AWS Insight: Reservations for EC2 - how it works
Hello! 
As you know, one of the basic rules for using cloud services is to optimize everything, and especially the financial side of the issue. Amazon Web Services has 3 basic methods for optimizing service costs:
Today I will talk about reservations in EC2, how, what and why it must be done.
Reservation is a prepayment of server capacity, which allows to significantly reduce the cost of these same capacities. There are 3 types of reservations:
The reservation is bought once a year or 3 years, i.e. reservation is:
The basic principle of choosing the desired reservation: the longer the server works, the more expensive the reservation is for it to buy. Let's do an experiment. Take one server size M1.XLarge and run it. Depending on the number of hours per day that the server will work, we can calculate the amount that will need to be paid for it for 1 year and 3 years. So, pricing for today:
The annual cost is calculated by the following formula:
')
HS = H * 365 * C + P , where
HS - Annual Cost
H - the number of hours per day that the machine is running.
C - cost per hour
- reservation cost
Take the “1 year” column from pricing and build a table of prices depending on the hours that the instance was launched:
Based on this table, we construct a graph:
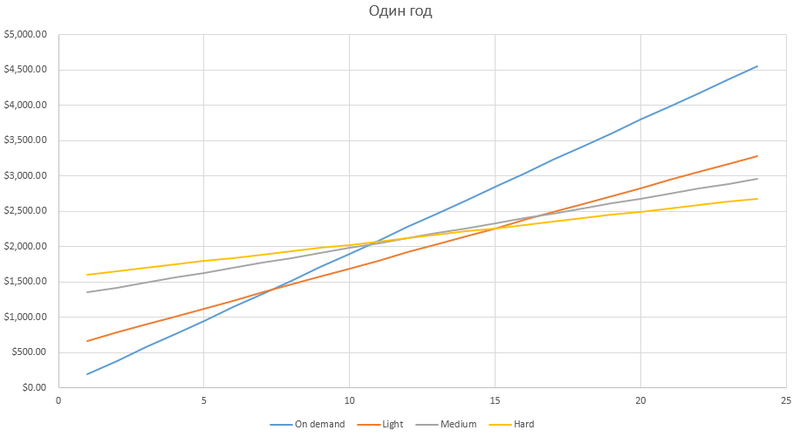
As you can see, up to 7 hours a day, inclusive, the cheapest option is On-Demand, i.e. no prepayments. If the server is used more than eight, then it makes sense to buy Light Utilization Reservation.
Before this research, I thought that everything has its place, but notice that after the 15th hour it is more advantageous to use Hard Utilization Reservation , and Medium - neither there nor here. UPD at the bottom of the post.
When using the machine from one to 7 hours a day, it is better not to make prepayments . From 7 to 15 - use Light Utilization Reservation . If the car runs more than 15 hours a day, then it will be better to buy Hard Utilization Reservation .
The same test, only a three-year reservation. Table of expenses:
Chart by table:
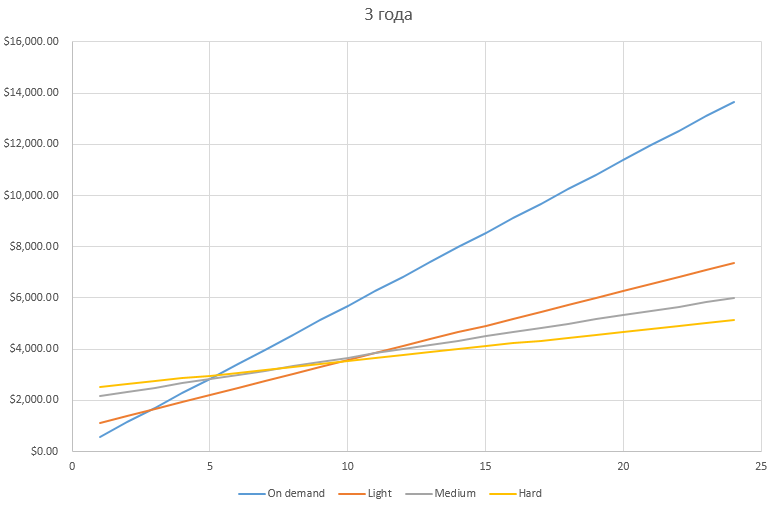
In the three-year period, the use of reservations is not justified if the instance works up to 3 hours per day. From 3 to 10 - it is better to use Light , after 10 hours a day - Hard Utilization Reservation .
Apparently, Medium is an average option in both cases, when it is more profitable than Light, but on singe pores it is cheaper than Hard reservations. It seems to be her only purpose.
So, looking at the results of calculations, it is clearly visible that the reason for using the reservation is simply necessary! With continuous use of the machine for one year in our example, you save:
($ 4,555.20 - $ 2,681.28) / $ 4,555.20 * 100% = 41%
For 3 years:
($ 13,665.60 - $ 5,133.12) / $ 13,665.60 * 100% = 62%
Impressive numbers, right?
