"IBM 5 in 5". Is the future close?
How much can technology transform in 5 years? And will they make our life better?
On the eve of the new 2013, we want to present the seventh annual list of “IBM 5 in 5”, dedicated to five innovations that could affect our life, work and entertainment in the next 5 years.

The IBM 5 in 5 list is based on market and social trends, as well as on IBM research laboratories around the world that can help in their implementation.
')
This year's list of IBM 5 in 5 presents innovations that form the principles of a new generation of computing systems that IBM calls cognitive. Cognitive machines will learn, adapt and develop a full-fledged perception of the world. This year, forecasts are devoted to the ability of the computers of the future to imitate the human sense organs, see, hear, touch, smell and taste in their own way.
 Cognitive computing systems will help to highlight key data, keep pace with their distribution, make more informed decisions, improve health and improve living standards, diversify lives and eliminate any obstacles and barriers: geographical, linguistic, associated with the cost and availability of services.
Cognitive computing systems will help to highlight key data, keep pace with their distribution, make more informed decisions, improve health and improve living standards, diversify lives and eliminate any obstacles and barriers: geographical, linguistic, associated with the cost and availability of services.
“IBM scientists around the world are working on technologies that will help computers understand the meaning of the world around them,” said Bernie Meyerson, an honorary employee of IBM and vice president of innovation. “By simulating human interaction with the outside world, cognitive systems, using a combination of breakthrough technologies, will bring us even more valuable information and knowledge, helping to solve the most complex problems.”
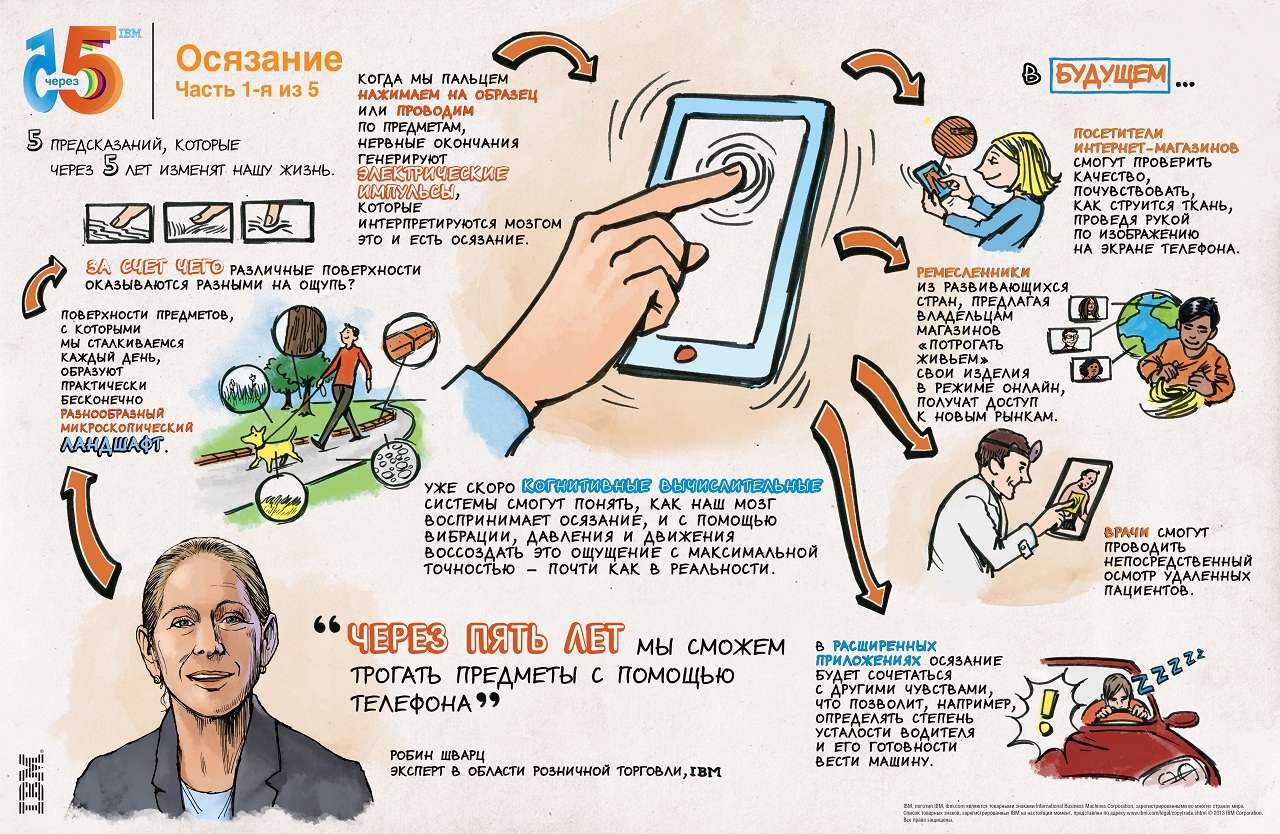
Imagine that when you buy a suit using a smartphone from an online store, you can feel the texture of the fabric using the touch screen of a mobile device. Over the next five years, the ability to “touch” a product through a mobile device will literally transform entire industries, such as retail.
