Smart home based on Z-Wave
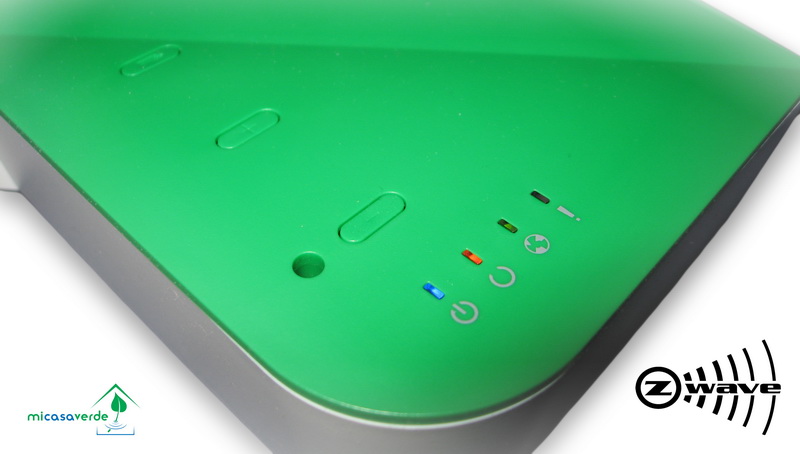

For a long time I had the idea of how best to make convenient control of light and electrical appliances in the apartment. At the same time, I wanted to have some kind of ready-made modular solution for relatively simple self-tuning. So, quite by chance, I came across equipment that can be implemented already in the existing home network completely “painlessly”. It turned out to be devices operating under the Z-Wave protocol.
Z-wave
Z-Wave is a patented wireless communication protocol designed for home automation, in particular for monitoring and controlling residential and commercial sites. The technology uses low-power and miniature radio frequency modules that are embedded in consumer electronics and various devices, such as lighting, heating, access control, entertainment systems and household appliances. This is a wireless radio technology designed specifically for remote control. Unlike Wi-Fi and other IEEE 802.11 data transmission standards, mainly for large streams of information, Z-Wave operates in the frequency range up to 1 GHz and is optimized for transmitting simple control commands (for example, turn on / off, change volume, brightness etc.). The choice of low radio frequency for Z-Wave is due to a small number of potential sources of interference.
Also, other advantages of Z-Wave include low energy consumption, low cost of manufacturing and embedding Z-Wave into various home appliances.
In the world there are more than 200 manufacturers offering products with Z-Wave chips or modules. A distinctive feature of Z-Wave is that all these products are compatible with each other.
The Z-Wave solution is based on mesh mesh technology, in which each node or device can receive and transmit control signals to other network devices using intermediate neighbors. Mesh is a self-organizing network with routing dependent on external factors — for example, if an obstacle occurs between two closest network nodes, the signal will go through other network nodes that are in range.
Iron
Of the devices offered to choose from on the Internet, there were various control centers (gateways) in the form of completely budget USB sticks with support for different operating systems:

')
and not very budget, like these:


I decided not to mess with the USB option for my FreeBSD server, but I chose the average price and functionality of the Vera Lite gateway:


The main “pros” for me was having a convenient UI when working via the web (plug-ins from the market, my own scripts) and software for Android when working not from the web.
Inside the device are:
- CPU RaLink RT3662 SoC, Linux 2.6
- Parallel NAND Flash 32 MB
- RAM DDR2 64 MB
For the sample, I decided to order a few dimmers to adjust the lighting.
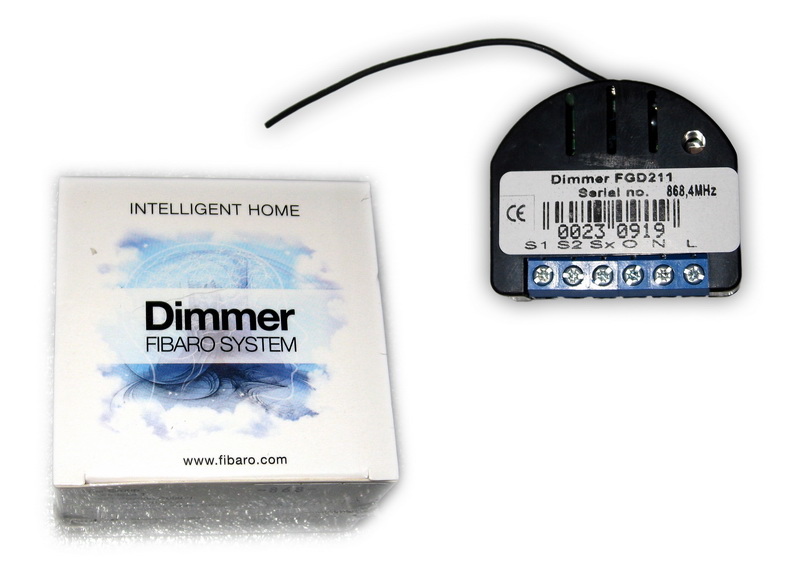