UPD: Thanks to m_z and his comment .
It turns out that by choosing Heavy Utilization Reservation we will pay for the instance cost, even if it doesn't work, i.e. its price per year will be direct:
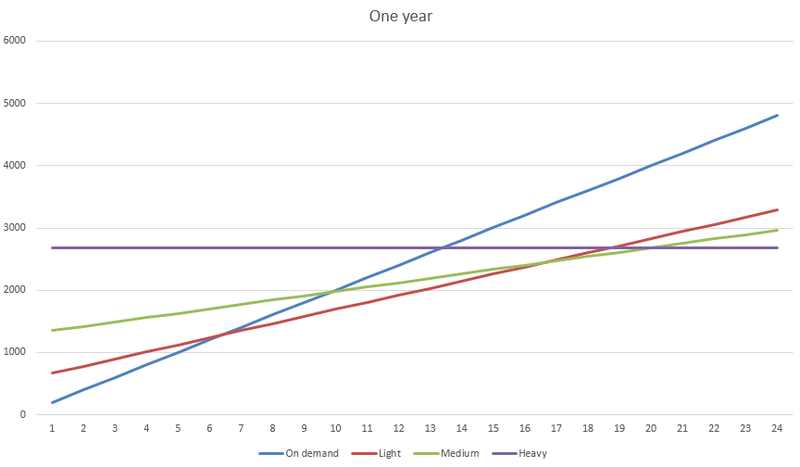
Well, the logic takes its own way: at first it's cheaper to have On-Demand instances, then Light Reservation, Medium Reservation and Heavy.
It is recommended that you create a template in the spreadsheet editor and for each type of instance you use to work out a profitable reservation policy.

As you know, one of the basic rules for using cloud services is to optimize everything, and especially the financial side of the issue. Amazon Web Services has 3 basic methods for optimizing service costs:
- autoscaling
- reservation
- use of spot instances
Today I will talk about reservations in EC2, how, what and why it must be done.
Reservation is a prepayment of server capacity, which allows to significantly reduce the cost of these same capacities. There are 3 types of reservations:
- Lightweight - Light Utilization
- Medium Utilization - Medium Utilization
- Heavy Duty - Hard Utilization
The reservation is bought once a year or 3 years, i.e. reservation is:
- one year old
- three years old
Economic justification
The basic principle of choosing the desired reservation: the longer the server works, the more expensive the reservation is for it to buy. Let's do an experiment. Take one server size M1.XLarge and run it. Depending on the number of hours per day that the server will work, we can calculate the amount that will need to be paid for it for 1 year and 3 years. So, pricing for today:
| Usage model | 1 year | 3 years | ||
| Prepayment | Hourly | Prepayment | Hourly | |
| On-demand | $ 0.52 | $ 0.52 | ||
| Light Utilization Reservation | $ 552 | $ 0.392 | $ 850.40 | $ 0.312 |
| Medium Utilization Reservation | $ 1280 | $ 0.248 | $ 2000 | $ 0.20 |
| Hard Utilization Reservation | $ 1,560 | $ 0.20 | $ 2400 | $ 0.16 |
Annual test
The annual cost is calculated by the following formula:
')
HS = H * 365 * C + P , where
HS - Annual Cost
H - the number of hours per day that the machine is running.
C - cost per hour
- reservation cost
Take the “1 year” column from pricing and build a table of prices depending on the hours that the instance was launched:
| One year, $ | ||||
| Hours per day | On demand | Light | Medium | Hard |
| one | 189.80 | 665.88 | 1,350.08 | 1,606.72 |
| 2 | 379.60 | 779.76 | 1,420.16 | 1,653.44 |
| 3 | 569.40 | 893.64 | 1,490.24 | 1,700.16 |
| four | 759.20 | 1,007.52 | 1,560.32 | 1,746.88 |
| five | 949.00 | 1,121.40 | 1,630.40 | 1,793.60 |
| 6 | 1,138.80 | 1,235.28 | 1,700.48 | 1,840.32 |
| 7 | 1,328.60 | 1,349.16 | 1,770.56 | 1,887.04 |
| eight | 1,518.40 | 1,463.04 | 1,840.64 | 1,933.76 |
| 9 | 1,708.20 | 1,576.92 | 1,910.72 | 1,980.48 |
| ten | 1,898.00 | 1,690.80 | 1,980.80 | 2,027.20 |
| eleven | 2,087.80 | 1,804.68 | 2,050.88 | 2,073.92 |
| 12 | 2,277.60 | 1,918.56 | 2,120.96 | 2,120.64 |
| 13 | 2,467.40 | 2,032.44 | 2,191.04 | 2,167.36 |
| 14 | 2,657.20 | 2,146.32 | 2,261.12 | 2,214.08 |
| 15 | 2,847.00 | 2,260.20 | 2,331.20 | 2,260.80 |
| sixteen | 3,036.80 | 2,374.08 | 2,401.28 | 2,307.52 |
| 17 | 3,226.60 | 2,487.96 | 2,471.36 | 2,354.24 |
| 18 | 3,416.40 | 2,601.84 | 2,541.44 | 2,400.96 |
| nineteen | 3,606.20 | 2,715.72 | 2,611.52 | 2,447.68 |
| 20 | 3,796.00 | 2,829.60 | 2,681.60 | 2,494.40 |
| 21 | 3,985.80 | 2,943.48 | 2,751.68 | 2,541.12 |
| 22 | 4,175.60 | 3,057.36 | 2,821.76 | 2,587.84 |
| 23 | 4,365.40 | 3,171.24 | 2,891.84 | 2,634.56 |
| 24 | 4,555.20 | 3,285.12 | 2,961.92 | 2,681.28 |
Based on this table, we construct a graph:

As you can see, up to 7 hours a day, inclusive, the cheapest option is On-Demand, i.e. no prepayments. If the server is used more than eight, then it makes sense to buy Light Utilization Reservation.
