Sending temperature data from the TL-MR3020 router and the Raspberry Pi to People's Monitoring
Introduction
In consequence of the questions, I will allow myself a small comment, a little clarifying the meaning of the article. The article describes two devices that are independent of each other and perform identical tasks for sending data to the People’s Monitoring site .
When I first saw the article on Habré “People’s temperature monitoring (vs forecast) in various cities. Is it necessary? ” , Devoted to the monitoring of the parameters of the environment narodmon.ru , I was somehow skeptical about this idea and forgot about it. Before the new year, I had a Raspberry Pi and some time was spent on its development and review of opportunities , in the end something Malinka would not stand idle, and even so for the general development under the article “The history of interaction between the“ teapot ”and DS18B20 through Raspberry Pi” did the same, but taking into account the source of the original source , which has already been amended on the grounds of the above article with reference to Habr. The temperature was measured, the graphs were built, but somehow it became boring to watch it, and the use of the raspberry for this purpose is like a cannon on sparrows, and one fine day I remembered People's Monitoring, on which all the information displayed on the site is displayed only on the basis of information about current environmental parameters (temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, etc.) transmitted from the client devices of the users of this service. I started searching and found the article “The best implementation of UART implementation => 1-wire and I2C / SPI based on routers” . Then I got excited about the idea of making such a device, though in the hope that someone had already done it, and I will only repeat, since the TL-MR3020 router was already on the farm, and inhuman experiments had been made to screw it to a scooter cart "with a camera based on the article" A simple wifi bot for monitoring premises or a "kitchen" robot-building .
So let's get started
I started with experiments on the router, at that time there was OR-WRT 0.70 firmware based on OpenWRT on it. A temperature sensor is connected to the router via the USB-UART adapter. The wiring diagram is extremely simple. Text and photos from the site http://cyber-place.ru
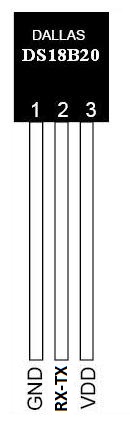
The sensor can be connected to the UART according to the figure below.
Connect RX and TX together and connect the data to them data line 1-Wire sensor DS18B20
VCC to VCC
GND to GND
')
When trying to connect and read data through the router's native UART, it turned out that this could not be done with a swoop. At one bourgeois forum, information was found that the limitation is hardware and the router port itself imposes it, which is sharpened for 8 data bits, and only 6 are used in the digitemp (package for reading data from 1-wire sensors). USB-COM adapter to FT232 or PL2303, another option is possible on the CP2102, but I do not have it, and therefore I will use what I have. After that, I decided to try my hand at writing a script to send the received data to the “People Monitoring”. Sending data to this service must be done using two methods to choose from, either telnet TCP / UDP (recommended) or HTTP POST. Examples of sending data to PHP are available on the website. PHP is a dark forest for me, but still it's better than nothing. After the first attempt to install PHP on the router, it became clear that the 4MB of memory available in it was not enough, and the focus would not succeed. Then I started thinking about increasing the amount of flash memory and came across the same cyber-place.ru on the topic "Replacing and restoring Flash ROM in the MR3020 and WR703n router" . But after some hesitation I came to the conclusion that this is not Feng Shui, for me and for the majority it is quite laborious, plus a programmer is needed, which everyone does not have, and scored on this matter. I decided to write the necessary script on bash, but the tips with Google did not bring results, and a couple of days passed in vain. As a result, it was decided to put the USB-HUB (I saw on the network successful experiments on implanting these into the inside of the router), and connect an external drive and a USB-UART bridge to it. It is said - done, but in the future, after successfully completing the experiments with Raspberry Pi and PHP, and at that moment I was thrown to these experiments. Fast forward to the future, conceived experiments on raspberry and PCP are successfully completed, as I will write below, we will continue experiments with the router. To increase the amount of memory used to transfer it to an external flash drive, which means that the router that I have been configured to work with “scooter cart” will be permanently transferred to use with additional memory, which I absolutely did not want to do. The next day, 1 more router and the smallest USB-HUB were bought, as it was a pity to lose the achieved results, especially since they still have to be different devices.


