Marketing roles in IT companies
Despite the fact that in any self-respecting IT company, as a rule, there is an independent division or individual employees who perform marketing tasks, the question of whether there is a place of marketing as such, and if so, in what manifestation and for what companies (outsourcing, service, grocery), for us still remains open.
Not without an element of easy provocation and an honestly declared desire to hear the opinions of those who know the situation firsthand, we want to bring to your attention a series of articles on marketing of IT products and IT services.
This series is the fruit of joint research and creative work of a team of authors, some of which are experts and practitioners of IT companies, and some are employees of Belarusian universities.
This study began as part of an academic project in 2011. Based on the study and generalization of the experience of a long range of Belarusian IT companies, articles, speeches at conferences and even a new training course for marketing students were prepared.
Currently, the authors want to translate the results of the research from the category of academic and generally relatively closed to the general public to the category of publicly available and possibly useful for practitioners.
We really hope that you will not only like the material, but also prove useful. And we count on objective criticism (or praise).
In the marketing process in the development of IT products or the provision of IT services, we can distinguish (in many respects, of course, arbitrarily) three different levels of marketing in accordance with the range of tasks addressed to them.
In addition, each of the levels includes certain marketing roles performed by employees of an IT company or external marketing companies.
The entire logical structure of this process can be simplifiedly presented in the form of the following scheme:
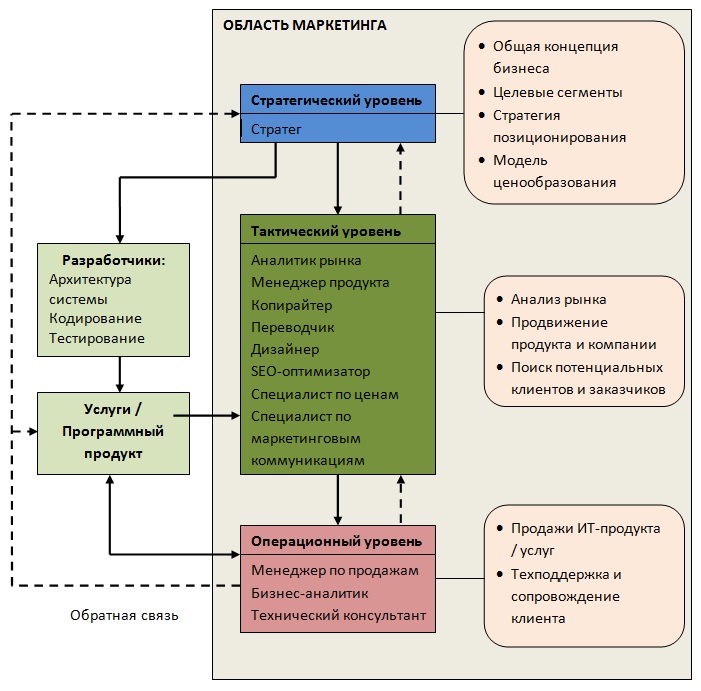
(Remember: like all schemes, this one is no exception and describes the reality of some “average case”!)
Consider the participants of the marketing process inscribed in this scheme and the functions they perform separately.
')
The strategic level is represented by only one, but an important role - “visionary strategist-ideologist” .
The top management of the company fulfills this role, however, employees of the marketing department of an IT company, as well as production personnel (project managers, business analysts, etc.) can take part in the generation of ideas.
According to marketing theory at this level, the overall, competitive and functional development strategies of the company should be determined. In practice, this usually comes down to choosing target markets and forming a long-term high-level plan for releasing a software product (a roadmap, or roadmap) for food companies, or deciding on specialization (technologies used, subject area, types of solutions) for outsourcing companies.
It is here that answers are given to the questions whether the company will work with a certain technology (Java, .Net or another), or is ready to take on everything; whether specialization is expected in a particular subject area (for example, in the banking sector or the tourist services market), or is there no such specialization. Having a clear specialization is a significant plus for an IT company. Of course, you can get a profitable order for development without having experience in this area, but other things being equal, the probability to receive an order will be higher for the company that has already made such decisions and has certain experience.
It also makes a strategic decision on pricing policy for the proposed software products and IT services provided.