IBM scientists are developing applications for the retail, healthcare and other industries, using tactile sensitivity, infrared light and pressure technologies to imitate touch, so that the customer can feel the fabric texture and patterns while tracing the image on the screen of her mobile device. The standard vibration feature of a cell phone allows each object to be assigned a unique set of vibration characteristics (related to their duration and strength), which will transmit tactile sensations. The vibrating pattern will allow to distinguish silk from flax or cotton, helping to imitate the sensations of touching the material.
Existing tactile and graphical technologies in the gaming industry are used to create a virtual environment. The task, the solution of which will open up the broadest possibilities, is to make these technologies comprehensive, closely integrated into our daily life. They will turn mobile phones into tools for natural and intuitive interaction with the outside world.
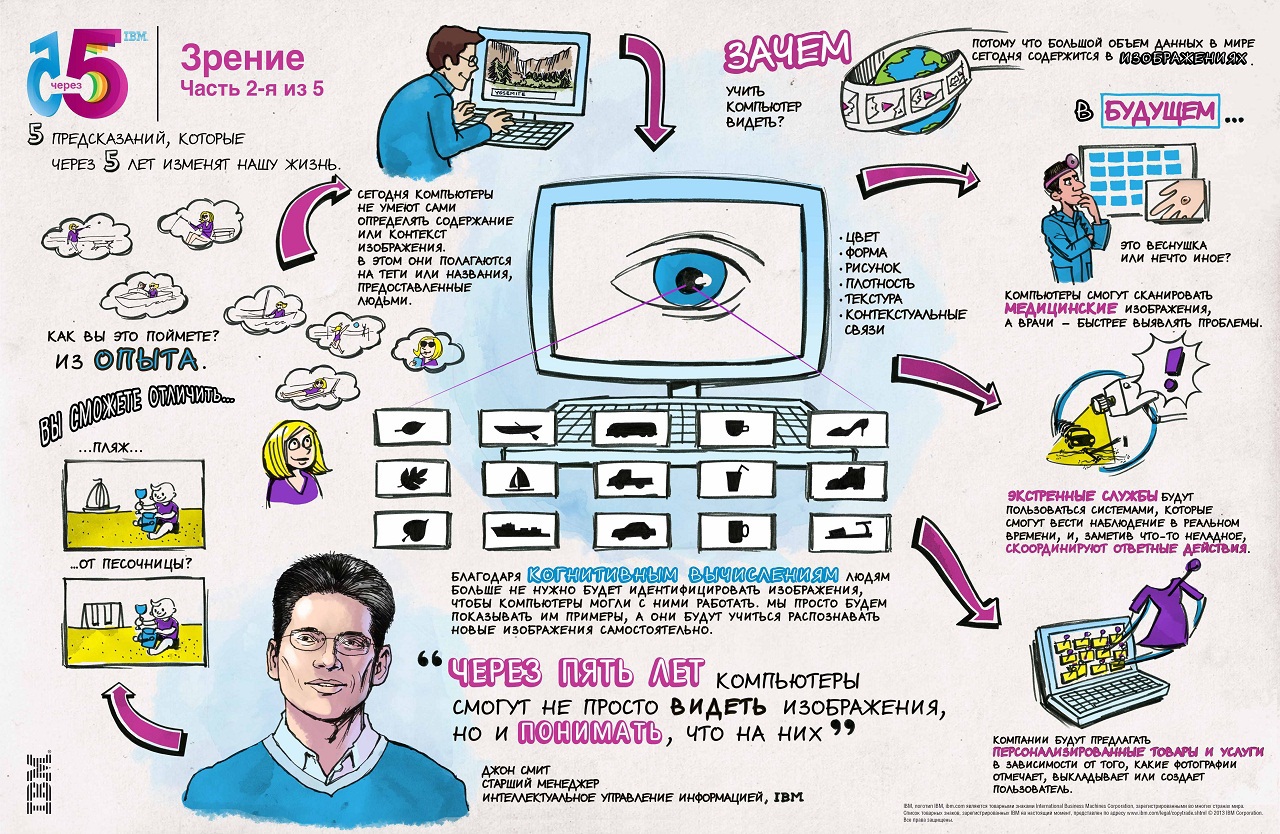
We make 500 billion photos a year. Every minute 72 hours of video is uploaded to YouTube. According to the forecast of experts, the market volume of medical diagnostic imaging tools will grow to 26.6 billion dollars by 2016.
