Cisco 1603 Router
Good afternoon, dear readers. I would like to continue the journey through the history of telecommunications equipment. Today it is the turn of the Cisco 160x series routers, or more precisely, the Cisco 1603.
Carrying out archaeological excavations at the warehouse, I found the Cisco 1603 route detector, in surprisingly good condition, in a regular box, complete with, among other things, a large amount of advertising and reference materials. For me, this find was especially pleasant because it was from this series that the acquaintance with the routers of this manufacturer began.
So, what is this device?
')
The following are the network interfaces: 10BaseT, while the AUI output allows using a different physical transmission medium, depending on the converter, for example, optics or coaxial. ISDN BRI S / T - in our country this interface is not widely spread, I have met this only in Moscow and the Krasnodar Territory (UTK). There is a WIC expansion slot for installing modules such as the WIC-1T.
Here is the inner world of the device:
As you can see, you can increase the amount of internal memory and replace the PCMCIA card, which will allow you to use the IOS 12 version and add support for OSPF, IPSec and other useful stuff.
I got a copy with 2 MB of RAM and PCMCIA Flash on 4 MB. By the way, as I understand it, the presence of Flash for this router is not mandatory; in its absence, the eprom loads c1600-boot-r.111-10.AA, which has some minimal functionality. Flash showed c1600-yl.113-11a.bin, possessing, despite its modest size, quite impressive functionality - support for dynamic routing protocols RIP, EIGRP, packet filtering functions (of course, not inspect and ZBF, but established and reflect).
After downloading and carrying out the password recovery procedure, a configuration file was discovered on it, which I want to bring in order to show how little the CLI has changed over a period of more than 10 years.
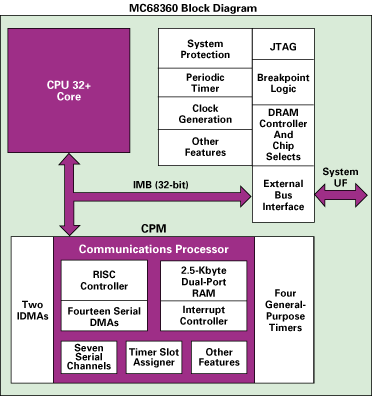
The core of the router is an MC68360 microprocessor that contains four serial communication controllers (SCC), two serial control controllers, and an SPI interface controller. The CPU performance is 8.3 MIPS at 33MHz, but it is possible to install an MC68040 coprocessor with up to 29 MIPS performance at 33 MHz (not in our case).
The processor architecture is shown below:
Data sheets
The performance of the device, by today's standards, may cause confusion, but it is worth considering that in 2001, when I first saw such a router, the 1 MB / s channel struck my imagination with a huge data transfer rate.
The sale of this series ended February 28, 2003. Link to the device description on cisco.com
Included were 2 floppy disks for initial configuration of the router (Win 3.11 / Win 95), but, unfortunately, it was not possible for me to check their performance.
Also, there is a CD with a complete set of documentation for all Cisco devices for December 1997.
My attention was attracted by the plain poster with the mention of Cisco Micro Webserver:
And who of you remembers when it was possible to connect to the manufacturer’s “site” via telnet?
And this is how the feedback form looked like. I never heard about most of the listed devices (with the exception of the Catalyst 1900 with CatOS and 3000, in which the duplex was set on the port by switching the DIP from the back of the device).
Instructions for connecting, using the initial configuration utilities and the router settings form:
Here is a page of history. Attach this device nowhere, and throw a pity. I'll put it back to the warehouse, to Cisco 2509, Catalyst 4000 and others ...
Carrying out archaeological excavations at the warehouse, I found the Cisco 1603 route detector, in surprisingly good condition, in a regular box, complete with, among other things, a large amount of advertising and reference materials. For me, this find was especially pleasant because it was from this series that the acquaintance with the routers of this manufacturer began.
So, what is this device?
')
The following are the network interfaces: 10BaseT, while the AUI output allows using a different physical transmission medium, depending on the converter, for example, optics or coaxial. ISDN BRI S / T - in our country this interface is not widely spread, I have met this only in Moscow and the Krasnodar Territory (UTK). There is a WIC expansion slot for installing modules such as the WIC-1T.
Here is the inner world of the device:
What is there?

