AWS Insight: How ELB Works
Hello! 
I want to tell Habrahabr readers about the Elastic Load Balancer service , which is part of the Enterprise Compute Cloud. Many have long been using the ELB service, but do not know how the service works from the inside. I own this information a little - hours-long meetings with AWS support are sometimes much more informative than the documentation on the site.
So let's start with the basics, then move on to the nuances.
')
Elastic Load Balancer is a service that provides query balancing between EC2 / VPC instances. Accordingly, there are 2 types of ELB that
ELB can proxy the following protocols:
And both listeners and recipients can be any combination. For example http-http (just a proxy) or tcp-https (if SSL termination is done on the side of the instances)
ELB can proxy ports:
In the console, we find the item Load Balancers and click Create Load Balancer. The first screen is setting up ports and protocols:
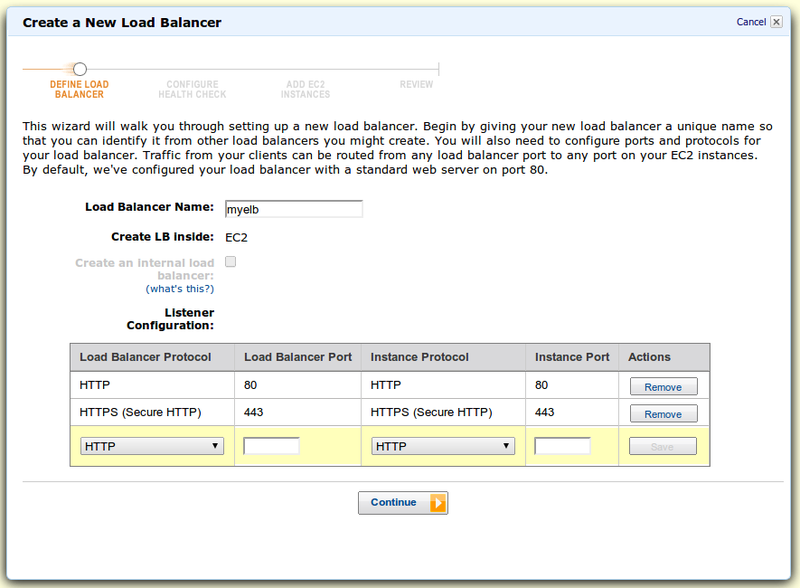
Further, because we chose HTTPS, we need a certificate for SSL termination. AWS asks for our settings:
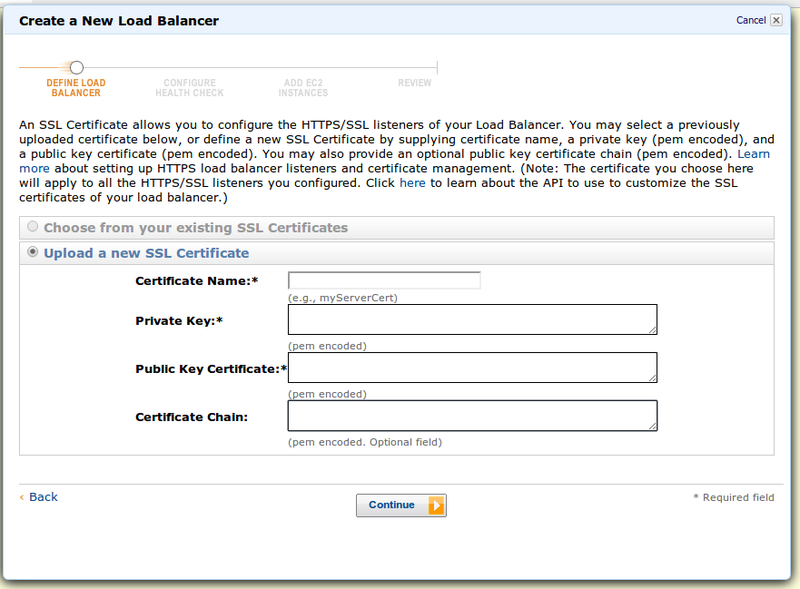
Next, set up a helsecchek - host health check. If the helper is positive, the instance will be listed on the balance sheet. Negative - no queries will be sent to the instance:

