Configure Hyper-V Replica in Windows Server 2012
All fiery mood!
Today I would like to tell you about a very interesting innovation that appeared in Windows Server 2012 - namely, Hyper-V Replica. This technology is of practical interest - let's get acquainted with it in more detail.
')
The point, as you might guess, is Hyper-V Replica in ... VM replication.
The meaning of replication, I think is known to all. In this particular case, the Hyper-V Replica feature is considered and positioned as a disaster recovery mechanism built into Windows Server 2012.
And you heard right - we are talking about disaster recovery, but not about high availability - clustering functions are used for high availability in Windows Server 2012, but Hyper-V Replica is the mechanism that allows you to replicate a VM instance outside the data center site to a remote site.
Immediately it is worth noting that before WS2012, disaster-resistant scenarios were implemented using the WS2008R2SP1 and SC2012 bundles, namely Orchestrator + DPM. From the point of view of VM infrastructure, Hyper-V Replica greatly simplifies life - but still the optimal effect will be achieved in conjunction with System Center 2012 SP1 Orchestrator.
Let's see how this mechanism is configured and working.
First of all, you need to understand that this mechanism works on a “point-to-point” principle - that is, a certain VM is replicated from the primary host or cluster to the remote backup host - both objects, of course, with the Hyper-V role.
First you need to configure the target host to receive replicated data.
1) Start Hyper-V Manager.
2) Select the desired target host in the Hyper-V Manager and go to its settings.
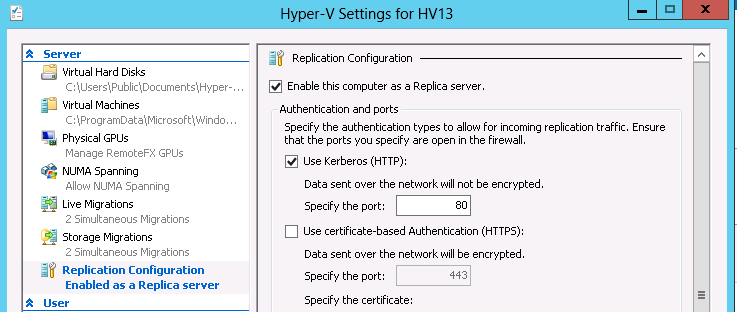
3) Select Replica Configuration.
4) Select the option Enable this computer as a Replica Server, as well as the method of data replication via Kerberos (HTTP) or more securely based on certificates (HTTPS).
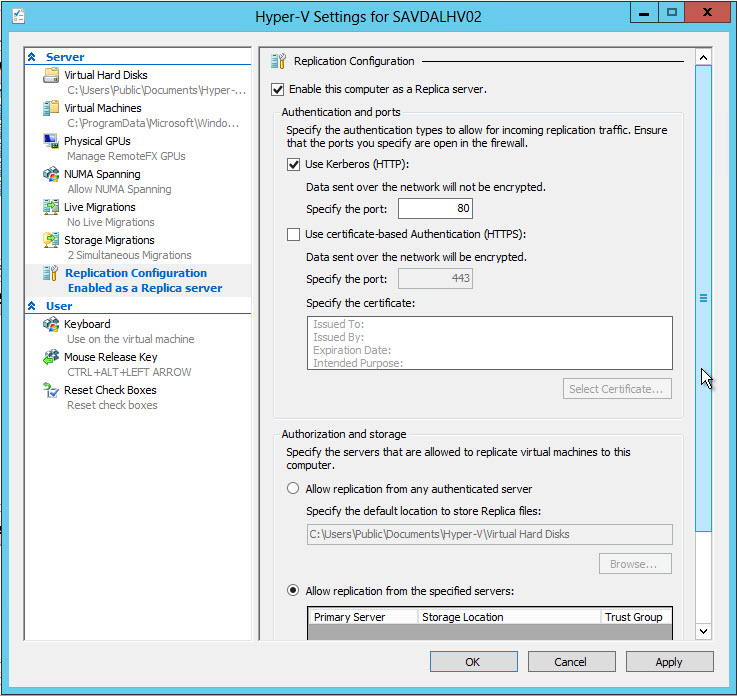
5) Next, you can select the servers from which you can receive replicas of the VM, as well as their target location. By default, we allow receiving replicas from any authenticated servers.