Computers today understand the meaning of the image only by text tags and name. Most of the information - the actual content of the image - remains a mystery to computers.
In the next five years, computer systems will not only learn to recognize what is depicted in a photo or picture - they will understand the meaning of the image, as a person does. In the future, these features will allow computers to analyze a variety of characteristics: the color of the object or the pattern on its surface, tangible boundaries, in general, to gain knowledge from visual data. These technologies will have a major impact on healthcare, retail and agriculture.
Within five years, these opportunities will find application in healthcare, where they will help to get valuable knowledge from medical data sets - MRI and computed tomography images, x-rays and ultrasound results. It is important that on these images there may be subtle or invisible to the human eye details that require careful study. With the ability to highlight key images — for example, to distinguish healthy tissues from diseased ones — and to relate information to a patient’s history or descriptions in the scientific literature, “sighted” computer systems will help physicians identify clinical problems with much greater speed and accuracy.
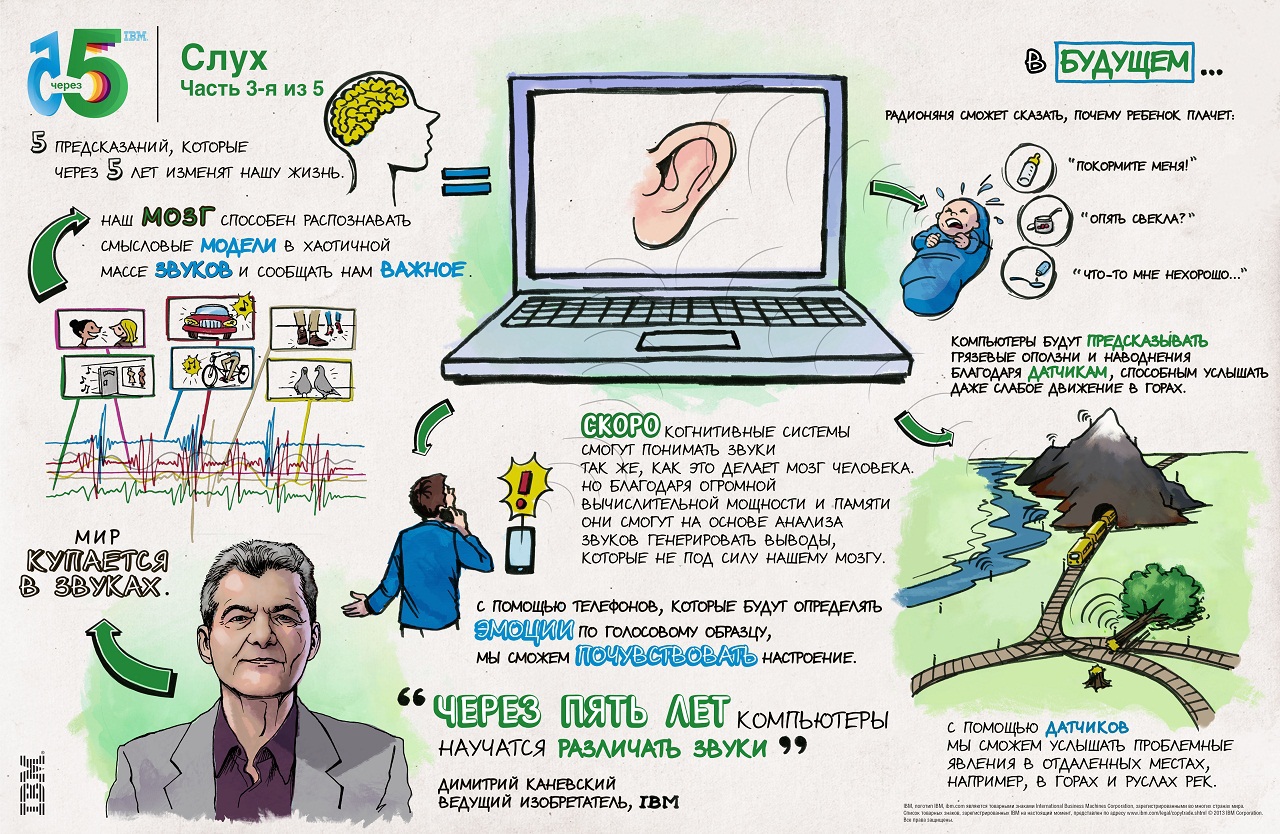
Have you ever regretted that it is impossible to hear all the sounds of the world and understand what lies behind the intonations of the interlocutor?