The tactical level of marketing in an IT company in a general way solves the problem of promoting a software product on previously selected target markets (for product companies), as well as promoting the company itself as a team of highly qualified and experienced developers and a reliable partner in providing IT services (for outsourcing companies) . At the same level, a database of potential customers interested in purchasing the proposed software product is being formed, its analysis, as well as a search for customers for outsourcing development.
To achieve these objectives, the tactical level of marketing in an IT company must be presented by a number of marketing roles, among which are the market analyst, product manager, copywriter, designer, SEO optimizer, translator, marketer, and price specialist.
Market analyst. The role of the analyst implies conducting systematic studies of target markets, collecting and analyzing information necessary for making both tactical and strategic decisions.
According to the results of the research, the marketing department of an IT company should have quantitative and qualitative indicators characterizing the current state of the market and be aware of its development trends. One of the sections of this study should be the analysis of competitors' price proposals and the study of the functionality of the products they offer.
The second activity of the analyst is to search for potential clients and enter information about them into specialized databases. The best option is to use for these purposes, customer relationship management systems (CRM-systems). At the same time, the information should include not only the contact details of the company, but also an assessment of its business needs, the level of financial support and the importance of this client for the company.
Product manager (product-manager). This role is found only in the grocery company. The product manager analyzes the requirements for the product and draws up production plans, as well as analyzes the business significance of the functional and non-functional characteristics of the product and sets the priority of their development.
An equally important task for the manager is to fix all requests coming from potential and current customers, because This database is an invaluable tool for making development decisions.
Price Specialist. The role of a specialist in prices that an economist or financial expert can perform is reduced to the practical implementation of an IT company pricing policy adopted at a strategic level. In none of the surveyed IT companies, the authors did not meet this role explicitly, i.e. in the form of a separate post with the same or similar name. In principle, “in theory” such a position is not distinguished. On the other hand, a similar task or role is always present.
Such a specialist develops tariffs for the proposed software products and outsourcing services, differentiating them depending on the sales markets, the size and financial status of the client, the accepted business model of sales (sales with installation on the customer’s server or a kind of “rent” of the acquired functional modules (SaaS, software provision as a service) and ultimately making up price lists that sales managers can use.
Copywriter The role of a copywriter in an IT company, as a rule, unites several related specialties around him at once.
First, the actual copywriter , as a person engaged in writing selling texts: numerous brochures, leaflets, booklets, press releases, articles for various media or texts for direct e-mailing, etc.
Secondly, the content manager or person responsible for filling the content and keeping up to date the site of the company and all its grocery sites.
In addition, sometimes a copywriter is entrusted with the functions of a technical writer who is responsible for writing technical documentation for users. Although this is a departure from the classic interpretations of the role of a copywriter, the specificity of a software product as a product sometimes compels to consider such types of purely technical texts as software product user guides, online reference books, instructions, or a list of frequently asked questions (FAQ) as selling texts. .
Translator. Since the main customers of IT services, as well as software products offered by Belarusian developers, are foreign companies from all over the world, the role of translator is of great importance in the marketing of IT services. For example, 80% of software produced in the Belarusian High-Tech Park is exported: 45-48% is supplied to the USA and Canada, 30-31% to Western European countries, 16-20% to Russia and other CIS countries.
Translation of site content and marketing materials is usually carried out only in English or the languages of the main target markets and therefore can be performed by the staff of the marketing department. At the same time, according to the terms of delivery of a software product, it is often necessary to translate all reference materials, user manuals, FAQ and the software itself into the language of the client. In the absence of competent specialists in the company, they use the services of external translators.
Designer. It is difficult to imagine modern marketing without the role of a designer. In an IT company, he will have to solve virtually the same range of tasks as in any other company: to develop a logo and other elements of corporate identity; o graphic design of all advertising and marketing materials; o respond to the design of the company's website; develop the concept of the design of the exhibition stand, etc.
SEO optimizer. For an IT company, like no other, its website is the main business card, which clearly demonstrates to the client the capabilities of the company. It looks somewhat strange if the company-developer offering its IT services to the market (with all the diversity of the latter), its own website looks faded and takes places on the outskirts of search engines. That is why website promotion in the leading search engines is an important marketing task solved by SEO-optimizer. This also includes tasks and other ways to promote the company's products on the Internet: banners, contextual advertising, social media marketing, etc.
