Expert system for predicting personal characteristics of a person based on Bayes theorem
The study, which began in October, is planned to be developed into a course project and, further, into a diploma.
The work was presented at the regional conference "Security of the Information Space".
This study is an attempt to approach the issue of security a bit from the other side.
It is known that the main source of all ills is the person himself, the employee of the organization. Therefore, not taking on the work in the selection of unreliable potential employees, it is possible to reduce the harm from them.
The aim of the work is to create an expert system for decision-making in the face of uncertainty, using a method based on the use of the Bayes theorem, to obtain a personality characteristic, provided that a person is not subjected to multiple testing.
')
The work is aimed at finding out the critical psychological personality traits in accepting a new employee in the organization, as a substitute for testing by a psychologist, reducing the time of testing, obtaining the results of many tests while passing only one.
Psychological testing is the term of psychology, denoting the procedure for establishing and measuring individual psychological differences. Psychological testing is used in various fields: vocational guidance, professional selection, psychological counseling, planning remedial work, etc.
In our time, psychodiagnostics is represented by a huge number of tests that extensively and many-sidedly investigate a person as a whole and particular features of a human character in particular.
Psychological test - a standardized task, the results of which are judged psycho-physiological and personal characteristics, knowledge, skills and abilities of the subject.
A huge number of existing tests, and the desired personality characteristics do not allow for the full necessary diagnostics.
However, it is possible to use a universal technique that gives diverse information about a person, from the results of which it is possible to draw conclusions about the results for other tests.
The 16-factor questionnaire Cattell was chosen as such a test, as the most universal, multidimensional, evaluating the properties of a normal personality, describes the personality structure of a person, reveals personality problems. At the same time, a person is described by a set of primary properties of a person, which determine his internal content and behavior.
Factors test Cattell:
Factor A: Openness - Closure
Factor B: Developed Thinking - Limited Thinking.
Factor C: Emotional Stability - Emotional Instability.
Factor E: Independence - Compliance.
Factor F: Carelessness - Concern.
Factor G: Consciousness - Unprincipled.
Factor H: Courage - Shyness.
Factor I: Sensuality - Hardness.
Factor L: Suspiciousness - Credulity.
Factor M: Dreaminess - Practicality.
Factor N: Refinement - “Simplicity.”
Factor O: Addiction to guilt - Calm self-confidence.
Factor Q1: Radicalism - Conservatism.
Factor Q2: Independence - Dependence on the group.
Factor Q3: Self-control, strong will - Lack of self-control, indifference.
Factor Q4: Inner Tension - Inner Relaxation.
The Leary interpersonal relationship test was chosen as the predicted one. It was designed to study the subject's ideas about himself and the ideal “I”, as well as to study relationships in groups. With the help of the test, the prevailing type of attitudes towards people is revealed in self-assessment and mutual evaluation, conclusions are made about the type of behavior, the degree of behavior adaptation - the degree of conformity (discrepancy) between the goals and the results achieved in the process.
Leary test scales:
I. Authoritarian (overbearing-leading)
Ii. Selfish (independent-dominant)
Iii. Aggressive (straight-aggressive)
Iv. Suspicious (incredulous-skeptical)
V. Submissive (submissively shy)
Vi. Dependent (dependent-obedient)
VII. Friendly (collaborative-conventional)
Viii. Altruistic (responsibly generous)
The expert system for decision making under uncertainty on the basis of the Bayes theorem is built using the previously obtained statistical data and without the participation of an expert.
The statistics of the results of passing both tests were divided into groups in accordance with the methodological guidelines for the tests. For the Cattell questionnaire, the obtained values were divided into three groups: low (1-3), medium (4-7) and high (8-10). For the Leary test, the values are divided into four groups: 0-4 points - low, 5-8 points - moderate, 9-12 points - high, 13-16 points - extreme.
The control group with the results used in our work consisted of one hundred people who passed both tests.
Each element of the matrix of conditional probabilities is the probability that each scale of each test falls into each group. For one factor of the Cattell questionnaire and one scale of the Leary test, the matrix of conditional probabilities will be 3x4.
Having performed the calculation of this matrix, we obtained the data for applying the Bayes theorem.
It is necessary to make a decision that comes down to choosing one of several well-known alternatives. The system draws information for decision making from a dialogue with the user, asking him questions and getting answers from him.
In our case, the questions will be sixteen values obtained using the Cattell questionnaire, the alternatives are the groups in the Leary test, and the result of the work is the probability of falling into one or another group of Leary test results.
Before the start of the survey, we do not know which results on which scale of the test will be more likely, so the prior probability at the beginning will be 0.25
After each answer to the question (processing the results of the following scale of the Cattell questionnaire), the situation will change.
