VDS, VDI, anyone you want to choose: desktop virtualization through the eyes of Dell
With the advent of cloud technologies, the utopian idea of “having access to anything, from anywhere, from anywhere” began to gradually become reality. In just a few years, the concepts of "private cloud", VDS, VDI, etc. became massively usable - not without the participation of marketers of almost all major international vendors. Nevertheless, there is still a certain confusion of terms and concepts in the market, as well as a number of "timeless" questions. For example, what is desktop virtualization? Is this technology or approach? What is the difference between desktop virtualization and virtual desktop infrastructure? Finally, what does Dell have to do with it? For answers to these and other questions we ask under cat.
Desktop virtualization or desktop virtualization is an approach that separates the user's working environment (OS, applications, data) and the physical device on which he is used to work (PC, laptop). Thanks to this approach, the employee is no longer tied to the physical workplace in the office, but can work with familiar applications and data from any device (tablet, smartphone, thin client, etc.) from anywhere (at home, on the road, from a hotel or from an internet cafe).
')
The basis of this approach is not one specific technology, but the joint use of various technological solutions in the field of client virtualization. The most popular of them today are:
1. Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a solution that allows you to run a user's OS (Windows 7, etc.) inside a virtual machine on a server in a data center and work with it remotely from any device (Citrix XenDesktop, VMware View, Microsoft VDI, Quest vWorkspace).
2. Remote Desktop Services or Terminal Services (Remote Desktop Services Host (RDSH) \ Terminal Services (TS)) is a classic terminal access that provides a server operating system (usually Windows Server 2008 R2 or 2012) to several users in a competitive mode (who the first one got up, that and sneakers). Each of the remote users works in his session. The most popular solutions are Citrix XenApp, Microsoft RDS, Quest vWorkspace.
3. Remote physical workstation (Blade PC) - a powerful high-performance workstation (often with an installed graphics adapter) in a server form factor, located in the data center, and provides its computing resources to remote users. The most popular solutions are Citrix HDX 3D Pro + Dell R5500, VMware View + Dell R5500.
4. Application Virtualization (Application Virtualization) - delivery and execution of applications on virtual machines, a terminal server or a PC without the usual installation of the program in the OS. Most popular solutions: Microsoft App-V, Citrix XenApp, VMware ThinApp.
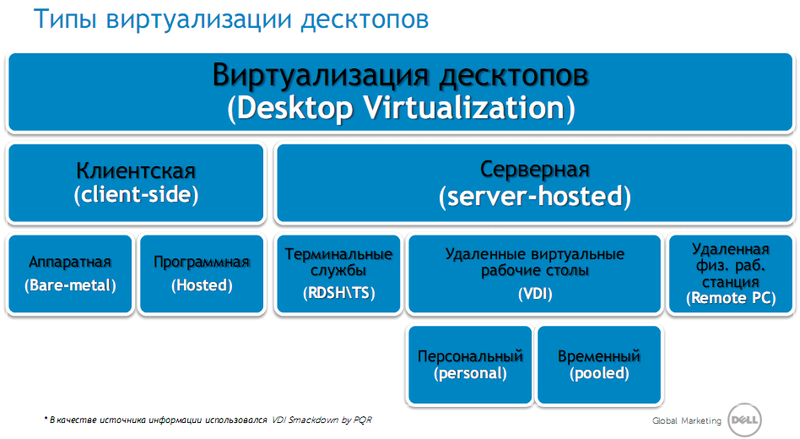
Here are the main types of currently used technologies, but IT, as you know, does not stand still and, perhaps, tomorrow a new version of desktop de-copying will appear.
The realities of today are: we must not forget that with such an approach, the usual personal computers of users can and will be subjected to changes. If before the computer required sufficient computing power to run business applications, as well as large disk space for storing user data, now, when the processes occur in the virtual space of data centers, this is simply not necessary.
We assume that we have dealt with the terminology. Therefore, we turn to a more interesting question.