For the "thermometer" I decided to use a clean OpenWRT. Downloading it when I tried to install in the file name selection field by searching for the first letters I found out that I had as many as 3 firmware with the same size and file name, only the sequence number of the file download was different. I decided that once I downloaded this firmware and chose one of the three to guess. After the firmware, I didn’t manage any of the primary actions from the manual on OpenWRT. I thought that something had gone wrong during the firmware and began to study methods of extracting the router from the brick through TFTP. I put the whole evening on it, since the practice didn’t get my hands on the practice, in theory there was a lot of incomprehensible. And at the end of the evening, something jerked me to try to perform the initial settings as for OR-WRT 0.70. I was lucky, it turned out that I filled it with her. Then, when comparing the names of downloaded files, it turned out that both OpenWRT and OR-WRT have the same name. Next, I spent an unlimited amount of time trying to expand the memory on an external USB flash drive, after which it was decided to upload another OR-WRT 0.75 alpha firmware with the existing flash drive support. Without problems, I flashed and configured my router according to the instructions and proceeded to further actions.
On the thumb in /etc/opkg.conf changed the repository address to downloads.openwrt.org/snapshots/trunk/ar71xx/packages , updated the list of packages
opkg updateinstalled digitemp-a packages
opkg install digitemp-usbopkg install digitempAfter that, the
dmesg found out where the FTDI adapter is connected, I had ttyUSB0. We search for devices 1-wiredigitemp_DS9097 -i -s /dev/ttyUSB0if found, then read the temperature readings and write to the file
digitemp_DS9097 -a -A -l /tmp/1wire_logto see the result we enter
cat /tmp/1wire_logEverything is working. Next, install the packages for PHP
opkg install php5opkg install php5-cgiAnd we start writing scripts. In this case, I'm not a whale, so please do not kick much for the curvature of the code and the huge crutches, substituted, so that it all works. Two scripts were written, one on bash, the other on php. Rather, the fact that php was made on the basis of the source code from the site "People's Monitoring". The first script extracts the data received from the digitemp package and recorded in the 1wire_log file, and fits them into a digestible form. Then transfers control to the second php script to send data to the server.
The first script get_send.sh
#! / bin / bash
rm / temperatura / 1wire_log
rm / temperatura / temp
rm / temperatura / temper
cd /
digitemp_DS9097 -i -s / dev / ttyUSB0
sleep 1s
digitemp_DS9097 -a -A -l / temperatura / 1wire_log
sleep 2s
cd / temperatura
cut -c29-33 1wire_log | sed 's / $ //'> temp
cat temp | tr -d '\ n'> temper
php-cgi /temperatura/send.php
echo "OK \ n"
rm / temperatura / 1wire_log
rm / temperatura / temp
rm / temperatura / temper
cd /
digitemp_DS9097 -i -s / dev / ttyUSB0
sleep 1s
digitemp_DS9097 -a -A -l / temperatura / 1wire_log
sleep 2s
cd / temperatura
cut -c29-33 1wire_log | sed 's / $ //'> temp
cat temp | tr -d '\ n'> temper
php-cgi /temperatura/send.php
echo "OK \ n"
The second script takes the data from the file prepared by the first script and sends it to the server.