Suppose there is a vector Pa of prior probabilities of target alternatives (in our case, it includes 4 components, equal to 0.25 each). If answer number i is chosen, then the a posteriori (that is, after the answer) probability of the jth target alternative is

Predicted may be another test that diagnoses the desired characteristics.
It is also worth remembering that any test gives a certain error.
The result of the research is a simulated test, Leary, based on the data of the subjects on the test of Cattell. The program works in two modes: the user is prompted to take a Cattell test questionnaire or enter already existing results (walls) on each scale.
The result of the program will be the decoding of values for the Cattell questionnaire and a table of predicted probabilities of a person belonging to one of the four groups according to Leary's test.
Comparing the data obtained from the simulator and the results of the control group of 100 people, we can conclude that the forecast was generally successful (Ie, 100 answers were given for each scale, the graph shows the number of correct predictions for subjects with mixed results of the Cattell questionnaire. on average, the probability of a correct prediction is 0.6 (60;).
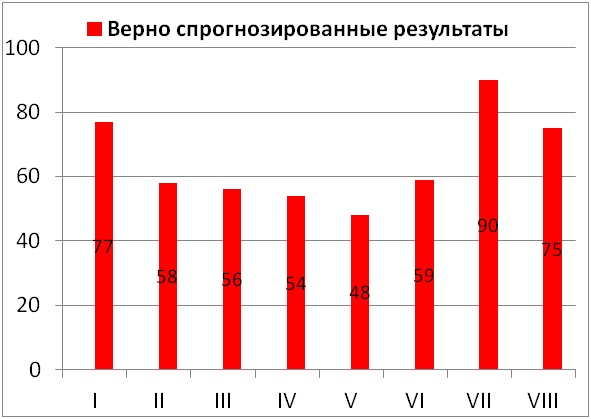
For subjects with critical characteristics of interest to us, whose results fell into the group of low results (35 people, respectively, 35 results for each Liri scale) according to the Cattell test questionnaire, the accuracy is 82%, in the opposite group with high values (34 people, 34 values for each scale) - 84%.
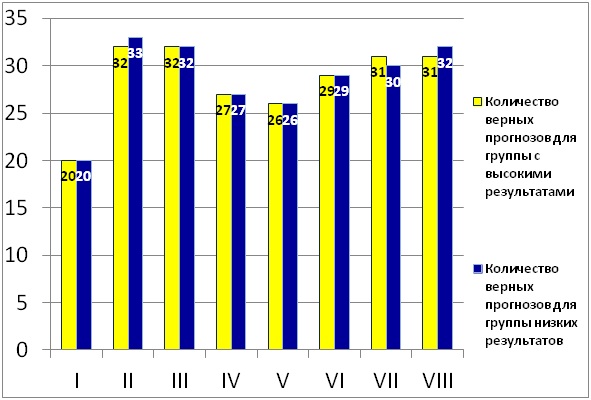
I note that to obtain higher accuracy and reliability of the results, it is necessary to use other, more complex mathematical methods and tools.
In the course of the research, results were obtained that allowed to continue work in the chosen direction and improve the accuracy of the results obtained.
The work was presented at the regional conference "Security of the Information Space".
This study is an attempt to approach the issue of security a bit from the other side.
It is known that the main source of all ills is the person himself, the employee of the organization. Therefore, not taking on the work in the selection of unreliable potential employees, it is possible to reduce the harm from them.
The aim of the work is to create an expert system for decision-making in the face of uncertainty, using a method based on the use of the Bayes theorem, to obtain a personality characteristic, provided that a person is not subjected to multiple testing.
')
The work is aimed at finding out the critical psychological personality traits in accepting a new employee in the organization, as a substitute for testing by a psychologist, reducing the time of testing, obtaining the results of many tests while passing only one.
Psychological testing is the term of psychology, denoting the procedure for establishing and measuring individual psychological differences. Psychological testing is used in various fields: vocational guidance, professional selection, psychological counseling, planning remedial work, etc.
In our time, psychodiagnostics is represented by a huge number of tests that extensively and many-sidedly investigate a person as a whole and particular features of a human character in particular.
Psychological test - a standardized task, the results of which are judged psycho-physiological and personal characteristics, knowledge, skills and abilities of the subject.
A huge number of existing tests, and the desired personality characteristics do not allow for the full necessary diagnostics.
However, it is possible to use a universal technique that gives diverse information about a person, from the results of which it is possible to draw conclusions about the results for other tests.