Marketing Communications Specialist. The role of a marketing communications specialist involves doing all the work necessary to successfully promote a company and its products in target markets. In fact, the communications specialist unites around him all the other tactical roles and uses their results in his work.
The main functions of such a specialist include: planning and conducting advertising campaigns, including holding presentations and direct mailing, maintaining public relations, preparing the company's participation in the exhibition and some others.
Sometimes within the framework of marketing communications, it makes sense to single out the role of a brand manager who is responsible for the development and promotion of a brand and allocated to an independent full-time unit.
The operational level of IT marketing is all activity directly related to the sale, implementation and maintenance of a software product or IT services to a specific customer for a specific transaction.
The main tasks solved at this level include not only the conclusion of contracts for the sale of a product or the provision of IT services, but also the introduction of the product itself, its timely updating to current versions, the solution of various issues arising during the operation of the system, the further development of the product as your business needs change. These functions can be conditionally distributed among the three main marketing roles: sales manager, business analyst and technical consultant.
Sales Manager. The task of the sales manager is to contact all potential customers, information about which was collected and entered into the CRM-database, in order to conclude a contract for the sale of a software product or the provision of outsourcing services. To solve this problem, the manager prepares and sends business proposals, assigns dates and place of meetings, conducts presentations of the software product and conducts the entire sales process.
In this case, in the case of a large company, it is optimal to divide the sales department into sub-departments (bureau, sector, group), one of which deals, for example, with the first phase of sales (calls and search for potential customers), the other brings together active sales managers (conducting presentations, determination of customer needs, selection of the necessary configuration and execution of the transaction), and the third includes all employees of the customer department, who are transferred to customers for service and re-sales after the first transaction. Their role is played by account managers, project managers or company business analysts.
The role of sales manager in general can be performed by such specialists as business development managers (Business Development), although their functional responsibilities are often much broader.
Business analyst. The role of a business analyst also involves direct communication with the client, but with the goal of formalizing its business requirements and presenting the latter in the form of technical specifications for the development team. The business analyst is deeper than the seller, understands production technology and is often used to evaluate tenders (presales).
The need for business analytics services arises both when approving an order for outsourcing projects and selling finished software products, provided that the client needs to adapt the basic solution to its specific business requirements.
In addition, analyzing private situations in the process of communicating with each client, the business analyst accumulates general information about the needs of the target audience as a whole and thus complements the information collected by the market analyst.
Technical consultant. The technical consultant, whose functions are usually performed by technical support staff, should also be considered as one of the specific roles of the operational level of marketing in the field of IT services.
The technical consultant is responsible for the timely updates of the software product, resolves all the issues that arise for the customer as they are used, advises the customer on the functionality of the product, and thus often acts as a “passive” salesman, identifying the unmet business need of the customer and bringing it to the sales manager .
***
The authors are grateful to Maria Bondarenko, managing partner of GP Solutions GmbH, for valuable critical comments and thoughtful work on the “zero” version of this post.
Not without an element of easy provocation and an honestly declared desire to hear the opinions of those who know the situation firsthand, we want to bring to your attention a series of articles on marketing of IT products and IT services.
This series is the fruit of joint research and creative work of a team of authors, some of which are experts and practitioners of IT companies, and some are employees of Belarusian universities.
This study began as part of an academic project in 2011. Based on the study and generalization of the experience of a long range of Belarusian IT companies, articles, speeches at conferences and even a new training course for marketing students were prepared.
Currently, the authors want to translate the results of the research from the category of academic and generally relatively closed to the general public to the category of publicly available and possibly useful for practitioners.
We really hope that you will not only like the material, but also prove useful. And we count on objective criticism (or praise).
Three levels of marketing
In the marketing process in the development of IT products or the provision of IT services, we can distinguish (in many respects, of course, arbitrarily) three different levels of marketing in accordance with the range of tasks addressed to them.
In addition, each of the levels includes certain marketing roles performed by employees of an IT company or external marketing companies.
The entire logical structure of this process can be simplifiedly presented in the form of the following scheme:

(Remember: like all schemes, this one is no exception and describes the reality of some “average case”!)
Consider the participants of the marketing process inscribed in this scheme and the functions they perform separately.