As you can see, you can increase the amount of internal memory and replace the PCMCIA card, which will allow you to use the IOS 12 version and add support for OSPF, IPSec and other useful stuff.
I got a copy with 2 MB of RAM and PCMCIA Flash on 4 MB. By the way, as I understand it, the presence of Flash for this router is not mandatory; in its absence, the eprom loads c1600-boot-r.111-10.AA, which has some minimal functionality. Flash showed c1600-yl.113-11a.bin, possessing, despite its modest size, quite impressive functionality - support for dynamic routing protocols RIP, EIGRP, packet filtering functions (of course, not inspect and ZBF, but established and reflect).
ACL

After downloading and carrying out the password recovery procedure, a configuration file was discovered on it, which I want to bring in order to show how little the CLI has changed over a period of more than 10 years.
Show version output

Configuration
! version 11.3 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime localtime show-timezone service timestamps log datetime localtime show-timezone service password-encryption service udp-small-servers service tcp-small-servers ! hostname isdn ! aaa new-model aaa authentication login default local tacacs+ enable aaa authentication ppp default local aaa authorization exec tacacs+ if-authenticated aaa authorization network none enable password 7 06050346324F41 ! username cisco privilege 15 password 7 08902455D0A16 ip subnet-zero ip nat inside source list PAT interface Ethernet0 overload ip telnet source-interface Ethernet0 ip domain-name rtsnet.ru ip name-server 194.247.133.3 ip name-server 172.16.32.3 ip accounting-threshold 8192 isdn switch-type basic-net3 isdn leased-line BRI0 clock timezone MSK 3 clock summer-time MSD recurring last Sun Mar 3:00 last Sun Oct 2:00 ! ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.38.100.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 194.247.149.49 255.255.255.248 ip accounting output-packets ip nat inside no cdp enable ! interface BRI0 no ip address ip nat outside no cdp enable ! interface BRI0:1 ip address 192.100.0.1 255.255.255.252 secondary ip address 10.38.0.2 255.255.255.252 ip nat outside encapsulation frame-relay IETF bandwidth 64 frame-relay map ip 192.100.0.2 17 frame-relay map ip 10.38.0.1 16 broadcast frame-relay interface-dlci 16 frame-relay interface-dlci 17 frame-relay lmi-type q933a ! interface BRI0:2 no ip address ip nat outside no cdp enable ! router rip version 2 timers basic 60 300 360 900 redistribute connected passive-interface Ethernet0 network 10.0.0.0 distribute-list 34 out no auto-summary ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.38.0.1 ! ! ip access-list extended PAT deny ip any 194.247.133.0 0.0.0.255 deny ip any 172.16.0.0 0.3.255.255 deny ip any 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 deny ip any 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 permit ip 10.38.100.0 0.0.0.255 any logging buffered 8192 debugging no logging console logging 172.16.32.15 access-list 13 permit 172.16.32.16 access-list 34 permit 10.38.100.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 34 permit 194.247.149.48 0.0.0.7 access-list 120 permit ip any any log no cdp run tacacs-server host 172.17.5.8 tacacs-server key TACx Kei123 snmp-server community public RO snmp-server community RW_COMM RW 13 snmp-server trap-source Ethernet0 snmp-server location Moscow snmp-server contact joker@ncc.rtsnet.ru (Serge Goncharov) alias exec .s sh conf alias exec .c conf t alias exec .n no deb all alias exec .tn term no mon alias exec .t term mon alias exec .r sh ip rou alias exec .a sh arp alias exec .g sh logg alias exec .l sh access-lists alias exec .d sh dialer alias exec .e0 sh int e0 alias exec .s0 sh int s0 alias exec .f sh fra pvc alias exec .v sh ver alias exec .b sh deb alias exec .i sh int alias exec .ac sh ip acco ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line vty 0 4 access-class 77 in exec-timeout 0 0 password 7 02123D4F0E0A36 ! end The core of the router is an MC68360 microprocessor that contains four serial communication controllers (SCC), two serial control controllers, and an SPI interface controller. The CPU performance is 8.3 MIPS at 33MHz, but it is possible to install an MC68040 coprocessor with up to 29 MIPS performance at 33 MHz (not in our case).
The processor architecture is shown below:

Data sheets
The performance of the device, by today's standards, may cause confusion, but it is worth considering that in 2001, when I first saw such a router, the 1 MB / s channel struck my imagination with a huge data transfer rate.
| Process Switching: PPS 600 / Mbps 0.3072 | Fast / CEF Switching: PPS 4,000 / Mbps 2.05 |
The sale of this series ended February 28, 2003. Link to the device description on cisco.com
Included were 2 floppy disks for initial configuration of the router (Win 3.11 / Win 95), but, unfortunately, it was not possible for me to check their performance.
Photo diskettes

Also, there is a CD with a complete set of documentation for all Cisco devices for December 1997.
Photo CD

My attention was attracted by the plain poster with the mention of Cisco Micro Webserver:
Big picture

And who of you remembers when it was possible to connect to the manufacturer’s “site” via telnet?
And this is how the feedback form looked like. I never heard about most of the listed devices (with the exception of the Catalyst 1900 with CatOS and 3000, in which the duplex was set on the port by switching the DIP from the back of the device).
Many large drawings



Instructions for connecting, using the initial configuration utilities and the router settings form:
Again large drawings





Here is a page of history. Attach this device nowhere, and throw a pity. I'll put it back to the warehouse, to Cisco 2509, Catalyst 4000 and others ...
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/169129/
All Articles