IT project management
Management, as a technical process, is the main and integral factor in the development of projects. In the overwhelming majority of cases, it is difficult for startups to hire an experienced manager - the services of a decent specialist are not cheap, and it will be difficult for an outsider to trust a startup person to an outsider. Therefore, as a rule, the project participants themselves are engaged in management.
On Habré there are many topics on specific aspects of project management. But it is the fundamentals of management that have not yet been covered.
Let's try to close this gap.
')
Briefly marked, highlighted and explained the main, most important points.
UPD. Post about management, not about managers.
Management is management. In our case, project management.
It is clear that project management is the work on its components.

The manager works with processes. Processes are an integral part of projects.
The process may be one-time or continuous, but it is in any case iterative. This means that each process has cyclical properties - it can be easily repeated, and even to start a new process, it is possible to apply the accumulated experience - academic methods, personal experience, experience of colleagues and so on.
One of the most popular and at the same time controversial methods of traditional management is delegation. There is a lot of academic information about how, who and when to assign tasks.
In a startup, as a rule, delegation in the general sense is not available. Too little money, too few people.
Direct participants in a newborn project, as a rule, are few. Hiring experts from the outside is expensive, and, besides, is fraught with information leakage and additional time costs.
Therefore, to ensure the effectiveness of management (successful project management), it is advisable to pay more attention to other available methods:
- system analysis;
- interactive control;
- Management of risks.
In fact, working with limited resources is more efficient.
1. Excessive resources dampen
2. In a small group, communication is shorter and more efficient.
3. A small group is easier to set up on the target.
4. In a small group, processes are more effectively controlled.
5. In a small group it is easier to protect commercial secrets.
Strong corporations, such as Google, use the small group method to solve almost all key tasks. There is a team of interested professionals who work on the project. As experience shows, problems are solved, and projects are “fired”.
Do not be shy about the small size of your team. Generally, no complexes! Only enthusiasm, only objectivism.
Thanks to the system analysis method, small working groups solve complex problems. And do it quickly and cheaply.
I do not encourage you to create tons of hard-to-read documentation. But using even some basic techniques will give your project life. Here are these techniques:
- division of tasks into subtasks;
- allocation of subprojects;
- recording (logging) of everything.
The objectives of system analysis are as follows:
- obtaining a transparent and obvious view of all the details of the project;
- identification of potential bottlenecks;
- identification of hidden factors, primarily costs;
- coordination of tactical and strategic vision between all project participants .
"Divide and dominate," the ancient rulers bequeathed to us. To this day, this project management technique is one of the most effective.
The method of dividing tasks into subtasks can be used both for developing a work plan and for analyzing other aspects and situations.
For each analytical element, for each factor and subtask, three questions are formalized: goal, objects, and methods. The scale, importance and complexity of the task is evaluated. If the task is complex, large-scale or critical - it is divided into subtasks or allocated in a separate project.
A simple task is one that contains obviously few details. From here it is easy to get a reverse thesis - any task that is not recognized as simple should be recognized as difficult, and will undergo division.
It is perfectly normal when, as a result of the development of an action plan, the content of the project is revised.

It makes sense to record everything and always. In a text editor, in euronote or in specialized software - it does not matter. The main thing is to record, and regularly inquire that all key project participants are aware of the records.
Everything was recorded not only by Stalin, but by all advanced scientists, businessmen and devotees.
Dana Scully recorded in detail on the recorder the process of opening the aliens, and notes on the investigations. If at some point you get bored of writing, remember it.

