion at the end of the article. Now we will focus on the most important. All that is written below is at least relevant for openwrt BARRIER BREAKER (Bleeding Edge, r35905).
We point out the module all packages related to asterisk18, as mentioned above, it is easier to assemble too much and not to install than to undeploy and track dependencies.
In order to build smsq add patch before building
cat ./trunk/feeds/packages/net/asterisk-1.8.x/patches/011-smsq_fix.patch
--- a/utils/utils.xml +++ b/utils/utils.xml @@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ <support_level>extended</support_level> </member> <member name="smsq"> - <defaultenabled>no</defaultenabled> + <defaultenabled>yes</defaultenabled> <depend>popt</depend> <support_level>extended</support_level> </member> ')
After the build we need to transfer ./trunk/build_dir/target-mips_r2_uClibc-0.9.33.2/asterisk-1.8.10.1/utils/smsq to the router in / usr / sbin /. Surely, smsq will issue “smsq: can't load library 'libstdc ++. So.6'” at startup - is treated with:
cd /lib/ ln -s libuClibc-0.9.33.2.so libstdc++.so.6 You will also need to transfer from the build directory ./trunk/build_dir/target-mips_r2_uClibc-0.9.33.2/asterisk-1.8.10.1/funcs/func_base64.so to the router in / usr / lib / asterisk / modules /
Since in the first part I didn’t give configs, here I’ll show everything, the voice part is made based on the links at the end of the first part, I’ll dwell on sms.
dongle.conf
[dongle0] audio=/dev/ttyUSB1 ; tty port for audio connection; no default value data=/dev/ttyUSB2 ; tty port for AT commands; no default value context=dongle-incoming group=0 rxgain=4; txgain=5; resetdongle=yes u2diag=-1 usecallingpres=yes callingpres=allowed_passed_screen imei= ; root @ OpenWrt: / lib # cat /etc/asterisk/sip.conf
[general] externip=10.10.10.10; externaddr=10.10.10.10; localnet=192.168.5.0/255.255.255.0; , gigaset context=private; allowguest=no; context=default ; Default context for incoming calls udpbindaddr=0.0.0.0 tcpenable=yes ; Enable server for incoming TCP connections (default is no) tcpbindaddr=0.0.0.0 ; IP address for TCP server to bind to (0.0.0.0 binds to all interfaces) srvlookup=yes ; Enable DNS SRV lookups on outbound calls [sg470ip] type=friend host=dynamic secret=pass context=from-sg470ip ; siemens 470 IP, canreinvite=yes dtmfmode=rfc2833 permit=192.168.5.200/255.255.255.255 qualify=yes root @ OpenWrt: / lib # cat /etc/asterisk/extensions.conf
[general] static=yes writeprotect=no clearglobalvars=no [dongle-incoming] include => dongle-incoming-sms-ussd exten => s,1,Dial(SIP/sg470ip) exten => h,n,Hangup() [from-sg470ip] exten => _7X.,1,Dial(Dongle/dongle0/holdother:+${FILTER(0-9,${EXTEN})}) exten => _+7X.,1,Dial(Dongle/dongle0/holdother:+${FILTER(0-9,${EXTEN})}) exten => _8X.,1,Dial(Dongle/dongle0/holdother:+7${FILTER(0-9,${EXTEN:1})}) exten => _007X.,1,Dial(Dongle/dongle0/holdother:+7${FILTER(0-9,${EXTEN:3})}) exten => 2000,1,NoOp(Receiving SMS from ${CALLERID(num)}) exten => 2000,n,Answer exten => 2000,n,SMS(2000,as) exten => 2000,n,System(/etc/asterisk/sms-out.sh) exten => h,n,Hangup() [dongle-incoming-sms-ussd] exten => sms,1,Verbose(Incoming SMS from ${CALLERID(num)} ${BASE64_DECODE(${SMS_BASE64})}) exten => sms,n,System(echo '${STRFTIME(${EPOCH},,%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S)} - ${DONGLENAME} - ${CALLERID(num)}: ${BASE64_DECODE(${SMS_BASE64})}' >> /var/log/asterisk/sms.txt) exten => sms,n,System(/usr/sbin/smsq --mt --oa="${CALLERID(num)}" --mttx-callerid="2001" --mttx-channel="SIP/sg470ip" --ud="${BASE64_DECODE(${SMS_BASE64})}") exten => sms,n,Hangup() exten => ussd,1,Verbose(Incoming USSD: ${BASE64_DECODE(${USSD_BASE64})}) exten => ussd,n,System(echo '${STRFTIME(${EPOCH},,%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S)} - ${DONGLENAME}: ${BASE64_DECODE(${USSD_BASE64})}' >> /var/log/asterisk/ussd.txt) exten => ussd,n,System(/usr/sbin/smsq --mt --oa="0" --mttx-callerid="2001" --mttx-channel="SIP/sg470ip" --ud="${DONGLENAME}: ${BASE64_DECODE(${USSD_BASE64})}") exten => ussd,n,Hangup() The last config regarding sms will be discussed in more detail. The fact is that when the sms center is specified in 470IP, then when sending messages, they come to the number and 0 at the end, I have the SMS center number 200 registered in C470IP, so all outgoing sms arrive at 2000 cm. [from-sg470ip] further an asterisk responds and SMS (2000, as) means 2000 the name of the queue, a - answer, s - act as SMS center, i.e. the message is saved in /var/spool/asterisk/sms/morx/2000.* where the asterisk is the date, time, for more detailed information on the SMS () you can refer to the links at the end of the post, then the script that parses the saved file and sends it via dongle
/etc/asterisk/sms-out.sh
#!/bin/sh SPOOL='/var/spool/asterisk/sms/morx' for SMS in `ls -1 "$SPOOL"`; do DST=`grep -e '^da=' "$SPOOL/$SMS" | sed 's/da=//'` MSG=`grep -e '^ud=' "$SPOOL/$SMS" | sed 's/ud=//'` valid="true" if [ ${#DST} -gt 1 ] ; then DSTPRFX=${DST:0:2} if [ $DSTPRFX = "89" ] ; then DST=`echo $DST | sed 's/8/\+7/'` asterisk -rx "dongle sms dongle0 $DST $MSG" else valid="false" fi else if [ $DST = "0" ] ; then asterisk -rx "dongle ussd dongle0 $MSG" else valid="false" fi fi if [ $valid = "false" ] ; then echo "unknown dest number $DST" >> /var/log/asterisk/sms-out.log smsq --mt --mttx-callerid="2001" --mttx-channel="SIP/sg470ip" --oa="200" --ud="ERR unknown dest $DST" fi rm -f "$SPOOL/$SMS" done Here, the fields to whom and the SMS body are selected, then there is a check, if the destination number starts at 89, then 8 is replaced with +7 (you cannot dial + in the number) and a message is sent through the dongle, if the destination number is 0, the body is sent as ussd request, this is done so that you can send USSD requests, for example, by sending * 100 # to 0 c sgc470ip you can check the balance on the sim card in the dongle :) If the conditions are not met, write to the log and send an error message to the phone using smsq , note that when answering from the SMS center, 1 is already added instead of 0 in n as the SMS center (although it seems to work on Siemens and from 0), knowing the number does not ring the phone as usual, but quietly tries to get a text message, in short the principle of the smsq command from the listing is to generate a file in / var / spool / sms / mttx / 0 . *, to generate a .call file, no additional actions are required, all the necessary parameters are on the command line, you can read the hints with the --help and --usage keys.
[dongle-incoming-sms-ussd] in extensions.conf I think is already clear, this is for SMS incoming via gsm channel “into the dongle” - logging and forwarding using smsq to 470ip, the same for incoming responses to USSD with the only difference that the USSD in caller-id will have “ussd”; gigaset doesn’t like this, so there is a parameter when sending from (- oa) to “0”
What it looks like:
SMS sent from a mobile phone to a number that in the dongle number began with "+", 810 came

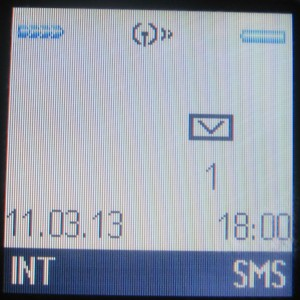
SMS itself

Call, if there is in the gigaset-a notebook

A call if not in the gigaset book

The gigaset setting itself is trivial, as you can see from the pictures, my provider is called GSM, the gigaset-a dialing plan sends everything that starts to 89 to this provider (mr-3020), sms center settings are made from the dextube, sms center number 200 , this center is selected for sending and the provider selected, which is interesting, may not coincide with the dialplan in the database, will still fly away to what is specified in the SMS settings, a few more SMS centers can also be set up, only at the reception.
