Making flexible graphene ionics using a regular DVD-drive
Scientists from the University of California at Los Angeles have developed a method for the production of thin and flexible graphene supercapacitors ( ionistors ) using a DVD-ROM drive that supports LightScribe. LightScribe technology was originally designed for applying a pattern on the reverse side of the disc. Scientists covered the disk with a layer of graphite oxide on a plastic substrate, and then burned out the outlines of the ionistor plates with a laser. Oxide of graphite under the action of a laser turned into graphene, the electrical conductivity of which is six orders of magnitude higher than that of graphite oxide. These graphene tracks formed the plates.
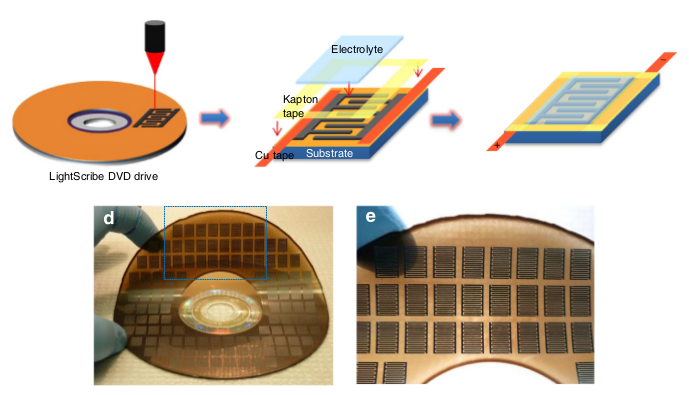
The plates are made in the form of two "comb" - the teeth of one are inserted into the gaps of the other. The thinner the teeth, the more energy such a flat ionistor can store. This design shows much better characteristics than the more familiar “sandwich” of two sheets of graphene with electrolyte between them. In addition, it is much more technological - both plates are created at the same time, after laser treatment, it is enough just to cover them with an electrolyte layer.
In laboratory samples, it was possible to achieve a power density of 200 watts per cubic centimeter. Like conventional ionistors, LSG (Laser Scribed Graphene) flat supercondensation devices withstand a tremendous amount of charge-discharge cycles. Their characteristics practically do not change when bent and twisted. You can create such a supercapacitor with a laser on almost any surface - not only on a flexible film, but also directly on a silicon crystal. In the future, this will allow to create microelectronic devices with an integrated battery on the chip.
')
Nature article (PDF) .
Video:

The plates are made in the form of two "comb" - the teeth of one are inserted into the gaps of the other. The thinner the teeth, the more energy such a flat ionistor can store. This design shows much better characteristics than the more familiar “sandwich” of two sheets of graphene with electrolyte between them. In addition, it is much more technological - both plates are created at the same time, after laser treatment, it is enough just to cover them with an electrolyte layer.
In laboratory samples, it was possible to achieve a power density of 200 watts per cubic centimeter. Like conventional ionistors, LSG (Laser Scribed Graphene) flat supercondensation devices withstand a tremendous amount of charge-discharge cycles. Their characteristics practically do not change when bent and twisted. You can create such a supercapacitor with a laser on almost any surface - not only on a flexible film, but also directly on a silicon crystal. In the future, this will allow to create microelectronic devices with an integrated battery on the chip.
')
Links and videos
Nature article (PDF) .
Video:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/170543/
All Articles