')
Strategic level: a roadmap for the company
The strategic level is represented by only one, but an important role - “visionary strategist-ideologist” .
The top management of the company fulfills this role, however, employees of the marketing department of an IT company, as well as production personnel (project managers, business analysts, etc.) can take part in the generation of ideas.
According to marketing theory at this level, the overall, competitive and functional development strategies of the company should be determined. In practice, this usually comes down to choosing target markets and forming a long-term high-level plan for releasing a software product (a roadmap, or roadmap) for food companies, or deciding on specialization (technologies used, subject area, types of solutions) for outsourcing companies.
It is here that answers are given to the questions whether the company will work with a certain technology (Java, .Net or another), or is ready to take on everything; whether specialization is expected in a particular subject area (for example, in the banking sector or the tourist services market), or is there no such specialization. Having a clear specialization is a significant plus for an IT company. Of course, you can get a profitable order for development without having experience in this area, but other things being equal, the probability to receive an order will be higher for the company that has already made such decisions and has certain experience.
It also makes a strategic decision on pricing policy for the proposed software products and IT services provided.
Tactical level: market analysis and promotion
The tactical level of marketing in an IT company in a general way solves the problem of promoting a software product on previously selected target markets (for product companies), as well as promoting the company itself as a team of highly qualified and experienced developers and a reliable partner in providing IT services (for outsourcing companies) . At the same level, a database of potential customers interested in purchasing the proposed software product is being formed, its analysis, as well as a search for customers for outsourcing development.
To achieve these objectives, the tactical level of marketing in an IT company must be presented by a number of marketing roles, among which are the market analyst, product manager, copywriter, designer, SEO optimizer, translator, marketer, and price specialist.
Market analyst. The role of the analyst implies conducting systematic studies of target markets, collecting and analyzing information necessary for making both tactical and strategic decisions.
According to the results of the research, the marketing department of an IT company should have quantitative and qualitative indicators characterizing the current state of the market and be aware of its development trends. One of the sections of this study should be the analysis of competitors' price proposals and the study of the functionality of the products they offer.
The second activity of the analyst is to search for potential clients and enter information about them into specialized databases. The best option is to use for these purposes, customer relationship management systems (CRM-systems). At the same time, the information should include not only the contact details of the company, but also an assessment of its business needs, the level of financial support and the importance of this client for the company.
Product manager (product-manager). This role is found only in the grocery company. The product manager analyzes the requirements for the product and draws up production plans, as well as analyzes the business significance of the functional and non-functional characteristics of the product and sets the priority of their development.
An equally important task for the manager is to fix all requests coming from potential and current customers, because This database is an invaluable tool for making development decisions.
Price Specialist. The role of a specialist in prices that an economist or financial expert can perform is reduced to the practical implementation of an IT company pricing policy adopted at a strategic level. In none of the surveyed IT companies, the authors did not meet this role explicitly, i.e. in the form of a separate post with the same or similar name. In principle, “in theory” such a position is not distinguished. On the other hand, a similar task or role is always present.
Such a specialist develops tariffs for the proposed software products and outsourcing services, differentiating them depending on the sales markets, the size and financial status of the client, the accepted business model of sales (sales with installation on the customer’s server or a kind of “rent” of the acquired functional modules (SaaS, software provision as a service) and ultimately making up price lists that sales managers can use.
Copywriter The role of a copywriter in an IT company, as a rule, unites several related specialties around him at once.
First, the actual copywriter , as a person engaged in writing selling texts: numerous brochures, leaflets, booklets, press releases, articles for various media or texts for direct e-mailing, etc.
Secondly, the content manager or person responsible for filling the content and keeping up to date the site of the company and all its grocery sites.
In addition, sometimes a copywriter is entrusted with the functions of a technical writer who is responsible for writing technical documentation for users. Although this is a departure from the classic interpretations of the role of a copywriter, the specificity of a software product as a product sometimes compels to consider such types of purely technical texts as software product user guides, online reference books, instructions, or a list of frequently asked questions (FAQ) as selling texts. .
Translator. Since the main customers of IT services, as well as software products offered by Belarusian developers, are foreign companies from all over the world, the role of translator is of great importance in the marketing of IT services. For example, 80% of software produced in the Belarusian High-Tech Park is exported: 45-48% is supplied to the USA and Canada, 30-31% to Western European countries, 16-20% to Russia and other CIS countries.