The list of packages that are used by me, not all are needed, but still better give full
opkg list-installed
asterisk18 - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-app-exec - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-app-readexten - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-app-senddtmf - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-app-setcallerid - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-app-sms - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-app-system - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-app-verbose - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-chan-dongle - 1.1.r10-18 asterisk18-chan-local - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-codec-alaw - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-func-shell - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-pbx-spool - 1.8.10.1-4 asterisk18-sounds - 1.8.10.1-4 base-files - 134-r35905 blkid - 2.21.2-1 block-mount - 0.2.0-10 busybox - 1.19.4-6 dnsmasq - 2.62-3 dropbear - 2012.55-2 e2fsprogs - 1.42.4-1 fdisk - 2.21.2-1 firewall3 - 2013-03-02 glib2 - 2.34.3-1 hotplug2 - 1.0-beta-4 httping - 1.5.2-1 iptables - 1.4.18-2 iw - 3.6-1 jshn - 2013-01-29-0bc317aa4d9af44806c28ca286d79a8b5a92b2b8 kernel - 3.8.2-1-f0811f6432963110cc6f2a1623174e3a kmod-ath - 3.8.2+2013-02-22-1 kmod-ath9k - 3.8.2+2013-02-22-1 kmod-ath9k-common - 3.8.2+2013-02-22-1 kmod-cfg80211 - 3.8.2+2013-02-22-1 kmod-crypto-aes - 3.8.2-1 kmod-crypto-arc4 - 3.8.2-1 kmod-crypto-core - 3.8.2-1 kmod-crypto-hash - 3.8.2-1 kmod-crypto-manager - 3.8.2-1 kmod-fs-ext4 - 3.8.2-1 kmod-gpio-button-hotplug - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ipt-conntrack - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ipt-core - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ipt-nat - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ipt-nathelper - 3.8.2-1 kmod-leds-gpio - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ledtrig-default-on - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ledtrig-netdev - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ledtrig-timer - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ledtrig-usbdev - 3.8.2-1 kmod-lib-crc-ccitt - 3.8.2-1 kmod-lib-crc16 - 3.8.2-1 kmod-mac80211 - 3.8.2+2013-02-22-1 kmod-nls-base - 3.8.2-1 kmod-nls-utf8 - 3.8.2-1 kmod-ppp - 3.8.2-1 kmod-pppoe - 3.8.2-1 kmod-pppox - 3.8.2-1 kmod-scsi-core - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb-core - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb-ohci - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb-serial - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb-serial-option - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb-serial-wwan - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb-storage - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb-uhci - 3.8.2-1 kmod-usb2 - 3.8.2-1 kmod-wdt-ath79 - 3.8.2-1 libblkid - 2.21.2-1 libblobmsg-json - 2013-01-29-0bc317aa4d9af44806c28ca286d79a8b5a92b2b8 libc - 0.9.33.2-1 libcom_err - 1.42.4-1 libcyassl - 1.6.5-2 libext2fs - 1.42.4-1 libffi - 3.0.11-1 libgcc - 4.6-linaro-1 libiconv-full - 1.11.1-1 libip4tc - 1.4.18-2 libip6tc - 1.4.18-2 libiwinfo - 39 libiwinfo-lua - 39 libjson - 0.9-2 liblua - 5.1.5-1 libncurses - 5.7-5 libnet1 - 1.1.2.1-2 libnl-tiny - 0.1-3 libopenssl - 1.0.1e-1 libpcap - 1.1.1-2 libpopt - 1.7-5 libpthread - 0.9.33.2-1 librpc - 0.9.32-rc2-0a2179bbc0844928f2a0ec01dba93d9b5d6d41a7 librt - 0.9.33.2-1 libubox - 2013-01-29-0bc317aa4d9af44806c28ca286d79a8b5a92b2b8 libubus - 2013-01-13-bf566871bd6a633e4504c60c6fc55b2a97305a50 libubus-lua - 2013-01-13-bf566871bd6a633e4504c60c6fc55b2a97305a50 libuci - 2013-01-04.1-1 libuci-lua - 2013-01-04.1-1 libusb-1.0 - 1.0.9-1 libusb-compat - 0.1.4-1 libustream-cyassl - 2013-01-22-da607e6272d789ed5dae3b0efff90912fda6f81f libuuid - 2.21.2-1 libxtables - 1.4.18-2 lua - 5.1.5-1 luci - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-app-diag-core - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-app-diag-devinfo - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-app-firewall - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-i18n-english - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-i18n-russian - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-lib-core - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-lib-ipkg - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-lib-nixio - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-lib-sys - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-lib-web - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-mod-admin-core - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-mod-admin-full - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-proto-core - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-proto-ppp - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-sgi-cgi - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-ssl - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-theme-base - trunk+svn9678-1 luci-theme-openwrt - trunk+svn9678-1 mac-to-devinfo - 1.0.0-2 mc - 4.7.5.3-2 mtd - 20 nano - 2.2.6-1 netdiscover - 0.3-beta6-3 netdiscover-to-devinfo - 1.0.0-2 netifd - 2013-02-19-486aa750a164d41905beb61afec89268e3eb7f48 opkg - 618-3 ppp - 2.4.5-9 ppp-mod-pppoe - 2.4.5-9 procd - 2012-12-20-d343dd9e9a64d4ae7d225ea29169e97fa8d116a1 px5g - 1 smap - 0.6.0-2 smap-to-devinfo - 1.0.0-2 swap-utils - 2.21.2-1 swconfig - 10 terminfo - 5.7-5 uboot-envtools - 2012.04.01-1 ubus - 2013-01-13-bf566871bd6a633e4504c60c6fc55b2a97305a50 ubusd - 2013-01-13-bf566871bd6a633e4504c60c6fc55b2a97305a50 uci - 2013-01-04.1-1 uhttpd - 2013-01-22-14e3971c37e6feb0ec5eda0988e07d8a786ba9f9 uhttpd-mod-ubus - 2013-01-22-14e3971c37e6feb0ec5eda0988e07d8a786ba9f9 usb-modeswitch - 1.2.5-1 usb-modeswitch-data - 20121109 wpad-mini - 20130302-1 zlib - 1.2.7-1 Nuances:
In no case do you need to create folders like / overlay / var or / overlay / tmp, otherwise they will start to be saved to flash, this causes 2 problems at once: the speed of access and the recovery of irrelevant files from the last download, i.e. if you see, for example, in the asterisk console: WARNING [1751]: db.c: 115 dbinit: Unable to open Asterisk database '/ var / lib / asterisk / astdb': No such file or directory
The right solution would be to add mkdir -p / var / lib / asterisk in the appropriate place in /etc/init.d/boot
Busybox in openwrt is built by default without unicode support, use the CONFIG_BUSYBOX_CONFIG_UNICODE_SUPPORT = y option.
The curvature of the hands did not allow soldering to the mini-USB, but the similarity of POE was possible at a distance of about 15 meters, a simple injector was used, a power supply unit from the d-link usb-hub 5V 3A and a converted "barrel" from the router side


And finally, the picture, which was supposed to be the first :)

UPD: do not forget to make make dirclean after updating svn, otherwise there may be problems with the build.
UPD: what I have gathered: www.dropbox.com/sh/xjldxibmzo6bdye/88eCAN2j9S
Useful links on the topic:
www.voip-info.org/wiki/index.php?page=Asterisk+cmd+SMS
wiki.e1550.mobi/doku.php?id=usage
www.automated.it/asterisk/sms.html
forum.ixbt.com/topic.cgi?id=88 : 1699-26
forum.asterisk.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=1160&start=10
Part 1
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/172345/
All Articles