The 16-factor questionnaire Cattell was chosen as such a test, as the most universal, multidimensional, evaluating the properties of a normal personality, describes the personality structure of a person, reveals personality problems. At the same time, a person is described by a set of primary properties of a person, which determine his internal content and behavior.
Factors test Cattell:
Factor A: Openness - Closure
Factor B: Developed Thinking - Limited Thinking.
Factor C: Emotional Stability - Emotional Instability.
Factor E: Independence - Compliance.
Factor F: Carelessness - Concern.
Factor G: Consciousness - Unprincipled.
Factor H: Courage - Shyness.
Factor I: Sensuality - Hardness.
Factor L: Suspiciousness - Credulity.
Factor M: Dreaminess - Practicality.
Factor N: Refinement - “Simplicity.”
Factor O: Addiction to guilt - Calm self-confidence.
Factor Q1: Radicalism - Conservatism.
Factor Q2: Independence - Dependence on the group.
Factor Q3: Self-control, strong will - Lack of self-control, indifference.
Factor Q4: Inner Tension - Inner Relaxation.
The Leary interpersonal relationship test was chosen as the predicted one. It was designed to study the subject's ideas about himself and the ideal “I”, as well as to study relationships in groups. With the help of the test, the prevailing type of attitudes towards people is revealed in self-assessment and mutual evaluation, conclusions are made about the type of behavior, the degree of behavior adaptation - the degree of conformity (discrepancy) between the goals and the results achieved in the process.
Leary test scales:
I. Authoritarian (overbearing-leading)
Ii. Selfish (independent-dominant)
Iii. Aggressive (straight-aggressive)
Iv. Suspicious (incredulous-skeptical)
V. Submissive (submissively shy)
Vi. Dependent (dependent-obedient)
VII. Friendly (collaborative-conventional)
Viii. Altruistic (responsibly generous)
The expert system for decision making under uncertainty on the basis of the Bayes theorem is built using the previously obtained statistical data and without the participation of an expert.
The statistics of the results of passing both tests were divided into groups in accordance with the methodological guidelines for the tests. For the Cattell questionnaire, the obtained values were divided into three groups: low (1-3), medium (4-7) and high (8-10). For the Leary test, the values are divided into four groups: 0-4 points - low, 5-8 points - moderate, 9-12 points - high, 13-16 points - extreme.
The control group with the results used in our work consisted of one hundred people who passed both tests.
Each element of the matrix of conditional probabilities is the probability that each scale of each test falls into each group. For one factor of the Cattell questionnaire and one scale of the Leary test, the matrix of conditional probabilities will be 3x4.
Having performed the calculation of this matrix, we obtained the data for applying the Bayes theorem.
It is necessary to make a decision that comes down to choosing one of several well-known alternatives. The system draws information for decision making from a dialogue with the user, asking him questions and getting answers from him.
In our case, the questions will be sixteen values obtained using the Cattell questionnaire, the alternatives are the groups in the Leary test, and the result of the work is the probability of falling into one or another group of Leary test results.
Before the start of the survey, we do not know which results on which scale of the test will be more likely, so the prior probability at the beginning will be 0.25
After each answer to the question (processing the results of the following scale of the Cattell questionnaire), the situation will change.
Suppose there is a vector Pa of prior probabilities of target alternatives (in our case, it includes 4 components, equal to 0.25 each). If answer number i is chosen, then the a posteriori (that is, after the answer) probability of the jth target alternative is

Predicted may be another test that diagnoses the desired characteristics.
It is also worth remembering that any test gives a certain error.
The result of the research is a simulated test, Leary, based on the data of the subjects on the test of Cattell. The program works in two modes: the user is prompted to take a Cattell test questionnaire or enter already existing results (walls) on each scale.
The result of the program will be the decoding of values for the Cattell questionnaire and a table of predicted probabilities of a person belonging to one of the four groups according to Leary's test.
Comparing the data obtained from the simulator and the results of the control group of 100 people, we can conclude that the forecast was generally successful (Ie, 100 answers were given for each scale, the graph shows the number of correct predictions for subjects with mixed results of the Cattell questionnaire. on average, the probability of a correct prediction is 0.6 (60;).

For subjects with critical characteristics of interest to us, whose results fell into the group of low results (35 people, respectively, 35 results for each Liri scale) according to the Cattell test questionnaire, the accuracy is 82%, in the opposite group with high values (34 people, 34 values for each scale) - 84%.

I note that to obtain higher accuracy and reliability of the results, it is necessary to use other, more complex mathematical methods and tools.
In the course of the research, results were obtained that allowed to continue work in the chosen direction and improve the accuracy of the results obtained.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/160731/
All Articles