Within five years, a distributed network of smart sensors will be presented to determine sound pressure and oscillations, as well as distinguish sound waves at different frequencies. She will be able to interpret sounds to calculate the risks of falling trees in the forest or avalanches in the mountains. Such a system will “listen” to the outside world, defining displacements or noting the degree of stress of materials, and warn us of potential danger.
The sounds of the world will be perceived by sensors that mimic the auditory system. This information in combination with other types of data, such as visual or tactile information, will be classified and interpreted according to acquired knowledge. When new sounds are detected, the system will formulate conclusions based on previous knowledge and using the ability to recognize patterns.
For example, it will be possible to interpret children's speech, so that the parents or the doctor understand what the child is trying to convey. Learning what these sounds mean — when they indicate that a child is hungry, tired, feels fever, discomfort, or pain — intelligent speech recognition will correlate them with other sensory or physiological data, such as heart rate and body temperature.
In the next five years, computer systems will be able to accurately record all the characteristics of a conversation and analyze the tone, timbre, and lack of confidence in the voice, focusing on changes in the emotional mood. This will allow, for example, the optimal way to organize communication of contact center personnel with clients or to facilitate the interaction of representatives of different cultures.
Currently, IBM scientists are beginning to use underwater sensors to detect noise in Galway Bay (off the west coast of Ireland) to interpret the sounds of a tidal generator and to study the effects of acoustics on the life of the sea.