6) Make sure that the firewall on the receiving host has an exception for the Hyper-V Replica HTTP Listener (TCP-In) or the Hyper-V Replica HTTPS Listener (TCP-In) - depending on your requirements.
Now we need to configure the VM for replication.
1) Select the necessary for replication VM and right-click on it, then select Enable Replication .
2) In the Replication Configuration Wizard that appears, click Next on the first dialog box and also on the next.
3) Specify the FQDN of the target server to which you intend to replicate the VM and click Next .
4) Select the authentication method (Kerberos or certificate based) and whether to compress the data during transmission. Click Next .
5) Select the virtual disks of the VMs to be replicated and click Next .
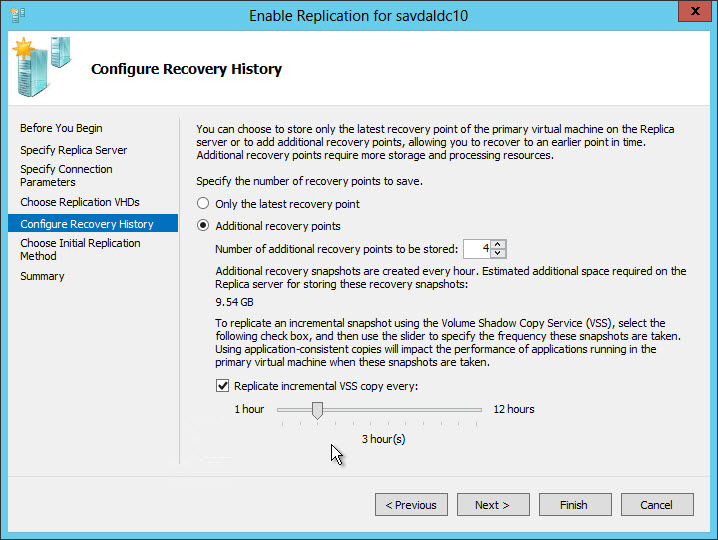
6) Configure the recovery point parameters - you will use only the most current and only recovery point (Only the latest recovery point) or decide to use the ability to create several points with a given periodicity (Additional recovery points) - you decide. In the second case, you can specify the required number of recovery points, as well as the interval between their creation. WS2012 uses VSS in combination with incremental snapshots of the VM to provide replication mechanisms. After you have made your choice, click Next .
7) Now you need to choose a mechanism for carrying out primary replication - via the network, via external media, or use an existing VM on the target server. Select the start time for replication and click Next .
8) Review the settings summary and click Finish to complete the configuration process.
To view the replication status, click on the Replication tab on the required VM. Also now in the VM network settings you can specify an alternative network configuration in case of a backup launch of the VM replica.
There is also a fairly detailed video on replication.
You should not use VM replication if there is a domain controller inside the VM, because if the replica is restored, the SID security key generation sequence inside the controller may fail. This can occur due to the fact that the replication mechanism asynchronously sends updates every 5 minutes - during this time the security keys can be updated, but on the replica - not yet. For such scenarios, it is recommended to keep another instance of the domain controller on the backup site.
And in general - the advice is this - if something you have has replication mechanisms separate from the lower level (for example, the application replicates itself, and the application level is higher than the container level of the VM - since this is the infrastructure level) - then it’s better to use these native mechanisms.
In general, there is nothing difficult in setting up a VM replica.
It remains only to check how it all works in a real environment - I’ll be happy to hear feedback from mega-admins!
PS> And of course, current and up-to-date materials on Microsoft solutions can always be found at MVA !
Respectfully,
Fireman
George A. Gadzhiev
Information Infrastructure Expert
Microsoft Corporation
Today I would like to tell you about a very interesting innovation that appeared in Windows Server 2012 - namely, Hyper-V Replica. This technology is of practical interest - let's get acquainted with it in more detail.

