Opportunity - forgotten record
Behind the hype around the phenomenal landing of the Curiosity rover, many have forgotten that its predecessor does not stop working there. Twin rovers Spirit and Opportunity ("Spirit" and "Opportunity") landed on Mars in the distant 2004. Their creators counted on 90 Martian days (solos) of work, but they surpassed their resource dozens of times. The connection with “Spirit” has already been lost, but “Opportunity” continues its work away from annoying journalists who wind around “Curiosity”. But not in oblivion!
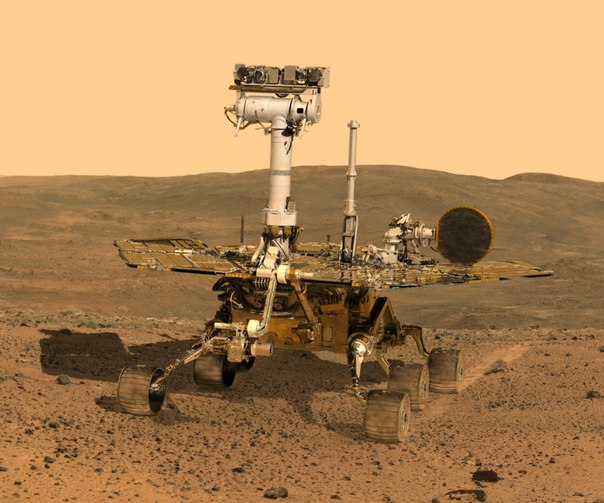

Opportunity visualization © Nick Sotiriadis 2011
Opportunity continues to work for more than 3,120 solos. He set a new record for the work of the product of human hands on the surface of Mars. The previous record belonged to the stationary Land Viking-1, which transmitted information to 2,245 soloes. Opportunity mileage exceeds 35 kilometers and it continues, with its inherent slowness, to approach the next record - the distance covered by the surface of a human apparatus outside the Earth. The record was set back in 1973 - Lunokhod-2 traveled exactly 37 kilometers. A couple hundred meters separates the Opportunity from the American record, which set the Moonbuggy of Apollo 17 - 35.89 km. The wind is blowing, the sun is shining, the wheels are spinning, and for now there is no reason to fear that both records will not be taken.
')
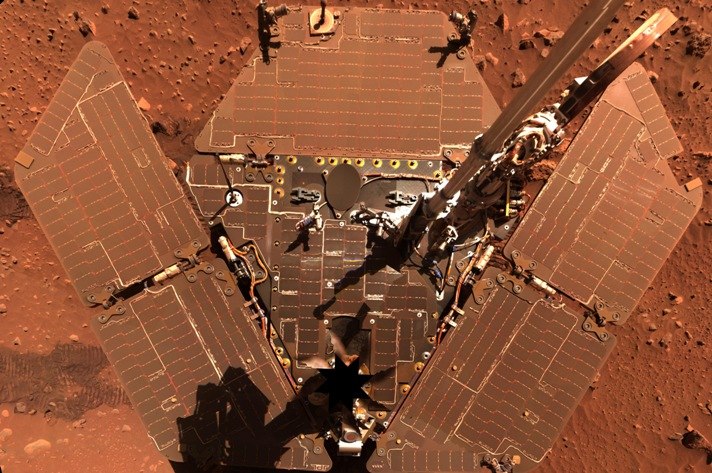

About the wind - this is a separate story. Mars rovers chose a short century because of the dustiness of solar panels. But Mars presented a gift to NASA in the form of short-term storms and frequent tornadoes - sand demons (dust devils). Together they set about cleaning the solar panels of the rovers and they rushed to the unplanned conquest of Mars.

The reason why interest in Opportunity has practically disappeared is that in the previous three years he was simply moving toward a new goal of his research. After exploring the interesting crater Victoria, there were no targets left for him nearby, and he went to the 19-km marathon along the Meridian Plateau, which he had already thoroughly studied. Three years without news and discoveries - then anyone will be forgotten.
But he has a promising goal - the crater Endeavor. When the rover just landed, its main goal was to find evidence of the existence of periods in the history of Mars when the planet had liquid water and free water. The first months of research have shown that there is the whole desert in this evidence - hematite globules.