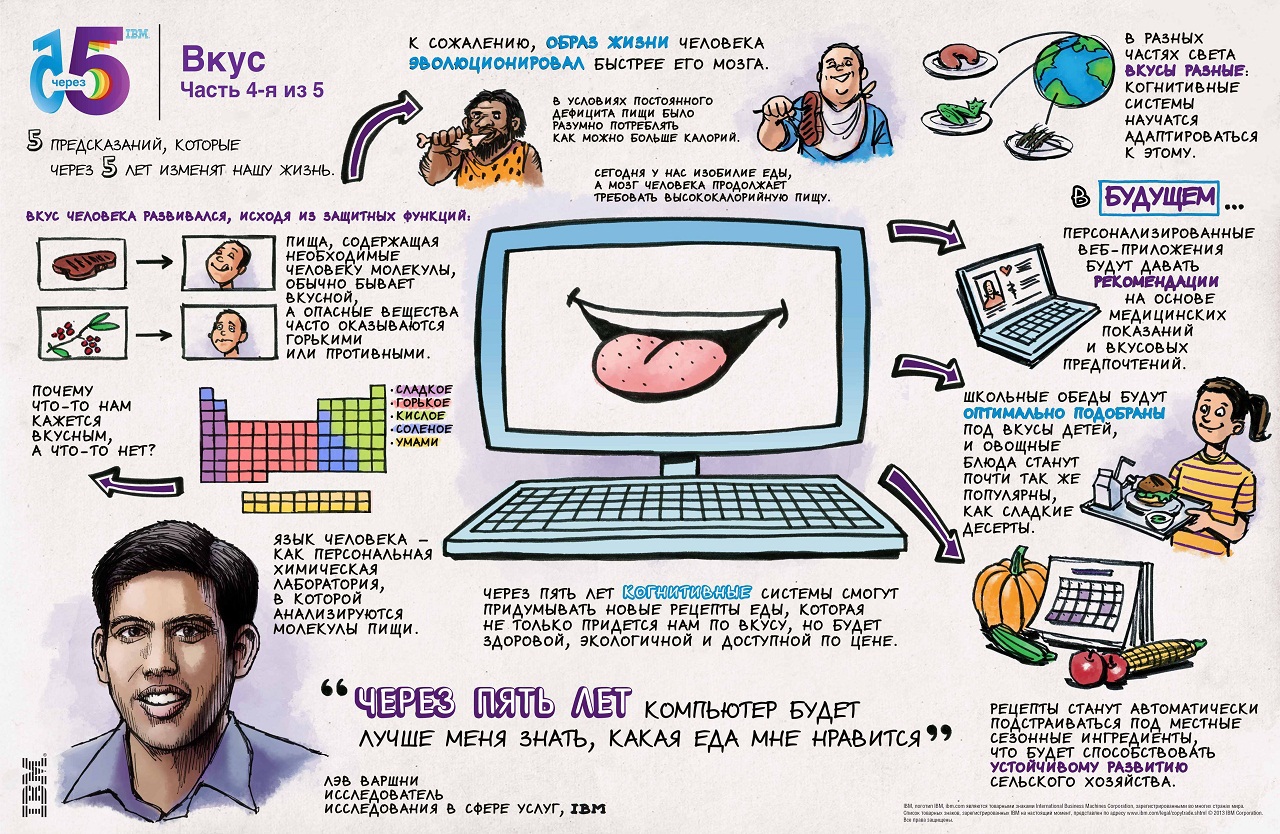
What if we could make healthy food taste good by creating new recipes using next-generation computers?
IBM researchers are developing a computer system that can truly taste; it will be used by chefs to create innovative recipes. It will “break down” the ingredients to their molecular level and make chemical compositions of food compounds, taking into account the taste and aromatic preferences of people. Comparing these combinations with millions of existing recipes, the system will be able to create new flavor combinations - for example, roasted chestnuts with boiled beets, with fresh fish caviar or with dried ham.
Such a system can also help to eat better, creating new combinations of smells that will make us love vegetables and give up potato chips.
The computer will use complex algorithms to determine the exact chemical structure of food products, as well as to investigate taste preferences. These algorithms will study how chemicals interact with each other, find out their taste components at the molecular level, and use this information in combination with perception models to predict the taste appeal of a product.
Such a system will not only help make healthy food more enjoyable, it will also surprise with unusual combinations of products created for the most vivid taste sensations. For people with a special diet, in particular, those suffering from diabetes, the system will develop special flavor combinations and recipes that will control blood sugar levels and, at the same time, satisfy cravings for sweets.

In the next five years, tiny sensors embedded in a computer or mobile phone will be able to detect symptoms of a cold or other illnesses. By analyzing odors, biomarkers and thousands of molecules in a person’s breathing and relating them to the norm, computer systems will help doctors diagnose and monitor diseases such as disorders of the liver and kidneys, asthma, diabetes and epilepsy.
Today, IBM scientists already control environmental performance to preserve works of art . This innovative method is beginning to be applied in the field of clinical hygiene to solve one of the biggest problems that healthcare faces today. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which in 2005 was associated with almost 19 thousand deaths of patients in US hospitals, are usually located on the skin and can be easily transmitted wherever people are in close contact together. One of the preventive ways to combat exposure to and the spread of MRSA in hospitals is strict control over the observance by medical personnel of the established regulatory requirements of clinical hygiene. In the next five years, the system based on IBM technology will be used to study hospital wards and other premises for traces of disinfectants to identify places that have not yet been sanitized. Intelligent sensors will use the latest wireless networks to collect and analyze data on various chemicals, and constantly learn and adapt to new smells.
