Work with time in Google
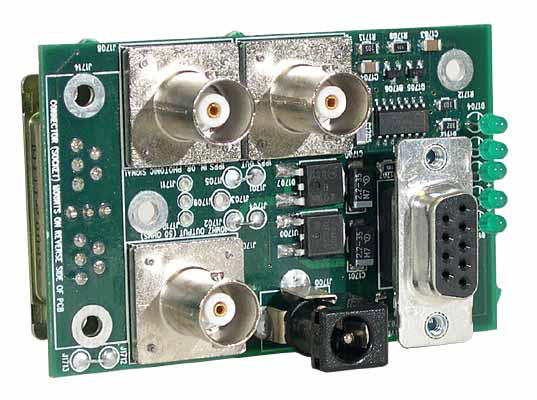
PRS10 High Precision Rubidium Oscillator
Google has decided to abandon the use of NTP (Network Time Protocol) and has created its own time checking system with GPS and atomic clocks, more accurate and reliable. It was called the TrueTime API. The system works to ensure the integrity of the world's largest Google Spanner database, distributed throughout the world.
In mid-September 2012, for the first time, Google released information about its unique database, which is globally distributed across Google data centers on different continents - while ensuring the integrity and synchronization of data. Experts believe that none of the other companies that work with large amounts of data, including Facebook, have anything like this.
As can be seen from a research paper published in September, a key innovation in Google Spanner is to ensure data integrity through a new coding system for transaction time information. Google engineers have developed a multi-level system for checking time, recording transaction time intervals, and assessing the level of time tagging. This is a key factor on which the reliability of the system depends.
')
Typically, data centers and web services rely on NTP (Network Time Protocol) - online services that provide information from atomic clocks, but because of network lags such methods do not provide accuracy that is suitable for a large data center. And sometimes NTP is seriously failing in general, as it happened recently, after adding a leap second .
In general, Google decided to abandon NTP and create its own time checking system, more accurate and reliable. It was called the TrueTime API.
Instead of receiving data from external clocks, Google has equipped data centers with its own atomic clocks and GPS receivers. This equipment is connected to some servers that distribute time stamps to all other servers in the data center. In fact, on each machine in the data center, the daemon runs in the background, which constantly polls the time server in its data center and similar time servers in other data centers. Thus, Google servers all over the world are guaranteed to work on the same time.
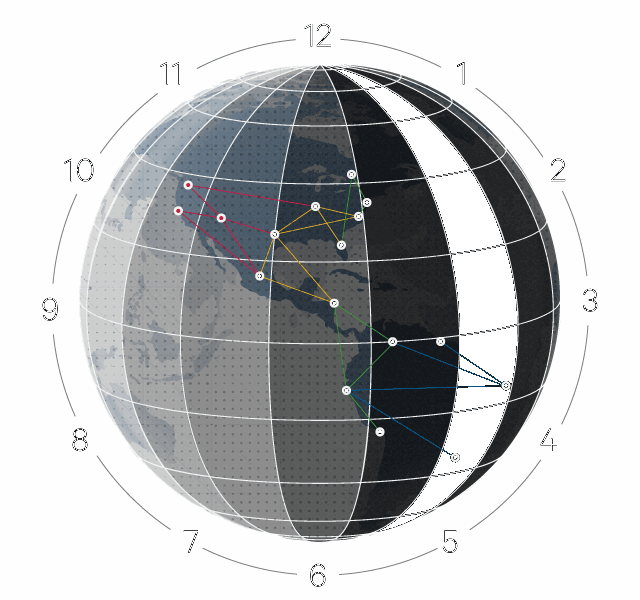
Through the Google TrueTime API, data synchronization is ensured when different data centers attempt to simultaneously write to the same cell in the database. The TrueTime API provides the value of the TTinterval time interval: this is a time with a measured measurement error and uncertainty. If the intervals TTinterval of two competitive transactions do not overlap, then it is safe to say which of them occurred earlier. If they intersect, it means a certain amount of uncertainty.
Google had to install GPS antennas on the roofs of its data centers and an atomic clock inside the server racks at the data centers. The cost of even very good atomic clocks is relatively small compared to the cost of servers in each rack.
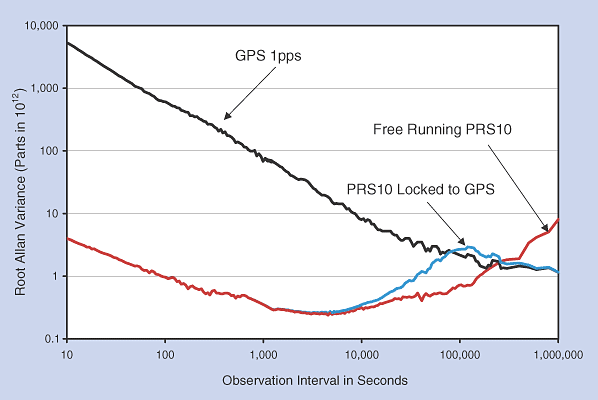
Atomic clocks work for a short time more reliably than GPS, but for a long time they need to be tied to GPS.
[ Source ]
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/160301/
All Articles