This is a kind of iron ore, which is formed at the bottom of shallow reservoirs. But the prospects for the Martian life, this discovery did not promise. In addition to hematite, called "blueberries", the soil had a high content of sulphates - substances that form in a very acidic aqueous medium. Some terrestrial extremophiles can survive in such an environment, but in such water, life does not self-organize (NASA does not seriously consider options for a non-carbon life form and does not deal with searches).
On the other hand, observations of the CRISM satellite spectrometer showed that phyllosilicates, olivine-pyroxene clays, can be deeper.
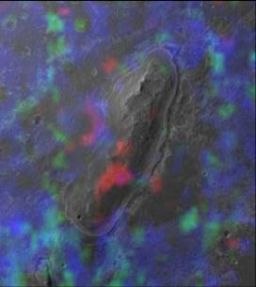
Cape York Hill. Red color - phyllosilicates, blue - sulfates.
The conditions of their formation are much more comfortable for life, the more they can save the remnants of representatives of the ancient fauna much better. Olivine and pyroxene are volcanic rocks that are practically ubiquitous on Mars. To get phyllosilicate you just need to add water. But such clays are very rare for the surface of Mars. Here we come to explaining why the Endeavor crater is interesting.
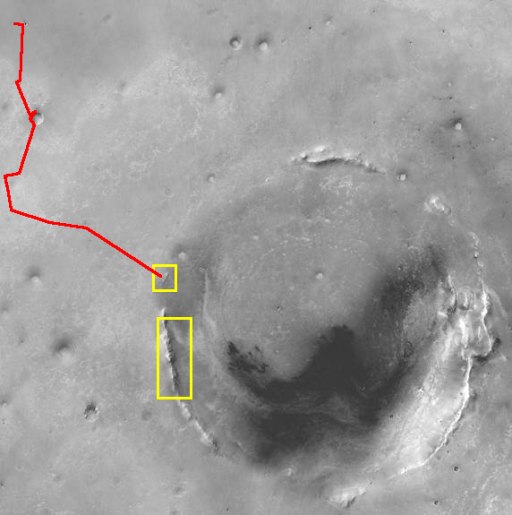
This is a very ancient 22 km crater - it is more than a billion years old. At a later time, when the plain was formed, it was sucked in with sulphates and hematite, as well as the entire plateau of Meridiani. But there were ring shafts! The impact of the meteorite lifted the edges of the crater over the surrounding landscape, revealing ancient layers. According to NASA, rocks that are much older than the surrounding plateaus, including the desired clays, can be found in them. Therefore, Opportunity embarked on a long journey, which diversified only small craters, but meteorites coming across.
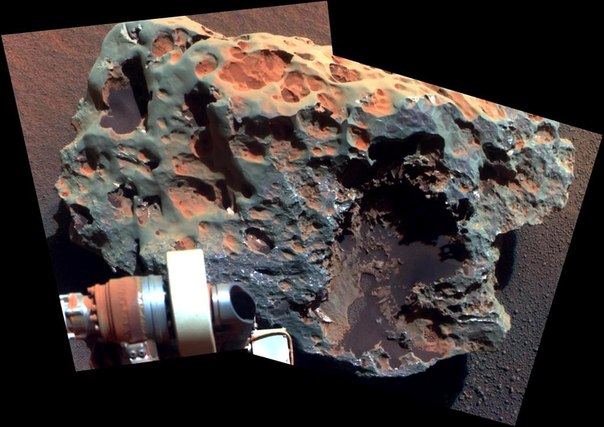

In the summer of 2011, he finally arrived at the first elevation related to the ring shaft of the crater. In fact, his second life began, as there was an object ahead that was geologically different from everything that the rover had encountered before. Tasks have changed: now, like Curiosity, the rover is looking for evidence of geological periods that were good for life. NASA representatives compared the arrival to the crater with the second landing.