Probably, this is the second most popular question in the world after a child's physical (children and physicists love to ask) why. Why virtualize desktops? The root cause is simple: of course, to save. Let's roughly estimate the benefits of switching from traditional PCs to thin clients. Of course, someone will say that not everything can be solved with the help of TC. But this is not quite true: the TC device itself is almost universal. Therefore, it is more correct to put the question as follows: “What are the most advantageous (or successful) scenarios for the use of VDI at the moment?”. And here they are:
1. Modernization of infrastructure or the creation of a new
a. Failure \ obsolescence of technology
b. Opening of new offices, branches
2. Security and Regulatory Compliance
a. Compliance with certification requirements
b. Preservation and prevention of data leaks
3. Temporary employees and “employees of the same task”
a. Temporary works (projects, audit, contract)
b. Employees with a narrow range of fixed responsibilities (call-center, etc.)
4. Training and development
a. Training classes
b. Application development, testing, etc.
Personally, I don’t even have to prove the benefits of using desktop virtualization in classrooms. So to say, the memories from university labs, when everyone had to create a separate folder for themselves and hope that the previous group had left the system in a sane state, had not yet faded into oblivion. Well, okay, back to our sheep financial issues.
1. The most obvious cost item that we face every month is energy consumption. TC in comparison with PC is not only space, but also energy saving. The thin client consumes around 7-15 W (depending on the model) against about 100 W in the case of a traditional PC. And if we want to compare the total costs for the month, multiply by the number of working hours (8 hours for 5 days for 4 weeks = 160).
2. Reliability. The presence of a large number of moving parts in the PC, as is known, can lead to failures and, as a result, permanent downtime in the work of employees. Here the principle “we are as strong as our weakest link” works.
3. Support and maintenance - maintaining a large fleet of PCs leads to significant IT costs.
4. Obsolescence - the average lifetime of a PC - 2-3 years, taking into account the constant growth of application needs. Looking ahead, we will say that in really large projects on desktop virtualization (when the bill goes to thousands of places), the payback just begins in the third year.
All this leads to an increase in the popularity of VDI (including switching to TC) in the following industries:
Telecom:
• Mobile employees
• Deployment of temporary infrastructures (elections, teleconference, etc.)
Education:
• Training classes
• Distance learning
• Electronic Libraries
Banks and financial institutions:
• Bank branches, remote offices
• Call centers
Retail:
• Opening of outlets
• Cashiers
Well, the time has come to go to the final stage of the article and answer the central question.
Dell has traditionally been known to society as an exceptionally “iron” company. We will not argue, once it was. But times have changed, and with them the approach of Dell has changed. Over the past year, the company announced two major acquisitions, the importance of which for the IT market, and especially for the desktop virtualization market, is difficult to overestimate. We are talking about companies Wyse and Quest Software.
Wyse (now Dell Wyse ) is the world leader in Tokan customer (TC). The company’s portfolio includes more than 150 different models of shopping malls (after all, they have been working since 1981) that meet various requirements for working with virtual infrastructure. TCs of Dell Wyse are certified to work with all major remote access protocols (ICA \ HDX, RDP, PCoIP), and also use various operating systems as a local system on TCs (Wyse ThinOS, Windows Embedded Standard, Linux). In addition to hardware solutions, the company provides software solutions for configuring, updating and managing thin clients - Wyse Device Manager. At the moment, the solution exists in two versions:
• Dell Wyse Device Manager - installed locally in your infrastructure software that has a server and agent components.
• Dell Wyse Cloud Client Manager is a Dell cloud service that allows you to manage not only thin clients, but also mobile devices based on iOS and Android platforms.
Quest Software is a manufacturer of IT management software solutions. Currently, the company's portfolio includes 6 main areas:
• Database Management
• Data Protection
• Performance Monitoring
• Virtual Desktop Management (User Workspace Management)
• Windows Server Management (Windows Server Management)
• Security Management (Identity & Access Management)
Thus, a typical solution for desktop virtualization can be represented as a “VDI-pie”.