Helschacks can be configured for the same protocols as balancing, for http / https you can add a page name or path.
Well, in the final - you need to select the instances that you want to add under ELB (in the screenshot just an example)

The last screen - as always checking the details:
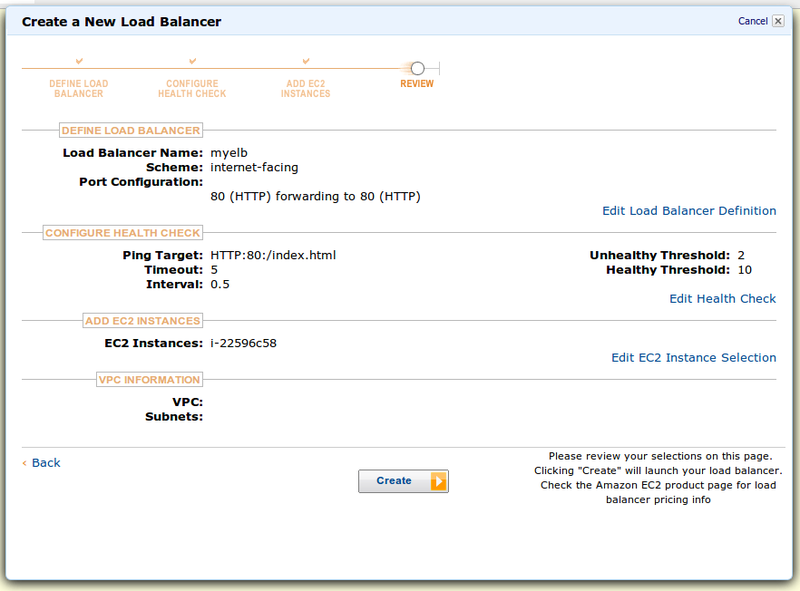
We looked, we decided that everything was OK and created ELB.
EC2 ELB has 3 addresses by which they can be accessed. These are not IP addresses, but URLs:
There are 2 ways to configure your domain on ELB and they depend on what name servers you use. It is recommended to use Amazon Route 53 , because It is integrated with ELB and everything is easily configured via the A record:
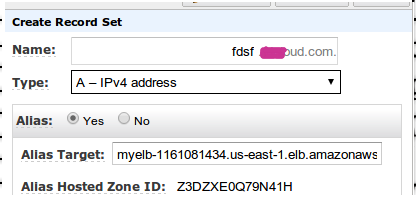
If you use other DNS services / servers - your CNAME path.
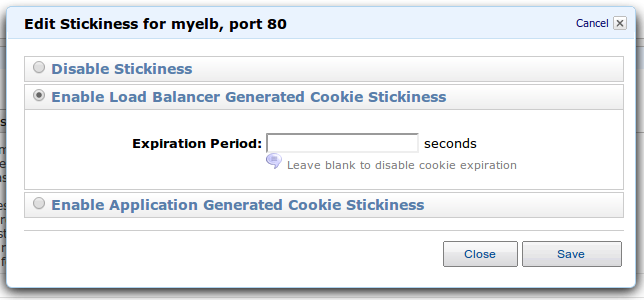
ELB is able to handle cookies for the Sticky session. These functions can be configured in the configuration after creating the ELB:
Here I would like to talk about how ELB is scaled and how it behaves under load. I have already published an article that compared the performance of ELB, NGINX and HAproxy. There I touched the moment of scaling. ELB vertically scaled from t1.micto to m1.small:
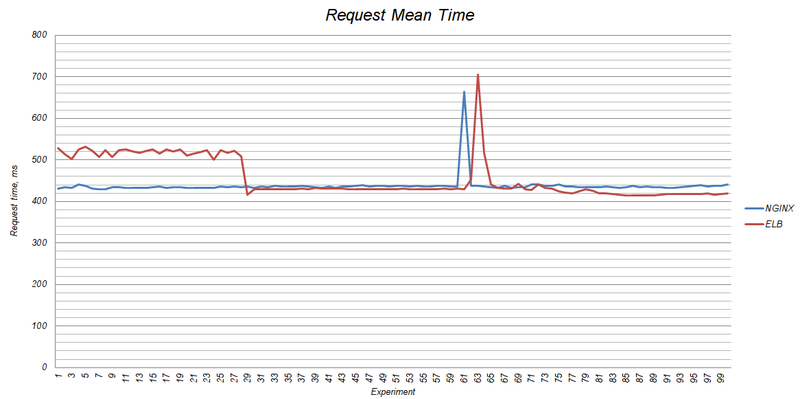
According to representatives of the technical support of Amazon Web Services with an increase in the load on the ELB passes from one to seven minutes before the server scaling occurs. The IP address can be changed, so it is not recommended to use IP addresses for domains (I described the way out above).
For some cases, ELB can be “warmed up” to the desired shape to withstand heavy loads. "Warming up is done" through requests to tech support.
ELB plays an important role in autoscaling EC2 instances. The name of the ELB is specified in the configurations of the autoscaling groups and, in fact, everything revolves around them. Read more about this in my article .
ELB still has a lot of nuances of work, but I told you the main thing.
Do you have experience with ELB? Interesting Facts?