The second script is send.php
<? php
$ file_name = "/ temperatura / temper";
$ file = fopen ("$ file_name", "r");
$ gradus_out = fread ($ file, filesize ($ file_name));
echo "$ gradus_out \ n";
fclose ($ file);
$ fp = @fsockopen ("tcp: //narodmon.ru", NNNN, $ errno, $ errstr);
# where NNNN is the port number available after registration
if (! $ fp) exit ("ERROR (". $ errno. "):". $ errstr);
fwrite ($ fp, "# 01-23-45-67-89-AF \ n # 0123456789ABCDEF # $ gradus_out \ n ##");
fclose ($ fp);
echo "OK \ n";
?>
$ file_name = "/ temperatura / temper";
$ file = fopen ("$ file_name", "r");
$ gradus_out = fread ($ file, filesize ($ file_name));
echo "$ gradus_out \ n";
fclose ($ file);
$ fp = @fsockopen ("tcp: //narodmon.ru", NNNN, $ errno, $ errstr);
# where NNNN is the port number available after registration
if (! $ fp) exit ("ERROR (". $ errno. "):". $ errstr);
fwrite ($ fp, "# 01-23-45-67-89-AF \ n # 0123456789ABCDEF # $ gradus_out \ n ##");
fclose ($ fp);
echo "OK \ n";
?>
where 01-23-45-67-89-AF is the mac address of the wlan network card (Wi-Fi), and 0123456789ABCDEF is the serial number of the temperature sensor DS16 (x) 20
For both implementations of the device, I used the wlan mac-address to bind the device on the People's Monitoring website. To find this address, you can enter the command
ifconfig .Next, we need to automate the receiving and sending data to the server using cron. At the time of debugging scripts, I sent data to the server at intervals of 5 minutes, but as soon as they were debugged, the period increased to 10 minutes. To do this, create a simple crontab for the root user with the contents.
Root crontab
SHELL = / bin / sh
PATH = / usr / local / sbin: / usr / local / bin: / sbin: / bin: / usr / sbin: / usr / bin
0.10,20,30,40,50 * * * * sh / temperatura/get_send.sh
PATH = / usr / local / sbin: / usr / local / bin: / sbin: / bin: / usr / sbin: / usr / bin
0.10,20,30,40,50 * * * * sh / temperatura/get_send.sh
According to this task, the sensor is polled and data is sent every 10 minutes. The last line of the script may well be the form
*/10 * * * * sh /temperatura/get_send.shSince at the moment I have two devices for sending temperature data, and the site ignores data coming in more than once every five minutes, the data from one of my devices is ignored. Therefore, for each of the devices, the time for sending data with an interval of 5 minutes between the devices was clearly set in the crown. Download scripts and crontab here . Next, copy the root user's crontab to / etc / crontabs and the temperatura folder to / (root filesystem).
To start and enable cron you need to run in the terminal
/etc/init.d/cron start/etc/init.d/cron enableGo to the assembly area
After everything has been verified in work, it is time to start assembling the entire farm into a single device. After opening the USB hub and the router, I began to estimate the layout of the devices inside the case, consulting with Google and peeping at the modding router page. It turned out that I bought the USB-HUB the same as the author of the first version of the improvements. Already well, since he managed to do it means and I will succeed. After the initial layout of the device's internal parts, it became clear that one could try to fit the same USB-UART adapter. As a USB-UART adapter, a data cable from some old phone on a PL2303 chip was tested and sacrificed, which came to me from nowhere to use as a USB-UART bridge. Before that, he was working on someone else, not the smallest details were soldered, which set the thickness of the board itself. After studying the circuits for telephone laces, these dimensional parts have been removed. The power switch was also removed and the protruding legs of the output elements were bitten off. Scarf immediately lost weight. One could use a handkerchief on FTDI, the dimensions of which are at least 2 times smaller than the applied board, but it was a pity because it has a useful DTR signal used for resetting the Arduino, and in PL2303 it is inverse and for its use you would have to fence an inverter. And for our purposes, this signal is absolutely not important.
After finalizing the USB-UART adapter, the line came and a USB hub, the sticking conclusions of which were also cut off. For him, this weight loss turned out to be almost not noticeable, but in general I think it has become useful for the construction. Based on the experience of people who have already done this, they started a second fitting. Those options that were offered did not suit me. would have to remove the fiber. Threw on the opposite side of the fiber, is better. But anyway, with the existing flash drive, some of the LEDs will close and you will also have to remove some of the light guide. But according to estimates, you can do without extreme measures by buying a flash drive that is shorter. I started looking for computer shops and found a decent option at the right price I bought the next day. As it turned out, the same model of flash drive was already used by the author of another version of modding . It turns out that the choice of the parts used is not so great, since I accidentally got 2 times the same, completely independent of the authors ahead of me.