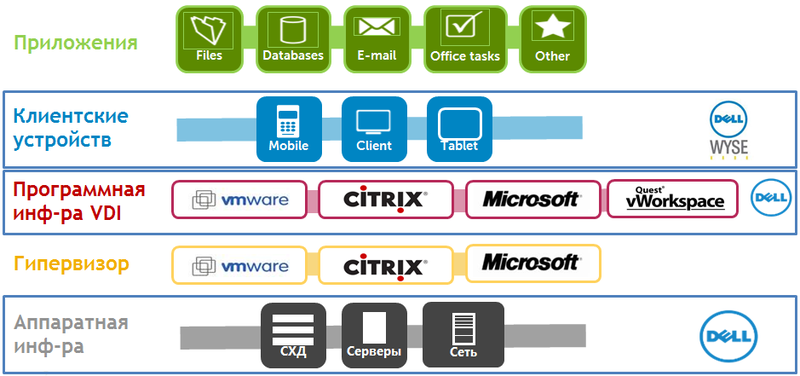
• Hardware infrastructure - the foundation of the solution is servers used as virtualization hosts, which will host either virtual machines or terminal servers for users to access them, data storage systems for storing virtual machine disks and user data, and network infrastructure for ensure fast communication of all components.
• Virtualization platform - as a virtualization platform, hypervisor, Dell, being a partner of all the leaders of this market (Microsoft, VMware, Citrix), invites you to determine which technology is closer. Also, do not forget about the fact that all of the above manufacturers of hypervisors have free editions that have a fairly extensive functionality.
• VDI \ TS software infrastructure - at this level, in addition to all the above-mentioned manufacturers of virtual solutions, Dell is ready to offer a competitive option in the form of Dell Virtualization (formerly Quest vWorkspace - www.quest.com/desktop-virtualization), which is a connection manager between users and the requested resource, the Experience Optimized Protocol (EOP), as well as support for most mobile platforms (Android, iOS). As a hypervisor, this solution supports Microsoft Hyper-V, Vmware ESX and Parallels Virtuozzo Containers.
• Client devices — virtually any device can be used as end devices (PCs, tablets, smartphones, etc.), but the most cost-effective option at the moment is to replace traditional PCs with thin clients. Dell Wyse thin clients support almost all well-known desktop virtualization infrastructures (Microsoft, VMware, Citrix, Quest, Redhat), as well as the ability to centrally manage using Wyse Device Manager or Dell Cloud Client Manager software. Support implies the availability of the appropriate protocol on the TK side (RDP, ICA \ HDX, PCoIP (both software and hardware implementations), EOP, SPICE).
• Applications - as an application virtualization technology, you can use any of the existing solutions, such as Microsoft App-V or VMware ThinApp.
But the Dell portfolio is not full of individual component solutions. There is something to say about the complexity. True, we risk increasing the volume of the article by a factor of two if we go into details. Therefore, if short and to the point.
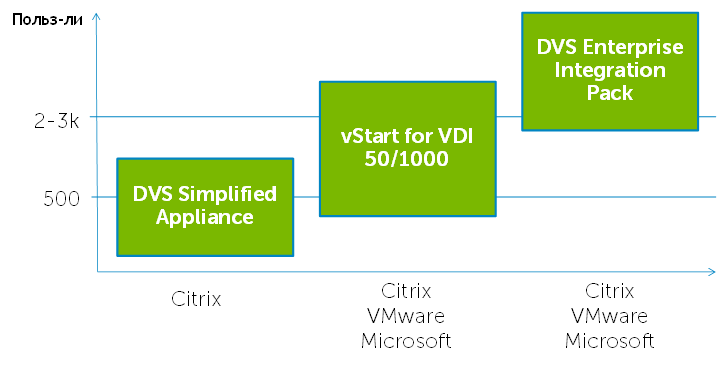
At the moment, in the line of solutions for desktop virtualization from Dell, I have the following options:
1. DVS Simplified Appliance
2. vStart for VDI
3. DVS Integrated Solution Stack
Each of them is focused on different sizes of business and is optimized for different tasks. In the simplest ranking (by the number of users), they can be arranged as follows:
We will write more about each of them. For now, let's finish the article with a practical example of desktop virtualization for a 3D modeling task.