relay for two 1.5 kW outputs for outlets

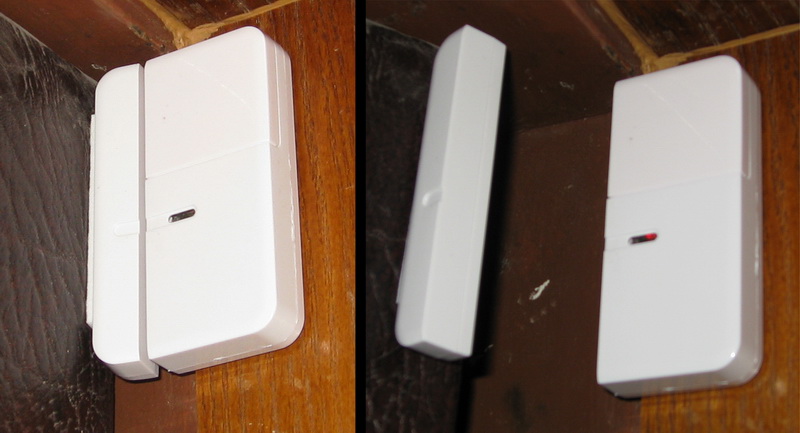
window / door sensor, which I immediately installed on the front door
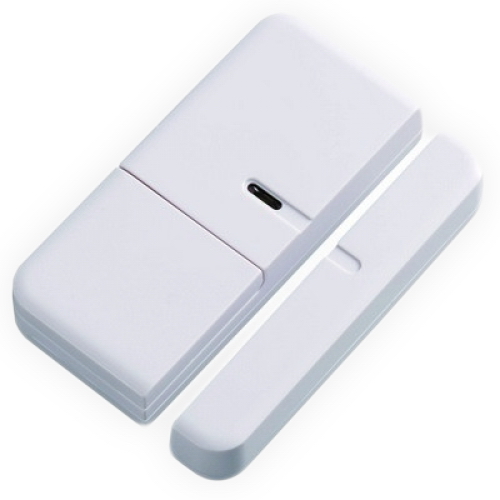

and a motion sensor in the corridor (could not resist, disassembled)
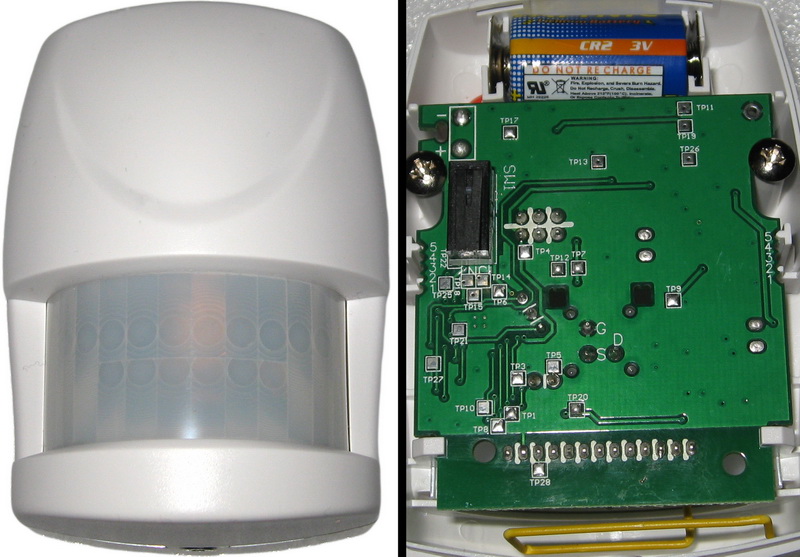


The whole set cost me about 20,000 rubles.
How it was
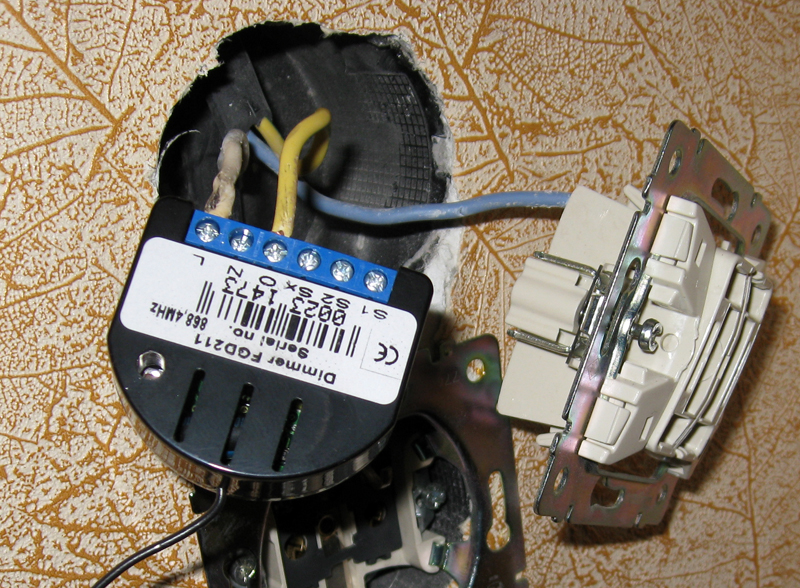
The first thing I decided to check is the remote control of the light. The main feature of this dimmer is that it only needs two wires, which are suitable for the switch.