When assessing risks, as well as choosing strategic and tactical decisions, unknown, implicit or complex (multicomponent) factors should be evaluated.
Within the framework of a low-budget start-up it is difficult, and often simply pointless, to conduct examinations. For making decisions, there are quite effective low-cost techniques.
One of these techniques is the use of weights.
A table is being compiled. Horizontal - solutions, including hypothetical. Vertical - factors. The cells contain subjective assessments - the degree of influence of factors on the effectiveness of the solution in question.
You can use the results in different ways, summing up the points in different directions and in different ways, finding the mean, etc. Thus, it is possible to evaluate both methodologies and choices in a variety of situations.
This method is also one of the means of resolving differences between project participants. The controversial solutions to the problem issue are scrupulously detailed, a questionnaire is drawn up from the obtained theses and questions, and each of the participants fills in their own version. The leading option is easy to identify, and participants are likely to agree on the expediency of his choice.
Calling something "expensive", the programmer implies the expenditure of resources of the machine or network. Similarly, an IT project manager has time in mind. Literally, time is the main dimension for which estimates of the “expensive” or “acceptable” type can be applied.
If your project requires software for tens of thousands of dollars, or it is a game project, where you need to pay for thousands of designer works, this is not so scary. As part of the analysis of the investment project, these costs can be estimated and adequately compared with the profit.
But the most expensive waste, and one of the most serious troubles that can happen to the project, will be delaying time.
In detail this question was revealed in a post about risk management .
Everywhere and always has a project manager the sense to look for ways and means of saving time. For this purpose, the assessment of priorities, and a deeper analysis to find bottlenecks and the actual minimization of labor, planning and control of work at different levels and other actions will serve.
Good ways to manage and optimize time is phased, and perhaps the sooner opening of the project on a smaller scale, with an eye to further development. In fact, in almost any plan, some of the actions can be transferred from preparatory to combat, or under another pretext — simply postpone. To save the most expensive - time.
Preparatory activities and the project in working mode are two different projects!
Naturally, it makes sense to work with them separately. Naturally, at first it makes sense to design the second, and only then - the first. In the overwhelming majority of startups, unnecessary actions, extra expenses are performed. And they are not so difficult to reduce - if you first focus on the question "what we want to have," and only then - "how we want to get it."
While the project is not - all actions to profitability relate to the first part. When the project is working - all actions relate to the second. Naturally, different mechanisms work at the same time, completely different specifics, therefore, it is necessary to work with these stages in different ways.
Marketing and business model, of course, belong to the second part. There can also be attributed most of the iterative costs (including advertising and technical support).
The package of actions required from zero to the opening of the project - in the first part.
By the way, it is easy to distinguish an experienced IT entrepreneur from an amateur. Experts in banks and investment funds often use this method as well.
Experienced as a rule does not allow gaps in the presentation, and has a clear vision of an already working project. The description of the business model he can not be limited to one or two sentences, because he already knows the mass of the details of his and competitive projects, as well as the specifics of the industry.
Inexperienced people always focus on actions related to the opening of the project, but have a broad idea of the future development of the project and the normal mode of its work.
For example, here are some of the differences in the subject area, showing the difference between the project phases:
Both processes have iterative features and common objective features, but at the same time have a lot of differences.
The expert, whose opinion will be considered by the investor, will be interested in the following.
The calendar schedule is usually drawn up by quarter.
In the process of business planning, it makes sense to try to predict the development of the project at least 1-2 years ahead. But that's another topic.
Maybe something missed? Let me know - I will write in the following topics.
Thank you for your attention and good luck!
On Habré there are many topics on specific aspects of project management. But it is the fundamentals of management that have not yet been covered.
Let's try to close this gap.
')
Briefly marked, highlighted and explained the main, most important points.
UPD. Post about management, not about managers.
- How to manage
- Main management process
- No delegation? And this is good
- Small combat sabotage group
- System analysis
- Divide et empera
- Logging
- Evaluation of multiple and implicit factors
- Time as the main factor
- Two in one
How to manage
Management is management. In our case, project management.
It is clear that project management is the work on its components.

