ETERNUS DX - disk arrays, what is inside. Part 1
Let us consider in more detail that the hare has what functionality and mechanisms are inside the ETERNUS DX disk arrays. As I wrote earlier , the first disk arrays were developed more than 40 years ago for FUJITSU mainframes. Actually, this largely determined the direction of the entire family to use additional and extended hardware mechanisms aimed at increasing the reliability of data storage. At the same time, the development of the product line was moving “from top to bottom” - initially there were only High-End models, and about 20 years ago, on the basis of these models and existing technologies, middle and lower level models appeared.
All arrays support basic RAID levels: 0, 1, 10, 5. 50, 6. High-End has certain strict requirements on the number of disks in a RAID group and the RAID levels that can be used. At the same time, there are also a number of requirements regarding how the disks of the same RAID group between the disk shelves should be located. For systems of the middle and entry level, there are no such hard limits. It is clear that in terms of both performance and reliability of storage, it is much better to place disks of the same group in different disk shelves - then the failure of, for example, a disk shelf controller or a disk shelf will allow you to continue working with the group data. On the other hand, such strict rules for entry-level and mid-level systems will significantly reduce the flexibility of the entire system. Therefore, there is no problem to create, for example, a disk group from all the disks on one shelf for systems of primary or secondary level, but, at the same time, the High-End array will not allow creating such a group. Although, I repeat, for systems of primary and secondary levels, it is also recommended to distribute disks of the same group along different shelves - it certainly will not be worse.
All systems support SAS, NL-SAS and SSD drives. In addition, 2.5 "and 3.5" drive shelves are supported. In the regiment, you can in any order to install disks of different types. It is clear that it is not recommended to combine disks of different types into one group, to put it mildly. There are no restrictions on the number of SSD-drives in the system. In addition to budget constraints, expediency and common sense.
')
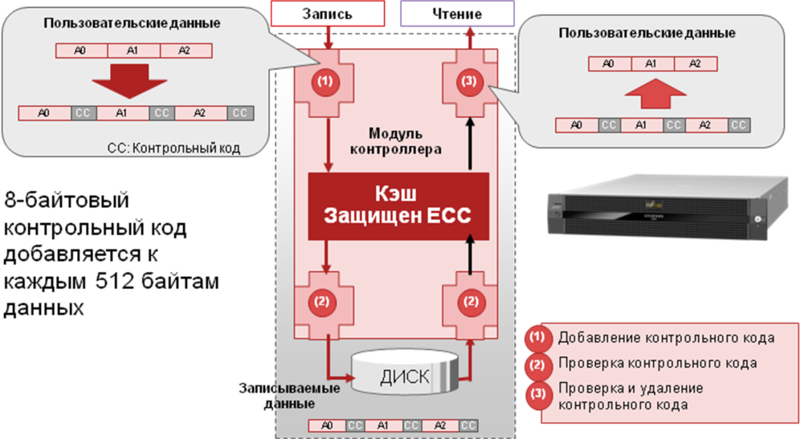
All disks are low-level formatted in a special way in blocks of 520 bytes. Of these, 512 are for data, 8 are for integrity control. When recording, the system calculates the control code for each block of 512 bytes and writes it after the block. At the block reading stage, data is necessarily checked for integrity, the control block is discarded and the original blocks without a control code are transferred to the system output to the hosts. Also, if the system has free computing resources and I / O resources are not loaded at 100%, then the correctness of the control code is also checked in the background. This mechanism is called Data Block Guard.
The next mechanism to increase the reliability of storage is Redundant Copy. Before we talk about this mechanism - a few horror stories. Hard drive failure is, of course, bad. Moreover, since the number of blocks and sectors increases with increasing hard disk capacity, the probability of failure of the entire device also increases. Of course, the probability of failure of a 3TB disk is not 3 times greater than that of a 1 TB disk, but, nevertheless, industrial-scale RAID6 has appeared relatively recently. And now let's consider the life of an average RAID group - it’s very likely that these are disks from the same factory batch that worked the same number of hours under the same conditions, then one of them broke down, the group began to rebuild, and the load on the other disks increased . Well, and then already the theory of failures, the statistics, plus some mystic coincidences begin to do their job. Sometimes even at the same time and checking the availability and integrity of backups :).