By the way, podrozetniki must be a depth of 50 mm or more, otherwise the design may not fit. But with my Legrand switches there were no such difficulties.
Skolhozil such a design and, connecting to the gateway from the phone, checked the work.
It is impossible to remove the dimmer directly into the box, since it must also be tied to the gateway by pressing the “B” button three times.
The command is transmitted to the controller immediately (if there are no commands from other devices in the queue), and the command execution status is transmitted a little later after confirmation.
If you adjust the light from the switch, then on the phone or in the web interface, the status immediately changes.
By default, the dimmer is configured to work with the so-called bell button (with spring return), but using the configurator in the Vera Lite web interface, following the instructions for the dimmer, you can also configure working with classic switches (in switch mode, when each position can and turn off the light, and in the mode, when up - on, down - off.). I liked the default option more, as it is more convenient to adjust the brightness, and there is no need to click the keys once again if the light was suddenly on / off by timer or remotely.
Here is a list of dimmer options available for configuration via the web interface:
- % step adjustment (Default 1)
- time of automatic achievement of extreme values of adjustment (0 - 2.5 seconds). Simply put, how long the chandelier will gain full brightness when turned on, or vice versa.
- maximum level of dimmer adjustment (from 2 to 99%)
- minimum level of dimmer adjustment (from 1 to 98%)
- switch type switch (bell monostable button or classic bistable switch)
- double click option (sets brightness to 100% regardless of the previous value)
- preservation of the previous level of adjustment in case of power loss
The only problem I didn’t know how to solve initially was the through switches in the corridor. But the solution was extremely simple. Dimmer with voice buttons are connected in exactly the same way, i.e. on the one hand, the zero from the lamp is immediately connected to the free wire to the other switch, and on the other hand the phase wire is connected to the same free wire to the first button. Thus, any number of buttons can be connected to the circuit.
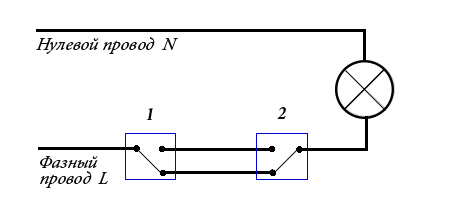
The diagram shows a variant in which one of the buttons is pressed and held.
The relay is not so fun as with a dimmer, because it already requires a neutral to work.
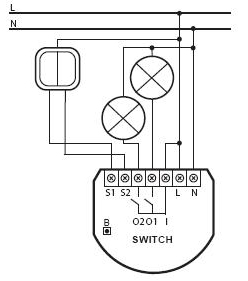
The only place where the adjustment of the light is not so critical, and there is a neutral in place - this is the switch block of the bathroom and the kitchen. Also, in order to save space in the podrozetniki, it was decided to put two relays (1 - light in the bathroom and toilet, 2 - light in the kitchen and a socket under the switches) and two dimmers (fans in the bathroom and toilet).
On the “test” stand with overlapping switches, the skolhozil design again tested and tuned the relay

This block of switches is now in the process of reworking, so I will not say anything more about the operation of devices there.
Scenarios
For example, consider the simplest scenario of switching on the light in the corridor when someone comes home.
I will not consider such nuances as the behavior of certain devices of the system with non-standard actions (take out the garbage and open and close the door just like that) - for this, various parameters are specified in the instructions of the devices used, which are set via the web interface
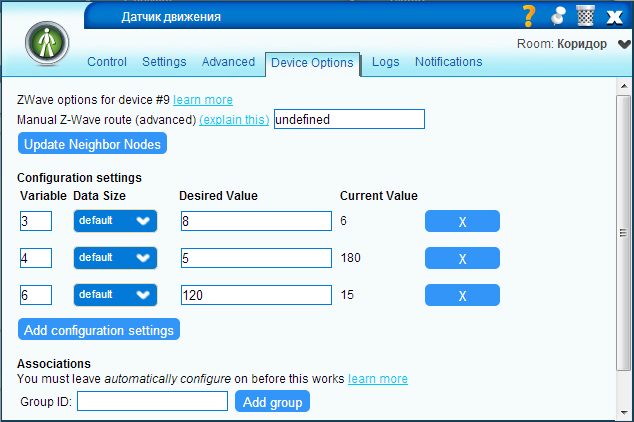
Note: Motion and door opening sensors have two operating modes: Armed and Bypass (in other words, observation and rest).
My script is very simple:
If the door-opening sensor is at rest, then switch the motion sensor to monitoring mode, and if the motion sensor is activated in monitoring mode, turn on the light and switch the motion sensor to rest mode. At the same time, it is necessary to set the re-triggering interval of the door sensor, in order to avoid violations of the script.

The plans are to create automation scenarios in various rooms of an apartment depending on the time of day, room temperature, brightness, and attach their temperature sensors through a special module for the gateway. While all additional equipment is in the process of delivery.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/160493/
All Articles