Conclusion
When using the machine from one to 7 hours a day, it is better not to make prepayments . From 7 to 15 - use Light Utilization Reservation . If the car runs more than 15 hours a day, then it will be better to buy Hard Utilization Reservation .
Three year test
The same test, only a three-year reservation. Table of expenses:
| Three Years, $ | ||||
| Hours per day | On demand | Light | Medium | Hard |
| one | 569.40 | 1,121.96 | 2,166.44 | 2,513.88 |
| 2 | 1,138.80 | 1,393.52 | 2,332.88 | 2,627.76 |
| 3 | 1,708.20 | 1,665.08 | 2,499.32 | 2,741.64 |
| four | 2,277.60 | 1,936.64 | 2,665.76 | 2,855.52 |
| five | 2,847.00 | 2,208.20 | 2,832.20 | 2,969.40 |
| 6 | 3,416.40 | 2,479.76 | 2,998.64 | 3,083.28 |
| 7 | 3,985.80 | 2,751.32 | 3,165.08 | 3,197.16 |
| eight | 4,555.20 | 3,022.88 | 3,331.52 | 3,311.04 |
| 9 | 5,124.60 | 3,294.44 | 3,497.96 | 3,424.92 |
| ten | 5,694.00 | 3,566.00 | 3,664.40 | 3,538.80 |
| eleven | 6,263.40 | 3,837.56 | 3,830.84 | 3,652.68 |
| 12 | 6,832.80 | 4,109.12 | 3,997.28 | 3,766.56 |
| 13 | 7,402.20 | 4,380.68 | 4,163.72 | 3,880.44 |
| 14 | 7,971.60 | 4,652.24 | 4,330.16 | 3,994.32 |
| 15 | 8,541.00 | 4,923.80 | 4,496.60 | 4,108.20 |
| sixteen | 9,110.40 | 5,195.36 | 4,663.04 | 4,222.08 |
| 17 | 9,679.80 | 5,466.92 | 4,829.48 | 4,335.96 |
| 18 | 10,249.20 | 5,738.48 | 4,995.92 | 4,449.84 |
| nineteen | 10,818.60 | 6,010.04 | 5,162.36 | 4,563.72 |
| 20 | 11,388.00 | 6,281.60 | 5,328.80 | 4,677.60 |
| 21 | 11,957.40 | 6,553.16 | 5,495.24 | 4,791.48 |
| 22 | 12,526.80 | 6,824.72 | 5,661.68 | 4,905.36 |
| 23 | 13,096.20 | 7,096.28 | 5,828.12 | 5,019.24 |
| 24 | 13,665.60 | 7,367.84 | 5,994.56 | 5,133.12 |
Chart by table:

findings
In the three-year period, the use of reservations is not justified if the instance works up to 3 hours per day. From 3 to 10 - it is better to use Light , after 10 hours a day - Hard Utilization Reservation .
Apparently, Medium is an average option in both cases, when it is more profitable than Light, but on singe pores it is cheaper than Hard reservations. It seems to be her only purpose.
Conclusion
So, looking at the results of calculations, it is clearly visible that the reason for using the reservation is simply necessary! With continuous use of the machine for one year in our example, you save:
($ 4,555.20 - $ 2,681.28) / $ 4,555.20 * 100% = 41%
For 3 years:
($ 13,665.60 - $ 5,133.12) / $ 13,665.60 * 100% = 62%
Impressive numbers, right?
UPD: Thanks to m_z and his comment .
It turns out that by choosing Heavy Utilization Reservation we will pay for the instance cost, even if it doesn't work, i.e. its price per year will be direct:

Well, the logic takes its own way: at first it's cheaper to have On-Demand instances, then Light Reservation, Medium Reservation and Heavy.
It is recommended that you create a template in the spreadsheet editor and for each type of instance you use to work out a profitable reservation policy.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/162345/
All Articles