Main management process
The manager works with processes. Processes are an integral part of projects.
The process may be one-time or continuous, but it is in any case iterative. This means that each process has cyclical properties - it can be easily repeated, and even to start a new process, it is possible to apply the accumulated experience - academic methods, personal experience, experience of colleagues and so on.
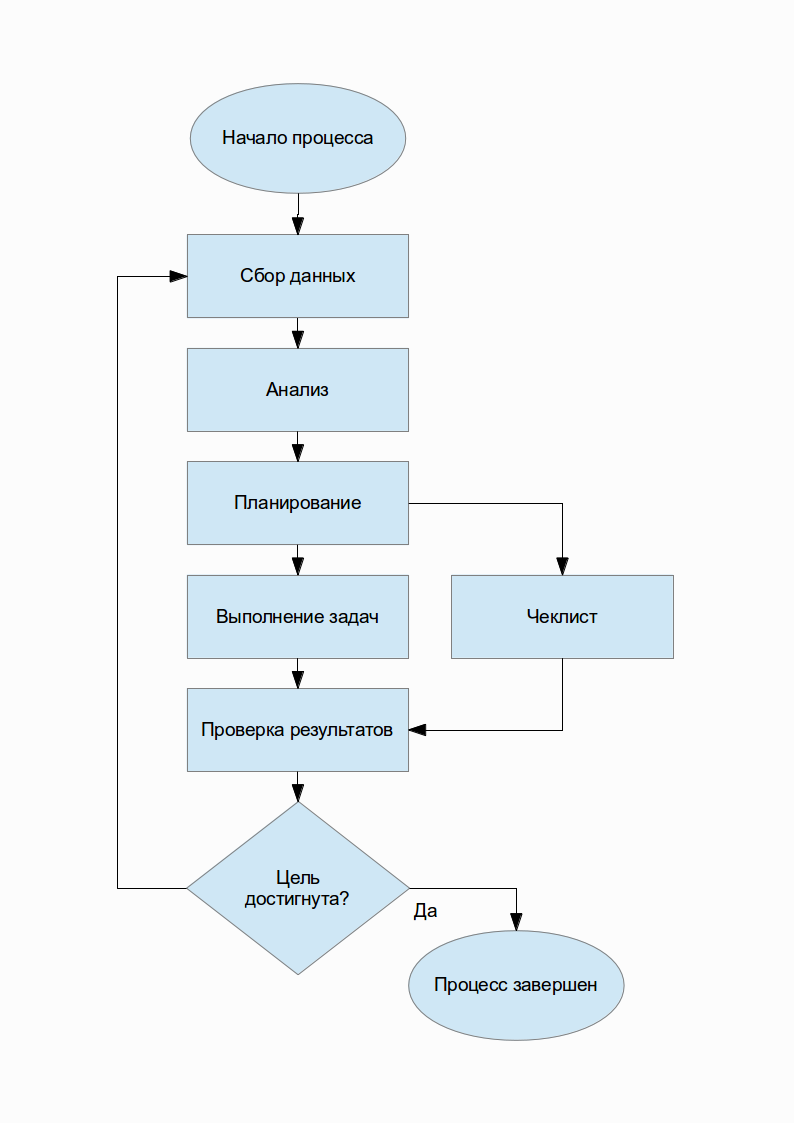
- Before starting the process, it is necessary to formalize the initial data and highlight the goals.
- The analysis stage is optional. It is carried out, depending on the scale and price of the process. If the process is expensive - all the initial data are subjected to detail, the information is supplemented with diagrams and summaries.
- At the planning stage, methods for solving the problem are selected, it is determined how the process will be carried out.
- To ensure the correctness of the acceptance, a checklist is drawn up at the planning stage - a list of criteria that clearly indicates that the project has been completed.
- Naturally, the contractor should be available to the maximum amount of information associated with the process in which he participates - the source data, goals and requirements in the checklist.
- If the process is not continuous, it can be completed when the goals are achieved.
- When the process is repeated, the results of the previous iteration are added to the source data.

No delegation? And this is good
One of the most popular and at the same time controversial methods of traditional management is delegation. There is a lot of academic information about how, who and when to assign tasks.
In a startup, as a rule, delegation in the general sense is not available. Too little money, too few people.
Direct participants in a newborn project, as a rule, are few. Hiring experts from the outside is expensive, and, besides, is fraught with information leakage and additional time costs.
Therefore, to ensure the effectiveness of management (successful project management), it is advisable to pay more attention to other available methods:
- system analysis;
- interactive control;
- Management of risks.
Small combat sabotage group
In fact, working with limited resources is more efficient.
1. Excessive resources dampen
2. In a small group, communication is shorter and more efficient.
3. A small group is easier to set up on the target.
4. In a small group, processes are more effectively controlled.
5. In a small group it is easier to protect commercial secrets.
Strong corporations, such as Google, use the small group method to solve almost all key tasks. There is a team of interested professionals who work on the project. As experience shows, problems are solved, and projects are “fired”.
Do not be shy about the small size of your team. Generally, no complexes! Only enthusiasm, only objectivism.
System analysis
Thanks to the system analysis method, small working groups solve complex problems. And do it quickly and cheaply.
I do not encourage you to create tons of hard-to-read documentation. But using even some basic techniques will give your project life. Here are these techniques:
- division of tasks into subtasks;
- allocation of subprojects;
- recording (logging) of everything.
The objectives of system analysis are as follows:
- obtaining a transparent and obvious view of all the details of the project;
- identification of potential bottlenecks;
- identification of hidden factors, primarily costs;
- coordination of tactical and strategic vision between all project participants .
Divide et empera
"Divide and dominate," the ancient rulers bequeathed to us. To this day, this project management technique is one of the most effective.
The method of dividing tasks into subtasks can be used both for developing a work plan and for analyzing other aspects and situations.
For each analytical element, for each factor and subtask, three questions are formalized: goal, objects, and methods. The scale, importance and complexity of the task is evaluated. If the task is complex, large-scale or critical - it is divided into subtasks or allocated in a separate project.
A simple task is one that contains obviously few details. From here it is easy to get a reverse thesis - any task that is not recognized as simple should be recognized as difficult, and will undergo division.
It is perfectly normal when, as a result of the development of an action plan, the content of the project is revised.