')
What is the meaning of Hyper-V Replica?
The point, as you might guess, is Hyper-V Replica in ... VM replication.
The meaning of replication, I think is known to all. In this particular case, the Hyper-V Replica feature is considered and positioned as a disaster recovery mechanism built into Windows Server 2012.
And you heard right - we are talking about disaster recovery, but not about high availability - clustering functions are used for high availability in Windows Server 2012, but Hyper-V Replica is the mechanism that allows you to replicate a VM instance outside the data center site to a remote site.
Immediately it is worth noting that before WS2012, disaster-resistant scenarios were implemented using the WS2008R2SP1 and SC2012 bundles, namely Orchestrator + DPM. From the point of view of VM infrastructure, Hyper-V Replica greatly simplifies life - but still the optimal effect will be achieved in conjunction with System Center 2012 SP1 Orchestrator.
Let's see how this mechanism is configured and working.
Configure Hyper-V Replica
First of all, you need to understand that this mechanism works on a “point-to-point” principle - that is, a certain VM is replicated from the primary host or cluster to the remote backup host - both objects, of course, with the Hyper-V role.
First you need to configure the target host to receive replicated data.
1) Start Hyper-V Manager.
2) Select the desired target host in the Hyper-V Manager and go to its settings.
3) Select Replica Configuration.
4) Select the option Enable this computer as a Replica Server, as well as the method of data replication via Kerberos (HTTP) or more securely based on certificates (HTTPS).

5) Next, you can select the servers from which you can receive replicas of the VM, as well as their target location. By default, we allow receiving replicas from any authenticated servers.
6) Make sure that the firewall on the receiving host has an exception for the Hyper-V Replica HTTP Listener (TCP-In) or the Hyper-V Replica HTTPS Listener (TCP-In) - depending on your requirements.
Now we need to configure the VM for replication.
1) Select the necessary for replication VM and right-click on it, then select Enable Replication .
2) In the Replication Configuration Wizard that appears, click Next on the first dialog box and also on the next.
3) Specify the FQDN of the target server to which you intend to replicate the VM and click Next .
4) Select the authentication method (Kerberos or certificate based) and whether to compress the data during transmission. Click Next .
5) Select the virtual disks of the VMs to be replicated and click Next .
6) Configure the recovery point parameters - you will use only the most current and only recovery point (Only the latest recovery point) or decide to use the ability to create several points with a given periodicity (Additional recovery points) - you decide. In the second case, you can specify the required number of recovery points, as well as the interval between their creation. WS2012 uses VSS in combination with incremental snapshots of the VM to provide replication mechanisms. After you have made your choice, click Next .

7) Now you need to choose a mechanism for carrying out primary replication - via the network, via external media, or use an existing VM on the target server. Select the start time for replication and click Next .
8) Review the settings summary and click Finish to complete the configuration process.
To view the replication status, click on the Replication tab on the required VM. Also now in the VM network settings you can specify an alternative network configuration in case of a backup launch of the VM replica.
There is also a fairly detailed video on replication.
Some precautions
You should not use VM replication if there is a domain controller inside the VM, because if the replica is restored, the SID security key generation sequence inside the controller may fail. This can occur due to the fact that the replication mechanism asynchronously sends updates every 5 minutes - during this time the security keys can be updated, but on the replica - not yet. For such scenarios, it is recommended to keep another instance of the domain controller on the backup site.
And in general - the advice is this - if something you have has replication mechanisms separate from the lower level (for example, the application replicates itself, and the application level is higher than the container level of the VM - since this is the infrastructure level) - then it’s better to use these native mechanisms.
In general, there is nothing difficult in setting up a VM replica.
It remains only to check how it all works in a real environment - I’ll be happy to hear feedback from mega-admins!
PS> And of course, current and up-to-date materials on Microsoft solutions can always be found at MVA !
Respectfully,
Fireman
George A. Gadzhiev
Information Infrastructure Expert
Microsoft Corporation
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/162145/
All Articles