Then I began to think about how to arrange the UART port on the router body to connect an external sensor in the most elegant way. It turned out that the USB port, which is not used from now on, whose power pins continue to perform the functions assigned to them, and the + D and -D pins that are cut off from the circuit, can be adapted to Rx and Tx. Fine. Soldered all together, checked.


For fixing the boards among themselves, I used the usual 2-sided adhesive tape. When assembling, you need to be extremely careful, so that nothing would ever go away and not to push the tape with sharp soldered leads. When gluing the hub, I used two layers of adhesive tape to increase the distance between the boards, 2 strips per layer folded “palenice”. For tests, I used the remaining tail from the same hub. That's what happened in the end


I was pleased with the result, there was even a little space left, and the unused integrated UART remained. The Bluetooth module HC-04 was found in the bins and was tried on the possible installation site. Stood like a native. It was immediately soldered and glued to the same tape on the USB port of the router.


Why do I need it? As already said above, it is a pity that the place disappears and the UART. Plus, the router will not do anything for 10 minutes, not order. You can hang some more functions. For example, the first because of what I did - on the Internet to look at the thermometer is good, but not always convenient. So I think to put the simplest arduin with a 7-segment indicator. And maybe the sign-synthesizer, so that the time / date is also shown. In general, the mass of options.
Close the lid prevented only one pin on it, which should rest against the board, and rests against the USB connector of the hub. He tried on the eye and cut it in half.


After that, the lid is normally in place. True, it also failed to put it tightly and it is slightly upwardly issued. But this is a normal phenomenon and all my improvements do not interfere with it. I have the same thing on the first unmodified router. As a result, he received a seemingly almost virginal new router, not counting the traces of a neat opening.


To remove the sensor to the street, I used a collapsible USB connector on the cable and cord from a Komovka mouse, it is softer than the rest of the cords I had, with a small piece of flat cable soldered to pass it between the window seals when closing the window.
.
Price issue when using the router
Router TL-MR3020 910r.
USB-HUB Ginzzu 210r.
Flash Drive Sandisk Cruzer Fit 8 GB 248r.
Adapter USB-UART to PL2303 from China ~ 50p.
Bluetooth module HC-04 from China ~ $ 7 = 210r.
Temperature sensor DS16 (x) 20 ~ 60r.
Total ~ 1688r.
Naturally, the Bluetooth module can be thrown out, and then the price will approach the bar ~ 1500r.
Improvement options
The first is the optimization of the scripts given in the article.
Secondly, if you manage to get rid of the PHP script and switch to bash completely, you will get rid of the USB flash drive and USB hub, which will significantly reduce the complexity and cost of the final device.
The third (just an assumption) - perhaps, if you clean the firmware by removing unused modules, you’ll make room for PHP, you will achieve the same results as in the second version.
The fourth is to make the hardware UART work, it will also reduce the cost, but it will slightly increase the labor intensity. All I could find on this topic is an incomprehensible pastebin script for me without comments, and a link to the recumbent site, where the link to pastebin comes from. I tried to run this script to no avail.
Fifth, use the GPIO output by writing the appropriate driver.
Sending with Raspberry Pi
As I already mentioned, I already had the malinka set up properly for measuring the temperature on two sensors and scheduling. Thus, it remains for the small, pull out the data on the temperature and send them to the server.
A further description of the process will be based on the fact that you have already set up a malinka to receive data from sensors and build graphs. However, I will briefly describe the principle of operation of those scripts, and those who wish can download my scripts completely for quick setup. In the version that I repeated and suggest that you repeat, there are 3 bash scripts, one perl and one database file for RRDTool. The first bash script runs once and creates a database file. The second bash script is added to cron, and all it does is run the rest of the scripts. First of all, it runs the get_temp.pl script, which is responsible for reading the readings from the temperature sensors and putting these readings into the database. In the second line, it runs the create_graphs.sh script, which takes temperature values from the database and builds graphs on them. Based on the fact that my Malinka already knows how to do all this, I proceed to implement the rest of my plans. Here one PHP script is already used to send data to the server. Plus, several lines of processing the data received from the sensors are added to the existing get_temp.pl script and one line to the get.sh script.