Translation of site content and marketing materials is usually carried out only in English or the languages of the main target markets and therefore can be performed by the staff of the marketing department. At the same time, according to the terms of delivery of a software product, it is often necessary to translate all reference materials, user manuals, FAQ and the software itself into the language of the client. In the absence of competent specialists in the company, they use the services of external translators.
Designer. It is difficult to imagine modern marketing without the role of a designer. In an IT company, he will have to solve virtually the same range of tasks as in any other company: to develop a logo and other elements of corporate identity; o graphic design of all advertising and marketing materials; o respond to the design of the company's website; develop the concept of the design of the exhibition stand, etc.
SEO optimizer. For an IT company, like no other, its website is the main business card, which clearly demonstrates to the client the capabilities of the company. It looks somewhat strange if the company-developer offering its IT services to the market (with all the diversity of the latter), its own website looks faded and takes places on the outskirts of search engines. That is why website promotion in the leading search engines is an important marketing task solved by SEO-optimizer. This also includes tasks and other ways to promote the company's products on the Internet: banners, contextual advertising, social media marketing, etc.
Marketing Communications Specialist. The role of a marketing communications specialist involves doing all the work necessary to successfully promote a company and its products in target markets. In fact, the communications specialist unites around him all the other tactical roles and uses their results in his work.
The main functions of such a specialist include: planning and conducting advertising campaigns, including holding presentations and direct mailing, maintaining public relations, preparing the company's participation in the exhibition and some others.
Sometimes within the framework of marketing communications, it makes sense to single out the role of a brand manager who is responsible for the development and promotion of a brand and allocated to an independent full-time unit.
Operational level: sales and transaction support
The operational level of IT marketing is all activity directly related to the sale, implementation and maintenance of a software product or IT services to a specific customer for a specific transaction.
The main tasks solved at this level include not only the conclusion of contracts for the sale of a product or the provision of IT services, but also the introduction of the product itself, its timely updating to current versions, the solution of various issues arising during the operation of the system, the further development of the product as your business needs change. These functions can be conditionally distributed among the three main marketing roles: sales manager, business analyst and technical consultant.
Sales Manager. The task of the sales manager is to contact all potential customers, information about which was collected and entered into the CRM-database, in order to conclude a contract for the sale of a software product or the provision of outsourcing services. To solve this problem, the manager prepares and sends business proposals, assigns dates and place of meetings, conducts presentations of the software product and conducts the entire sales process.
In this case, in the case of a large company, it is optimal to divide the sales department into sub-departments (bureau, sector, group), one of which deals, for example, with the first phase of sales (calls and search for potential customers), the other brings together active sales managers (conducting presentations, determination of customer needs, selection of the necessary configuration and execution of the transaction), and the third includes all employees of the customer department, who are transferred to customers for service and re-sales after the first transaction. Their role is played by account managers, project managers or company business analysts.
The role of sales manager in general can be performed by such specialists as business development managers (Business Development), although their functional responsibilities are often much broader.
Business analyst. The role of a business analyst also involves direct communication with the client, but with the goal of formalizing its business requirements and presenting the latter in the form of technical specifications for the development team. The business analyst is deeper than the seller, understands production technology and is often used to evaluate tenders (presales).
The need for business analytics services arises both when approving an order for outsourcing projects and selling finished software products, provided that the client needs to adapt the basic solution to its specific business requirements.
In addition, analyzing private situations in the process of communicating with each client, the business analyst accumulates general information about the needs of the target audience as a whole and thus complements the information collected by the market analyst.
Technical consultant. The technical consultant, whose functions are usually performed by technical support staff, should also be considered as one of the specific roles of the operational level of marketing in the field of IT services.
The technical consultant is responsible for the timely updates of the software product, resolves all the issues that arise for the customer as they are used, advises the customer on the functionality of the product, and thus often acts as a “passive” salesman, identifying the unmet business need of the customer and bringing it to the sales manager .
***
The authors are grateful to Maria Bondarenko, managing partner of GP Solutions GmbH, for valuable critical comments and thoughtful work on the “zero” version of this post.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/160071/
All Articles