Thanks to the development of sensory, telecommunication and self-learning technologies, sensors will be able to collect and analyze data where it was considered inaccessible. In particular, computer systems can be used in agriculture for odor determination and soil analysis of agricultural crops. Under urban conditions, this technology will be used to monitor the sanitary condition and level of contamination of territories and premises, helping the city services to identify potential problems before they cause real damage.
Additional materials are available here .
On the eve of the new 2013, we want to present the seventh annual list of “IBM 5 in 5”, dedicated to five innovations that could affect our life, work and entertainment in the next 5 years.

The IBM 5 in 5 list is based on market and social trends, as well as on IBM research laboratories around the world that can help in their implementation.
')
This year's list of IBM 5 in 5 presents innovations that form the principles of a new generation of computing systems that IBM calls cognitive. Cognitive machines will learn, adapt and develop a full-fledged perception of the world. This year, forecasts are devoted to the ability of the computers of the future to imitate the human sense organs, see, hear, touch, smell and taste in their own way.
 Cognitive computing systems will help to highlight key data, keep pace with their distribution, make more informed decisions, improve health and improve living standards, diversify lives and eliminate any obstacles and barriers: geographical, linguistic, associated with the cost and availability of services.
Cognitive computing systems will help to highlight key data, keep pace with their distribution, make more informed decisions, improve health and improve living standards, diversify lives and eliminate any obstacles and barriers: geographical, linguistic, associated with the cost and availability of services.“IBM scientists around the world are working on technologies that will help computers understand the meaning of the world around them,” said Bernie Meyerson, an honorary employee of IBM and vice president of innovation. “By simulating human interaction with the outside world, cognitive systems, using a combination of breakthrough technologies, will bring us even more valuable information and knowledge, helping to solve the most complex problems.”
Touch: The phone interface can convey tactile sensations.

Imagine that when you buy a suit using a smartphone from an online store, you can feel the texture of the fabric using the touch screen of a mobile device. Over the next five years, the ability to “touch” a product through a mobile device will literally transform entire industries, such as retail.
IBM scientists are developing applications for the retail, healthcare and other industries, using tactile sensitivity, infrared light and pressure technologies to imitate touch, so that the customer can feel the fabric texture and patterns while tracing the image on the screen of her mobile device. The standard vibration feature of a cell phone allows each object to be assigned a unique set of vibration characteristics (related to their duration and strength), which will transmit tactile sensations. The vibrating pattern will allow to distinguish silk from flax or cotton, helping to imitate the sensations of touching the material.
Existing tactile and graphical technologies in the gaming industry are used to create a virtual environment. The task, the solution of which will open up the broadest possibilities, is to make these technologies comprehensive, closely integrated into our daily life. They will turn mobile phones into tools for natural and intuitive interaction with the outside world.
Vision: Pixel sense will become available to computers

We make 500 billion photos a year. Every minute 72 hours of video is uploaded to YouTube. According to the forecast of experts, the market volume of medical diagnostic imaging tools will grow to 26.6 billion dollars by 2016.
Computers today understand the meaning of the image only by text tags and name. Most of the information - the actual content of the image - remains a mystery to computers.
In the next five years, computer systems will not only learn to recognize what is depicted in a photo or picture - they will understand the meaning of the image, as a person does. In the future, these features will allow computers to analyze a variety of characteristics: the color of the object or the pattern on its surface, tangible boundaries, in general, to gain knowledge from visual data. These technologies will have a major impact on healthcare, retail and agriculture.
Within five years, these opportunities will find application in healthcare, where they will help to get valuable knowledge from medical data sets - MRI and computed tomography images, x-rays and ultrasound results. It is important that on these images there may be subtle or invisible to the human eye details that require careful study. With the ability to highlight key images — for example, to distinguish healthy tissues from diseased ones — and to relate information to a patient’s history or descriptions in the scientific literature, “sighted” computer systems will help physicians identify clinical problems with much greater speed and accuracy.