I want to tell Habrahabr readers about the Elastic Load Balancer service , which is part of the Enterprise Compute Cloud. Many have long been using the ELB service, but do not know how the service works from the inside. I own this information a little - hours-long meetings with AWS support are sometimes much more informative than the documentation on the site.
So let's start with the basics, then move on to the nuances.
')
What is ELB.
Elastic Load Balancer is a service that provides query balancing between EC2 / VPC instances. Accordingly, there are 2 types of ELB that
- visible from the internet - EC2 / VPC
- not visible from the internet - VPC
ELB features
ELB can proxy the following protocols:
- http
- https
- tcp
- ssl (secure tcp)
And both listeners and recipients can be any combination. For example http-http (just a proxy) or tcp-https (if SSL termination is done on the side of the instances)
ELB can proxy ports:
- 25
- 80
- 443
- 1024-65535
ELB Setup
In the console, we find the item Load Balancers and click Create Load Balancer. The first screen is setting up ports and protocols:

Further, because we chose HTTPS, we need a certificate for SSL termination. AWS asks for our settings:

Next, set up a helsecchek - host health check. If the helper is positive, the instance will be listed on the balance sheet. Negative - no queries will be sent to the instance:

Helschacks can be configured for the same protocols as balancing, for http / https you can add a page name or path.
Well, in the final - you need to select the instances that you want to add under ELB (in the screenshot just an example)

The last screen - as always checking the details:

We looked, we decided that everything was OK and created ELB.
How to set up a domain on ELB
EC2 ELB has 3 addresses by which they can be accessed. These are not IP addresses, but URLs:
- myelb-1161081434.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com (A Record)
- ipv6.myelb-1161081434.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com (AAAA Record)
- dualstack.myelb-1161081434.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com (A or AAAA Record)
There are 2 ways to configure your domain on ELB and they depend on what name servers you use. It is recommended to use Amazon Route 53 , because It is integrated with ELB and everything is easily configured via the A record:

If you use other DNS services / servers - your CNAME path.
Sticky session
ELB is able to handle cookies for the Sticky session. These functions can be configured in the configuration after creating the ELB:

ELB autoscaling
Here I would like to talk about how ELB is scaled and how it behaves under load. I have already published an article that compared the performance of ELB, NGINX and HAproxy. There I touched the moment of scaling. ELB vertically scaled from t1.micto to m1.small:

According to representatives of the technical support of Amazon Web Services with an increase in the load on the ELB passes from one to seven minutes before the server scaling occurs. The IP address can be changed, so it is not recommended to use IP addresses for domains (I described the way out above).
For some cases, ELB can be “warmed up” to the desired shape to withstand heavy loads. "Warming up is done" through requests to tech support.
EC2 / VPC autoscaling
ELB plays an important role in autoscaling EC2 instances. The name of the ELB is specified in the configurations of the autoscaling groups and, in fact, everything revolves around them. Read more about this in my article .
ELB still has a lot of nuances of work, but I told you the main thing.
Do you have experience with ELB? Interesting Facts?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/161163/
All Articles