My script for receiving data from sensors with the addition of processing temperature readings looks like this
get_temp.pl
################################################## #####################
Here, I ask you to forgive me, whether something interferes with the script, or if there’s a glitch, but I didn’t manage to insert it properly under the spoiler, so I’m giving you a piece of the original code with my modifications.
################################################## #####################
foreach $ device (@deviceIDs)
{
$ reading = & read_device ($ device);
if ($ reading == 9999) {
$ reading = "U";
}
push (@ temp_readings, $ reading);
}
if ($ temp_readings [0] ne 'U') {$ temp_readings [0] - = $ in_correction;}
if ($ temp_readings [1] ne 'U') {$ temp_readings [1] - = $ out_correction;}
#update the database
`/ usr / bin / rrdtool update /home/pi/temperature/multirPItemp.rrd N: $ temp_readings [0]: $ temp_readings [1]`;
print "Temp 1 = $ temp_readings [0] Temp 2 = $ temp_readings [1] \ n";
################################################## #####################
# My additions
open (FILE, "> / home / pi / temperature / temp_out");
print FILE "$ temp_readings [0]";
close (FILE);
open (FILE, "> / home / pi / temperature / temp_in");
print FILE "$ temp_readings [1]";
close (FILE);
################################################## #####################
Here, I ask you to forgive me, whether something interferes with the script, or if there’s a glitch, but I didn’t manage to insert it properly under the spoiler, so I’m giving you a piece of the original code with my modifications.
################################################## #####################
foreach $ device (@deviceIDs)
{
$ reading = & read_device ($ device);
if ($ reading == 9999) {
$ reading = "U";
}
push (@ temp_readings, $ reading);
}
if ($ temp_readings [0] ne 'U') {$ temp_readings [0] - = $ in_correction;}
if ($ temp_readings [1] ne 'U') {$ temp_readings [1] - = $ out_correction;}
#update the database
`/ usr / bin / rrdtool update /home/pi/temperature/multirPItemp.rrd N: $ temp_readings [0]: $ temp_readings [1]`;
print "Temp 1 = $ temp_readings [0] Temp 2 = $ temp_readings [1] \ n";
################################################## #####################
# My additions
open (FILE, "> / home / pi / temperature / temp_out");
print FILE "$ temp_readings [0]";
close (FILE);
open (FILE, "> / home / pi / temperature / temp_in");
print FILE "$ temp_readings [1]";
close (FILE);
################################################## #####################
The essence of my additions is to retrieve the data on temperature, which are entered into the database, and record them in separate files for each sensor.
After all this has worked, you can do the script to send data to the server. For this we need to install PHP.
sudo apt-get install php5-cgiThe script to send data is made from the example presented on the site "People's Monitoring". It accesses the files created by the previous script, takes temperature data from them and sends them.
My send.php script looks like this
send.php
#! / usr / bin / php-cgi -q
<?
$ file_name = "/ home / pi / temperature / temp_out";
$ file = fopen ("$ file_name", "r");
$ gradus_out = fread ($ file, filesize ($ file_name));
echo "$ gradus_out \ n";
fclose ($ file);
$ file_name = "/ home / pi / temperature / temp_in";
$ file = fopen ("$ file_name", "r");
$ gradus_in = fread ($ file, filesize ($ file_name));
echo "$ gradus_in \ n";
fclose ($ file);
$ fp = @fsockopen ("tcp: //narodmon.ru", NNNN, $ errno, $ errstr);
# where NNNN is the port number available after registration
if (! $ fp) exit ("ERROR (". $ errno. "):". $ errstr);
fwrite ($ fp, "# 01-23-45-67-89-AF \ n # 0123456789ABCDEF # $ gradus_out \ n # 0123456789ABCDEF # $ gradus_in \ n ##");
fclose ($ fp);
?>
<?