Logging
It makes sense to record everything and always. In a text editor, in euronote or in specialized software - it does not matter. The main thing is to record, and regularly inquire that all key project participants are aware of the records.
Everything was recorded not only by Stalin, but by all advanced scientists, businessmen and devotees.
Dana Scully recorded in detail on the recorder the process of opening the aliens, and notes on the investigations. If at some point you get bored of writing, remember it.

Evaluation of multiple and implicit factors
When assessing risks, as well as choosing strategic and tactical decisions, unknown, implicit or complex (multicomponent) factors should be evaluated.
Within the framework of a low-budget start-up it is difficult, and often simply pointless, to conduct examinations. For making decisions, there are quite effective low-cost techniques.
One of these techniques is the use of weights.
A table is being compiled. Horizontal - solutions, including hypothetical. Vertical - factors. The cells contain subjective assessments - the degree of influence of factors on the effectiveness of the solution in question.
You can use the results in different ways, summing up the points in different directions and in different ways, finding the mean, etc. Thus, it is possible to evaluate both methodologies and choices in a variety of situations.
This method is also one of the means of resolving differences between project participants. The controversial solutions to the problem issue are scrupulously detailed, a questionnaire is drawn up from the obtained theses and questions, and each of the participants fills in their own version. The leading option is easy to identify, and participants are likely to agree on the expediency of his choice.
Time as the main factor
Calling something "expensive", the programmer implies the expenditure of resources of the machine or network. Similarly, an IT project manager has time in mind. Literally, time is the main dimension for which estimates of the “expensive” or “acceptable” type can be applied.
If your project requires software for tens of thousands of dollars, or it is a game project, where you need to pay for thousands of designer works, this is not so scary. As part of the analysis of the investment project, these costs can be estimated and adequately compared with the profit.
But the most expensive waste, and one of the most serious troubles that can happen to the project, will be delaying time.
In detail this question was revealed in a post about risk management .
Everywhere and always has a project manager the sense to look for ways and means of saving time. For this purpose, the assessment of priorities, and a deeper analysis to find bottlenecks and the actual minimization of labor, planning and control of work at different levels and other actions will serve.
Good ways to manage and optimize time is phased, and perhaps the sooner opening of the project on a smaller scale, with an eye to further development. In fact, in almost any plan, some of the actions can be transferred from preparatory to combat, or under another pretext — simply postpone. To save the most expensive - time.
Two in one
Preparatory activities and the project in working mode are two different projects!
Naturally, it makes sense to work with them separately. Naturally, at first it makes sense to design the second, and only then - the first. In the overwhelming majority of startups, unnecessary actions, extra expenses are performed. And they are not so difficult to reduce - if you first focus on the question "what we want to have," and only then - "how we want to get it."
While the project is not - all actions to profitability relate to the first part. When the project is working - all actions relate to the second. Naturally, different mechanisms work at the same time, completely different specifics, therefore, it is necessary to work with these stages in different ways.
Marketing and business model, of course, belong to the second part. There can also be attributed most of the iterative costs (including advertising and technical support).
The package of actions required from zero to the opening of the project - in the first part.
By the way, it is easy to distinguish an experienced IT entrepreneur from an amateur. Experts in banks and investment funds often use this method as well.
Experienced as a rule does not allow gaps in the presentation, and has a clear vision of an already working project. The description of the business model he can not be limited to one or two sentences, because he already knows the mass of the details of his and competitive projects, as well as the specifics of the industry.
Inexperienced people always focus on actions related to the opening of the project, but have a broad idea of the future development of the project and the normal mode of its work.
For example, here are some of the differences in the subject area, showing the difference between the project phases:
| Preparatory work | Main process |
| Software purchase or programming | Technical support |
| Design | Business model, revenue plan and cost plan |
| Research, first marketing and advertising planning | Marketing and advertising plan execution |
| Definition of specialists | FOT |
Both processes have iterative features and common objective features, but at the same time have a lot of differences.
The expert, whose opinion will be considered by the investor, will be interested in the following.
- Separate cost estimates for the two phases
- Separate time estimates (time to prototype, alpha, beta, discovery, time to profitability)
- Evaluation of the business model and its detailed parameters
- Evaluation of marketing and advertising costs before the project is opened and in progress
The calendar schedule is usually drawn up by quarter.
In the process of business planning, it makes sense to try to predict the development of the project at least 1-2 years ahead. But that's another topic.
Maybe something missed? Let me know - I will write in the following topics.
Thank you for your attention and good luck!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/169693/
All Articles