Without delaying, we get acquainted with the logic of the solution:

The presented scheme clearly demonstrates one of the options for virtualization. Forwarding maps to a virtual machine opens up new horizons for those who use the XenApp infrastructure, because instead of a dedicated server, you can use virtual machines, each of which will have its own dedicated graphics card. This was made possible by the advent of NVIDIA GRID K1 and K2 cards, the first graphics adapter for cloud computing. In terms of applications, the Dell PowerEdge R720 server solution with GRID K1 and K2 cards allows you to create a high-density infrastructure, both regular VDI users and users of heavy 3D applications, i.e. covers all of the above areas of virtualization. When a server solution is not acceptable, using the Dell Precision R5500 with the NVIDIA Quadro also opens up all the possibilities of virtualization.
If you have a task to transfer your office users to a virtual environment, then the most optimal server solution will be the Dell PowerEdge R720 with GRID K1. Due to the fact that the card has 4 graphics chips on the Kepler architecture and a 16GB framebuffer (4GB per chip), a high density of people per server is provided. You can also achieve high density for simple CAD applications (AutoCAD, Kompas-3D, etc.) by placing up to 8 users on a 1U server using the card forwarding mechanism in a virtual machine.
If you have the task of transferring users of heavy 3D applications, the Dell PowerEdge solution with GRID K2 opens up the possibility to transfer 4 engineers to a 1U server and at the same time give them the opportunity to feel the speed of work comparable to a normal workstation.
Using the Dell Precision R5500 with NVIDIA Quadro will open up small companies that do not have dedicated server rooms to use virtualization and experience its benefits.
More and more often, the term “post-PC era” appears in the media. In fact, the rejection of the classic PC will not be so categorical. There are still business problems that are difficult (or too costly) to solve using TC, using desktop virtualization (which only costs the battle for IOPs). However, it should be understood that with the development of virtualization technologies there are more and more opportunities to reduce costs and optimize the work of employees through the use of more modern technologies.
In order
Desktop virtualization or desktop virtualization is an approach that separates the user's working environment (OS, applications, data) and the physical device on which he is used to work (PC, laptop). Thanks to this approach, the employee is no longer tied to the physical workplace in the office, but can work with familiar applications and data from any device (tablet, smartphone, thin client, etc.) from anywhere (at home, on the road, from a hotel or from an internet cafe).
')
The basis of this approach is not one specific technology, but the joint use of various technological solutions in the field of client virtualization. The most popular of them today are:
1. Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a solution that allows you to run a user's OS (Windows 7, etc.) inside a virtual machine on a server in a data center and work with it remotely from any device (Citrix XenDesktop, VMware View, Microsoft VDI, Quest vWorkspace).
2. Remote Desktop Services or Terminal Services (Remote Desktop Services Host (RDSH) \ Terminal Services (TS)) is a classic terminal access that provides a server operating system (usually Windows Server 2008 R2 or 2012) to several users in a competitive mode (who the first one got up, that and sneakers). Each of the remote users works in his session. The most popular solutions are Citrix XenApp, Microsoft RDS, Quest vWorkspace.
3. Remote physical workstation (Blade PC) - a powerful high-performance workstation (often with an installed graphics adapter) in a server form factor, located in the data center, and provides its computing resources to remote users. The most popular solutions are Citrix HDX 3D Pro + Dell R5500, VMware View + Dell R5500.
4. Application Virtualization (Application Virtualization) - delivery and execution of applications on virtual machines, a terminal server or a PC without the usual installation of the program in the OS. Most popular solutions: Microsoft App-V, Citrix XenApp, VMware ThinApp.

Here are the main types of currently used technologies, but IT, as you know, does not stand still and, perhaps, tomorrow a new version of desktop de-copying will appear.
The realities of today are: we must not forget that with such an approach, the usual personal computers of users can and will be subjected to changes. If before the computer required sufficient computing power to run business applications, as well as large disk space for storing user data, now, when the processes occur in the virtual space of data centers, this is simply not necessary.
We assume that we have dealt with the terminology. Therefore, we turn to a more interesting question.
What for?
