Optimizing HSV to RGB Conversion for Microcontrollers
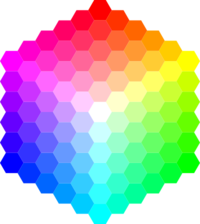
As a hobby, I work on LED props and faced an interesting challenge - to show something “beautiful” on a controlled LED strip instead of a traditional rainbow, without spending half the microcontroller’s memory and a significant portion of processor time.
LED strip pixels are different from screen pixels by the lack of backlighting. The black pixel will not look “black” - it will merge with the background, and in motion it will actually be “transparent”, but if you add at least one to any color channel, this pixel will glow. In turn, the “gray” pixel will differ from white only in brightness and will appear dimmer, but still “white”.
The color of the pixel is stored and transmitted in 24-bit RGB, but a large part of this color range (unsaturated and bright colors) is not very representative in individual LEDs. In addition, building nice gradients in the RGB model will not work - mixing RGB colors does not give an intuitively obvious result ( yellow + blue = gray , but I want it - green). The HSL and HSV models fit better, but standard implementations use non-integer arithmetic. It will be convenient to use a model that can compactly store color parameters and quickly read their RGB values, without using floating-point numbers and dividing by an arbitrary number — this is a microcontroller and complex algorithms do not need anything, and division (except for small powers of two ) and is completely contraindicated.
Decision
For my needs, I use the HSV (HSB) model with defined ranges for each of the coordinates (some magic numbers).
')
- Hue - tone, cyclic angular coordinate.
- Value, Brightness - brightness, perceived as an alpha channel, with
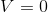 pixel does not glow when
pixel does not glow when 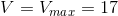 - glows as brightly as possible, depending on
- glows as brightly as possible, depending on 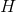 and
and 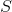 .
. - Saturation. No background value
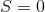 will give not gray, but white of different brightness, therefore the parameter
will give not gray, but white of different brightness, therefore the parameter 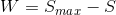 can be called Whiteness - it reflects the degree of "whiteness" of color. With
can be called Whiteness - it reflects the degree of "whiteness" of color. With 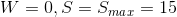 color is completely determined by Hue, with
color is completely determined by Hue, with 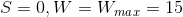 pixel color will be white.
pixel color will be white.
Mathematics of the model is based on the integer division by one sixth of the maximum tone value (size of one sector), therefore, as
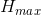 convenient to take the maximum value equal
convenient to take the maximum value equal 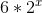 , for example, 48 or 96. This will allow you to conveniently calculate the RGB color, and a value less than 128 will allow you to build a gradient that several times contains a full color circle. On HSV / HSL models
, for example, 48 or 96. This will allow you to conveniently calculate the RGB color, and a value less than 128 will allow you to build a gradient that several times contains a full color circle. On HSV / HSL models 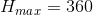 , in MS Paint - 240, in some libraries - 255.
, in MS Paint - 240, in some libraries - 255.When choosing the maximum values
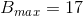 and
and 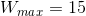 multiplication
multiplication 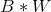 gives the result lying in the range
gives the result lying in the range 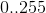 .
.Minimal HSV configuration, simple to calculate and limited to 8-bit values, with ranges
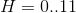 ,
, 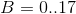 and
and 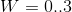 gives us
gives us 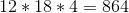 colors, some of which are almost the same, and some are far enough apart ( for fairness, I note that all color models that operate on H are sinning - Mercator could not stretch the three sides of the cube on a cone without distorting the length ). The figure seems scant compared to the 24-bit color in a typical monitor ( 16.7 million unique colors), but it is enough to diversify the LED props, in which earlier and seven colors instead of one were often a pleasant bonus. The color coordinates in this model can be stored in two bytes.
colors, some of which are almost the same, and some are far enough apart ( for fairness, I note that all color models that operate on H are sinning - Mercator could not stretch the three sides of the cube on a cone without distorting the length ). The figure seems scant compared to the 24-bit color in a typical monitor ( 16.7 million unique colors), but it is enough to diversify the LED props, in which earlier and seven colors instead of one were often a pleasant bonus. The color coordinates in this model can be stored in two bytes.Of course, HSV resolution can and should be increased to a convenient one. I use
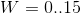 and 96 tones, which gives already 27.6 thousand shades. An example of code with such parameters (model configuration - max_value, max_whiteness, sixth_hue):
and 96 tones, which gives already 27.6 thousand shades. An example of code with such parameters (model configuration - max_value, max_whiteness, sixth_hue):Code
typedef struct { uint8_t r; uint8_t g; uint8_t b; } RGB_t; typedef struct { uint8_t h; uint8_t s; uint8_t v; } HSV_t; const uint8_t max_whiteness = 15; const uint8_t max_value = 17; const uint8_t sixth_hue = 16; const uint8_t third_hue = sixth_hue * 2; const uint8_t half_hue = sixth_hue * 3; const uint8_t two_thirds_hue = sixth_hue * 4; const uint8_t five_sixths_hue = sixth_hue * 5; const uint8_t full_hue = sixth_hue * 6; inline RGB_t rgb(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) { return (RGB_t) {r, g, b}; } inline HSV_t hsv(uint8_t h, uint8_t s, uint8_t v) { return (HSV_t) {h, s, v}; } const RGB_t black = {0, 0, 0}; RGB_t hsv2rgb(HSV_t hsv) { if (hsv.v == 0) return black; uint8_t high = hsv.v * max_whiteness;//channel with max value if (hsv.s == 0) return rgb(high, high, high); uint8_t W = max_whiteness - hsv.s; uint8_t low = hsv.v * W;//channel with min value uint8_t rising = low; uint8_t falling = high; uint8_t h_after_sixth = hsv.h % sixth_hue; if (h_after_sixth > 0) {//not at primary color? ok, h_after_sixth = 1..sixth_hue - 1 uint8_t z = hsv.s * uint8_t(hsv.v * h_after_sixth) / sixth_hue; rising += z; falling -= z + 1;//it's never 255, so ok } uint8_t H = hsv.h; while (H >= full_hue) H -= full_hue; if (H < sixth_hue) return rgb(high, rising, low); if (H < third_hue) return rgb(falling, high, low); if (H < half_hue) return rgb(low, high, rising); if (H < two_thirds_hue) return rgb(low, falling, high); if (H < five_sixths_hue) return rgb(rising, low, high); return rgb(high, low, falling); } PS
TeX-codes in the topic included in the experiment. If there is a way to do it more conveniently or more correctly - hint at the PM.
If it is interesting, I can separately explain the features of HSV calculation, in particular, the mechanics of rising / falling functions and the function of reverse calculation in “such” HSV.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/166317/
All Articles