Rumor: Computers will hear what is happening around

Have you ever regretted that it is impossible to hear all the sounds of the world and understand what lies behind the intonations of the interlocutor?
Within five years, a distributed network of smart sensors will be presented to determine sound pressure and oscillations, as well as distinguish sound waves at different frequencies. She will be able to interpret sounds to calculate the risks of falling trees in the forest or avalanches in the mountains. Such a system will “listen” to the outside world, defining displacements or noting the degree of stress of materials, and warn us of potential danger.
The sounds of the world will be perceived by sensors that mimic the auditory system. This information in combination with other types of data, such as visual or tactile information, will be classified and interpreted according to acquired knowledge. When new sounds are detected, the system will formulate conclusions based on previous knowledge and using the ability to recognize patterns.
For example, it will be possible to interpret children's speech, so that the parents or the doctor understand what the child is trying to convey. Learning what these sounds mean — when they indicate that a child is hungry, tired, feels fever, discomfort, or pain — intelligent speech recognition will correlate them with other sensory or physiological data, such as heart rate and body temperature.
In the next five years, computer systems will be able to accurately record all the characteristics of a conversation and analyze the tone, timbre, and lack of confidence in the voice, focusing on changes in the emotional mood. This will allow, for example, the optimal way to organize communication of contact center personnel with clients or to facilitate the interaction of representatives of different cultures.
Currently, IBM scientists are beginning to use underwater sensors to detect noise in Galway Bay (off the west coast of Ireland) to interpret the sounds of a tidal generator and to study the effects of acoustics on the life of the sea.
Taste: Digital taste buds will help you eat wiser

What if we could make healthy food taste good by creating new recipes using next-generation computers?
IBM researchers are developing a computer system that can truly taste; it will be used by chefs to create innovative recipes. It will “break down” the ingredients to their molecular level and make chemical compositions of food compounds, taking into account the taste and aromatic preferences of people. Comparing these combinations with millions of existing recipes, the system will be able to create new flavor combinations - for example, roasted chestnuts with boiled beets, with fresh fish caviar or with dried ham.
Such a system can also help to eat better, creating new combinations of smells that will make us love vegetables and give up potato chips.
The computer will use complex algorithms to determine the exact chemical structure of food products, as well as to investigate taste preferences. These algorithms will study how chemicals interact with each other, find out their taste components at the molecular level, and use this information in combination with perception models to predict the taste appeal of a product.
Such a system will not only help make healthy food more enjoyable, it will also surprise with unusual combinations of products created for the most vivid taste sensations. For people with a special diet, in particular, those suffering from diabetes, the system will develop special flavor combinations and recipes that will control blood sugar levels and, at the same time, satisfy cravings for sweets.
Smell: Computers will gain a sense of smell

In the next five years, tiny sensors embedded in a computer or mobile phone will be able to detect symptoms of a cold or other illnesses. By analyzing odors, biomarkers and thousands of molecules in a person’s breathing and relating them to the norm, computer systems will help doctors diagnose and monitor diseases such as disorders of the liver and kidneys, asthma, diabetes and epilepsy.
Today, IBM scientists already control environmental performance to preserve works of art . This innovative method is beginning to be applied in the field of clinical hygiene to solve one of the biggest problems that healthcare faces today. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which in 2005 was associated with almost 19 thousand deaths of patients in US hospitals, are usually located on the skin and can be easily transmitted wherever people are in close contact together. One of the preventive ways to combat exposure to and the spread of MRSA in hospitals is strict control over the observance by medical personnel of the established regulatory requirements of clinical hygiene. In the next five years, the system based on IBM technology will be used to study hospital wards and other premises for traces of disinfectants to identify places that have not yet been sanitized. Intelligent sensors will use the latest wireless networks to collect and analyze data on various chemicals, and constantly learn and adapt to new smells.
Thanks to the development of sensory, telecommunication and self-learning technologies, sensors will be able to collect and analyze data where it was considered inaccessible. In particular, computer systems can be used in agriculture for odor determination and soil analysis of agricultural crops. Under urban conditions, this technology will be used to monitor the sanitary condition and level of contamination of territories and premises, helping the city services to identify potential problems before they cause real damage.
Additional materials are available here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/164355/
All Articles