Amazon Redshift: New Petabyte Data Warehouse
Amazon has rolled out a fundamentally new Redshift service for storing databases ranging in size from a few hundred gigabytes to many petabytes. The product is aimed at corporate customers who are constrained by the limit of 1 terabyte of traditional RDS, while they want to use familiar SQL applications and ensure instant data availability.
The Redshift cluster rises in a couple of mouse clicks from the AWS admin panel. The cost of storing data here is comparable to a regular S3 and depends on the type of cluster and tariff plan. For example, on a three-year plan, it is $ 999 per terabyte per year.
Redshift users are offered two types of servers for the cluster: XL and 8XL.
')
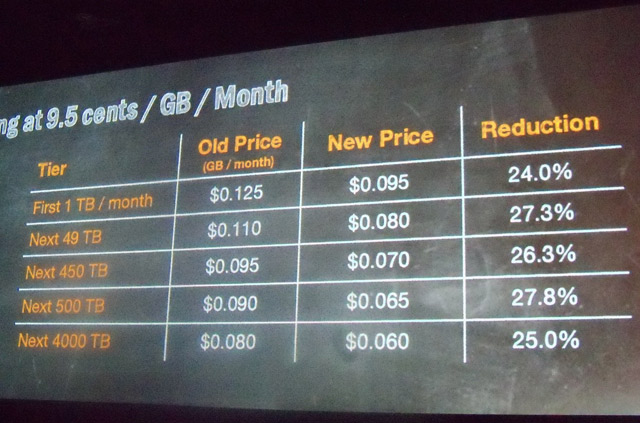
Simultaneously, with the announcement of Redshift, Amazon reduced the prices for S3 hosting by 25% .
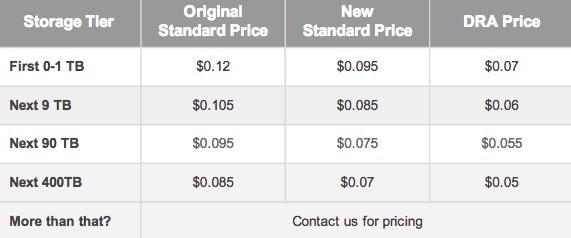
On the same day, Google also reduced prices by 20% for data storage in the Google Cloud Platform, and announced the launch of a new service for cheap long-term storage of Durable Reduced Availability Storage archives, like AWS Glacier.
The Redshift cluster rises in a couple of mouse clicks from the AWS admin panel. The cost of storing data here is comparable to a regular S3 and depends on the type of cluster and tariff plan. For example, on a three-year plan, it is $ 999 per terabyte per year.
Redshift users are offered two types of servers for the cluster: XL and 8XL.
High Storage Extra Large (XL) DW Node
- CPU: 2 virtual cores
- ECU: 4.4
- Memory: 15 GiB
- Drives: 3 HDD with 2 TB of local attached storage
- Network: medium
- Disk I / O Speed: Medium
- API: dw.hs1.xlarge
')
High Storage Eight Extra Large (8XL) DW
- CPU: 16 virtual cores
- ECU: 35
- Memory: 120 GiB
- Drives: 24 HDD with 16 TB of local space
- Network: 10 Gigabit Ethernet
- I / O speed with disc: very high
- API: dw.hs1.8xlarge
Simultaneously, with the announcement of Redshift, Amazon reduced the prices for S3 hosting by 25% .

On the same day, Google also reduced prices by 20% for data storage in the Google Cloud Platform, and announced the launch of a new service for cheap long-term storage of Durable Reduced Availability Storage archives, like AWS Glacier.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/160653/
All Articles