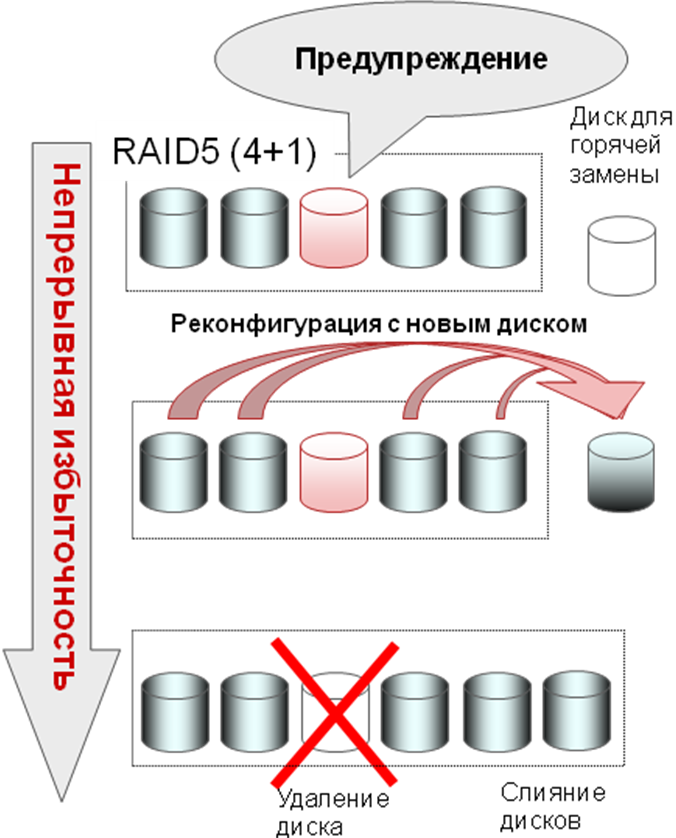
Let's see what is implemented in ETERNUS DX to significantly reduce the likelihood of bad scenarios. The disk system constantly monitors the status of hard drives. Today, due to a fair amount of signs, such as an increase in the average response time from a disk, an increase in the number of repeated read / write cycles, when the disk failed to read / write one or another block the first time, an increase in the number of data Block Guard actuations, the disk array According to the results of the continuous collection and analysis of this information from all hard drives, it can with a very high degree of probability predict that a hard drive will soon fail. And start transferring data from this disk to a hot-swap disk in advance. Moreover, the “suspicious” disk during this process remains fully readable, only write operations are blocked and redirected to the new disk. Thus, the reliability of the disk group operation significantly increases.
In this case, such an event is a fully warranty case. A standard warranty, by the way, for all ETERNUS DX is 3 years.
All arrays support basic RAID levels: 0, 1, 10, 5. 50, 6. High-End has certain strict requirements on the number of disks in a RAID group and the RAID levels that can be used. At the same time, there are also a number of requirements regarding how the disks of the same RAID group between the disk shelves should be located. For systems of the middle and entry level, there are no such hard limits. It is clear that in terms of both performance and reliability of storage, it is much better to place disks of the same group in different disk shelves - then the failure of, for example, a disk shelf controller or a disk shelf will allow you to continue working with the group data. On the other hand, such strict rules for entry-level and mid-level systems will significantly reduce the flexibility of the entire system. Therefore, there is no problem to create, for example, a disk group from all the disks on one shelf for systems of primary or secondary level, but, at the same time, the High-End array will not allow creating such a group. Although, I repeat, for systems of primary and secondary levels, it is also recommended to distribute disks of the same group along different shelves - it certainly will not be worse.
All systems support SAS, NL-SAS and SSD drives. In addition, 2.5 "and 3.5" drive shelves are supported. In the regiment, you can in any order to install disks of different types. It is clear that it is not recommended to combine disks of different types into one group, to put it mildly. There are no restrictions on the number of SSD-drives in the system. In addition to budget constraints, expediency and common sense.
')
All disks are low-level formatted in a special way in blocks of 520 bytes. Of these, 512 are for data, 8 are for integrity control. When recording, the system calculates the control code for each block of 512 bytes and writes it after the block. At the block reading stage, data is necessarily checked for integrity, the control block is discarded and the original blocks without a control code are transferred to the system output to the hosts. Also, if the system has free computing resources and I / O resources are not loaded at 100%, then the correctness of the control code is also checked in the background. This mechanism is called Data Block Guard.

The next mechanism to increase the reliability of storage is Redundant Copy. Before we talk about this mechanism - a few horror stories. Hard drive failure is, of course, bad. Moreover, since the number of blocks and sectors increases with increasing hard disk capacity, the probability of failure of the entire device also increases. Of course, the probability of failure of a 3TB disk is not 3 times greater than that of a 1 TB disk, but, nevertheless, industrial-scale RAID6 has appeared relatively recently. And now let's consider the life of an average RAID group - it’s very likely that these are disks from the same factory batch that worked the same number of hours under the same conditions, then one of them broke down, the group began to rebuild, and the load on the other disks increased . Well, and then already the theory of failures, the statistics, plus some mystic coincidences begin to do their job. Sometimes even at the same time and checking the availability and integrity of backups :).
Let's see what is implemented in ETERNUS DX to significantly reduce the likelihood of bad scenarios. The disk system constantly monitors the status of hard drives. Today, due to a fair amount of signs, such as an increase in the average response time from a disk, an increase in the number of repeated read / write cycles, when the disk failed to read / write one or another block the first time, an increase in the number of data Block Guard actuations, the disk array According to the results of the continuous collection and analysis of this information from all hard drives, it can with a very high degree of probability predict that a hard drive will soon fail. And start transferring data from this disk to a hot-swap disk in advance. Moreover, the “suspicious” disk during this process remains fully readable, only write operations are blocked and redirected to the new disk. Thus, the reliability of the disk group operation significantly increases.

In this case, such an event is a fully warranty case. A standard warranty, by the way, for all ETERNUS DX is 3 years.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/162571/
All Articles