Probably, this is the second most popular question in the world after a child's physical (children and physicists love to ask) why. Why virtualize desktops? The root cause is simple: of course, to save. Let's roughly estimate the benefits of switching from traditional PCs to thin clients. Of course, someone will say that not everything can be solved with the help of TC. But this is not quite true: the TC device itself is almost universal. Therefore, it is more correct to put the question as follows: “What are the most advantageous (or successful) scenarios for the use of VDI at the moment?”. And here they are:
1. Modernization of infrastructure or the creation of a new
a. Failure \ obsolescence of technology
b. Opening of new offices, branches
2. Security and Regulatory Compliance
a. Compliance with certification requirements
b. Preservation and prevention of data leaks
3. Temporary employees and “employees of the same task”
a. Temporary works (projects, audit, contract)
b. Employees with a narrow range of fixed responsibilities (call-center, etc.)
4. Training and development
a. Training classes
b. Application development, testing, etc.
Personally, I don’t even have to prove the benefits of using desktop virtualization in classrooms. So to say, the memories from university labs, when everyone had to create a separate folder for themselves and hope that the previous group had left the system in a sane state, had not yet faded into oblivion. Well, okay, back to our sheep financial issues.
1. The most obvious cost item that we face every month is energy consumption. TC in comparison with PC is not only space, but also energy saving. The thin client consumes around 7-15 W (depending on the model) against about 100 W in the case of a traditional PC. And if we want to compare the total costs for the month, multiply by the number of working hours (8 hours for 5 days for 4 weeks = 160).
2. Reliability. The presence of a large number of moving parts in the PC, as is known, can lead to failures and, as a result, permanent downtime in the work of employees. Here the principle “we are as strong as our weakest link” works.
3. Support and maintenance - maintaining a large fleet of PCs leads to significant IT costs.
4. Obsolescence - the average lifetime of a PC - 2-3 years, taking into account the constant growth of application needs. Looking ahead, we will say that in really large projects on desktop virtualization (when the bill goes to thousands of places), the payback just begins in the third year.
All this leads to an increase in the popularity of VDI (including switching to TC) in the following industries:
Telecom:
• Mobile employees
• Deployment of temporary infrastructures (elections, teleconference, etc.)
Education:
• Training classes
• Distance learning
• Electronic Libraries
Banks and financial institutions:
• Bank branches, remote offices
• Call centers
Retail:
• Opening of outlets
• Cashiers
Well, the time has come to go to the final stage of the article and answer the central question.
What does Dell have to do with it?
Dell has traditionally been known to society as an exceptionally “iron” company. We will not argue, once it was. But times have changed, and with them the approach of Dell has changed. Over the past year, the company announced two major acquisitions, the importance of which for the IT market, and especially for the desktop virtualization market, is difficult to overestimate. We are talking about companies Wyse and Quest Software.
Wyse (now Dell Wyse ) is the world leader in Tokan customer (TC). The company’s portfolio includes more than 150 different models of shopping malls (after all, they have been working since 1981) that meet various requirements for working with virtual infrastructure. TCs of Dell Wyse are certified to work with all major remote access protocols (ICA \ HDX, RDP, PCoIP), and also use various operating systems as a local system on TCs (Wyse ThinOS, Windows Embedded Standard, Linux). In addition to hardware solutions, the company provides software solutions for configuring, updating and managing thin clients - Wyse Device Manager. At the moment, the solution exists in two versions:
• Dell Wyse Device Manager - installed locally in your infrastructure software that has a server and agent components.
• Dell Wyse Cloud Client Manager is a Dell cloud service that allows you to manage not only thin clients, but also mobile devices based on iOS and Android platforms.
Quest Software is a manufacturer of IT management software solutions. Currently, the company's portfolio includes 6 main areas:
• Database Management
• Data Protection
• Performance Monitoring
• Virtual Desktop Management (User Workspace Management)
• Windows Server Management (Windows Server Management)
• Security Management (Identity & Access Management)
Thus, a typical solution for desktop virtualization can be represented as a “VDI-pie”.

• Hardware infrastructure - the foundation of the solution is servers used as virtualization hosts, which will host either virtual machines or terminal servers for users to access them, data storage systems for storing virtual machine disks and user data, and network infrastructure for ensure fast communication of all components.