$ file_name = "/ home / pi / temperature / temp_out";
$ file = fopen ("$ file_name", "r");
$ gradus_out = fread ($ file, filesize ($ file_name));
echo "$ gradus_out \ n";
fclose ($ file);
$ file_name = "/ home / pi / temperature / temp_in";
$ file = fopen ("$ file_name", "r");
$ gradus_in = fread ($ file, filesize ($ file_name));
echo "$ gradus_in \ n";
fclose ($ file);
$ fp = @fsockopen ("tcp: //narodmon.ru", NNNN, $ errno, $ errstr);
# where NNNN is the port number available after registration
if (! $ fp) exit ("ERROR (". $ errno. "):". $ errstr);
fwrite ($ fp, "# 01-23-45-67-89-AF \ n # 0123456789ABCDEF # $ gradus_out \ n # 0123456789ABCDEF # $ gradus_in \ n ##");
fclose ($ fp);
?>
where, just like in the version with the router 01-23-45-67-89-AF, the mac-address of the wlan network card (Wi-Fi) or lan, if the malinka is connected through it, and 0123456789ABCDEF is the serial number of the DS16 temperature sensor ( x) 20.
Then we add a line to the get.sh script indicating the execution of the send.php script.
Get.sh script
#! / bin / bash
/home/pi/temperature/get_temp.pl
/home/pi/temperature/create_graphs.sh
################################################## #####################
# My addition
/home/pi/temperature/send.php
echo "OK \ n"
################################################## #####################
/home/pi/temperature/get_temp.pl
/home/pi/temperature/create_graphs.sh
################################################## #####################
# My addition
/home/pi/temperature/send.php
echo "OK \ n"
################################################## #####################
In crown, I changed the schedule for sending data every 10 minutes with a clear time reference, not intersecting with the time the data was sent by the router.
Task in the crown looks like this
5,15,25,35,45,55 * * * * /home/pi/temperature/get.shAfter that, everything should work. Download these scripts here.
Price issue when using the Raspberry Pi
Here it is already impossible to count so unequivocally. The fact is that the cost of the raspberry itself and the additional components for it can vary greatly from person to person.
Conclusion
In my opinion, if you do not have either one or the other, the most rational is to use a router. Using raspberry makes sense only if you already have it, is always on and performs any tasks.
But in general, the regiment of devices sending data to the People's Monitoring service has arrived, and this is good.
UPD
Together, we managed to get rid of the PHP script and write everything in BASH, for which we thank everyone who responded. I would like to express special gratitude to the Ssar user, his hint was decisive in writing the script for the router. At the moment, there is only one get_send.sh script, and two auxiliary files.
get_send.sh
#! / bin / bash
rm / temperatura / 1wire_log
rm / temperatura / temp
rm / temperatura / out
cd /
digitemp_DS9097 -i -s / dev / ttyUSB0
sleep 1s
digitemp_DS9097 -a -A -l / temperatura / 1wire_log
sleep 2s
cd / temperatura
cut -c29-33 1wire_log | sed 's / $ //'> temp
cat / temperatura / mac_id> / temperatura / out
cat /temperatura/temp >> /temperatura/out
cat /temperatura/end >> /temperatura/out
cat /temperatura/out | /usr/bin/nc narodmon.ru NNNN
# NNNN —
echo «OK»
rm / temperatura / 1wire_log
rm / temperatura / temp
rm / temperatura / out
cd /
digitemp_DS9097 -i -s / dev / ttyUSB0
sleep 1s
digitemp_DS9097 -a -A -l / temperatura / 1wire_log
sleep 2s
cd / temperatura
cut -c29-33 1wire_log | sed 's / $ //'> temp
cat / temperatura / mac_id> / temperatura / out
cat /temperatura/temp >> /temperatura/out
cat /temperatura/end >> /temperatura/out
cat /temperatura/out | /usr/bin/nc narodmon.ru NNNN
# NNNN —
echo «OK»
. crontab.
, .
UPD 2
Ssar BASH mac- ID . , .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/166373/
All Articles