• Virtualization platform - as a virtualization platform, hypervisor, Dell, being a partner of all the leaders of this market (Microsoft, VMware, Citrix), invites you to determine which technology is closer. Also, do not forget about the fact that all of the above manufacturers of hypervisors have free editions that have a fairly extensive functionality.
• VDI \ TS software infrastructure - at this level, in addition to all the above-mentioned manufacturers of virtual solutions, Dell is ready to offer a competitive option in the form of Dell Virtualization (formerly Quest vWorkspace - www.quest.com/desktop-virtualization), which is a connection manager between users and the requested resource, the Experience Optimized Protocol (EOP), as well as support for most mobile platforms (Android, iOS). As a hypervisor, this solution supports Microsoft Hyper-V, Vmware ESX and Parallels Virtuozzo Containers.
• Client devices — virtually any device can be used as end devices (PCs, tablets, smartphones, etc.), but the most cost-effective option at the moment is to replace traditional PCs with thin clients. Dell Wyse thin clients support almost all well-known desktop virtualization infrastructures (Microsoft, VMware, Citrix, Quest, Redhat), as well as the ability to centrally manage using Wyse Device Manager or Dell Cloud Client Manager software. Support implies the availability of the appropriate protocol on the TK side (RDP, ICA \ HDX, PCoIP (both software and hardware implementations), EOP, SPICE).
• Applications - as an application virtualization technology, you can use any of the existing solutions, such as Microsoft App-V or VMware ThinApp.
But the Dell portfolio is not full of individual component solutions. There is something to say about the complexity. True, we risk increasing the volume of the article by a factor of two if we go into details. Therefore, if short and to the point.
At the moment, in the line of solutions for desktop virtualization from Dell, I have the following options:
1. DVS Simplified Appliance
2. vStart for VDI
3. DVS Integrated Solution Stack
Each of them is focused on different sizes of business and is optimized for different tasks. In the simplest ranking (by the number of users), they can be arranged as follows:

We will write more about each of them. For now, let's finish the article with a practical example of desktop virtualization for a 3D modeling task.
Without delaying, we get acquainted with the logic of the solution:

The presented scheme clearly demonstrates one of the options for virtualization. Forwarding maps to a virtual machine opens up new horizons for those who use the XenApp infrastructure, because instead of a dedicated server, you can use virtual machines, each of which will have its own dedicated graphics card. This was made possible by the advent of NVIDIA GRID K1 and K2 cards, the first graphics adapter for cloud computing. In terms of applications, the Dell PowerEdge R720 server solution with GRID K1 and K2 cards allows you to create a high-density infrastructure, both regular VDI users and users of heavy 3D applications, i.e. covers all of the above areas of virtualization. When a server solution is not acceptable, using the Dell Precision R5500 with the NVIDIA Quadro also opens up all the possibilities of virtualization.
If you have a task to transfer your office users to a virtual environment, then the most optimal server solution will be the Dell PowerEdge R720 with GRID K1. Due to the fact that the card has 4 graphics chips on the Kepler architecture and a 16GB framebuffer (4GB per chip), a high density of people per server is provided. You can also achieve high density for simple CAD applications (AutoCAD, Kompas-3D, etc.) by placing up to 8 users on a 1U server using the card forwarding mechanism in a virtual machine.
If you have the task of transferring users of heavy 3D applications, the Dell PowerEdge solution with GRID K2 opens up the possibility to transfer 4 engineers to a 1U server and at the same time give them the opportunity to feel the speed of work comparable to a normal workstation.
Using the Dell Precision R5500 with NVIDIA Quadro will open up small companies that do not have dedicated server rooms to use virtualization and experience its benefits.
Conclusion
More and more often, the term “post-PC era” appears in the media. In fact, the rejection of the classic PC will not be so categorical. There are still business problems that are difficult (or too costly) to solve using TC, using desktop virtualization (which only costs the battle for IOPs). However, it should be understood that with the development of virtualization technologies there are more and more opportunities to reduce costs and optimize the work of employees through the use of more modern technologies.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/170241/
All Articles