The oblong hill from which they decided to begin exploring the crater was called Cape York. As soon as Opportunity approached him, discoveries began. At the foot of the hill there was a gypsum vein. This was another proof of the water past of Mars, but it was still not the kind of water that NASA would have liked, and carbon life forms.

Phyllosilicates were waiting at the top, but it should still be reached. But the ascent had to be postponed for six months - it was wintering time. Rover, though metallic, but much of the animal is not alien to him. At night, he sleeps to save energy, and uses it only for heating. In winter, almost all the energy goes to heating and the rover is immobilized during the entire cold season. It is placed at an optimum angle to the winter sun and it hibernates.
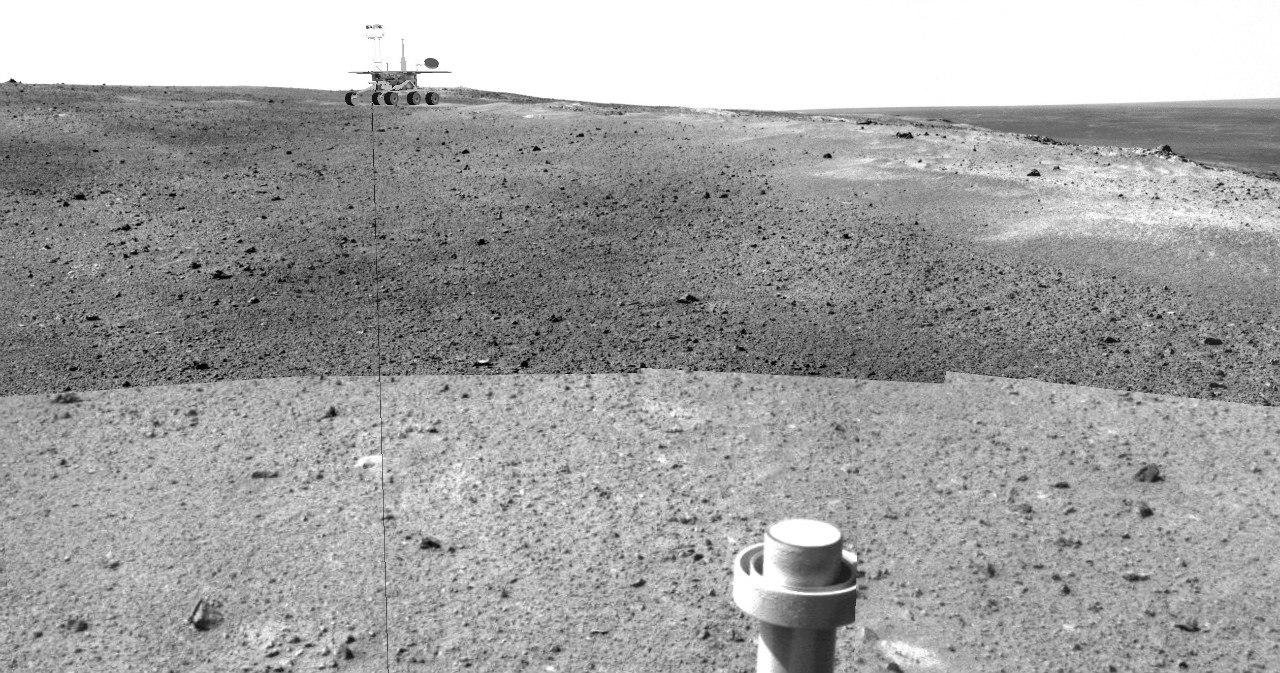

From January to May 2012, he did not move, but he took off and passed on a full color 360-degree panorama of the place, called Greeley Haven. In August, after the landing of Curiosity, this panorama dispersed on social networks, and often attributed authorship to a novice.
In the summer, Opportunity continued bypassing Cape York, and began climbing in September.
And almost immediately came across a sensation.
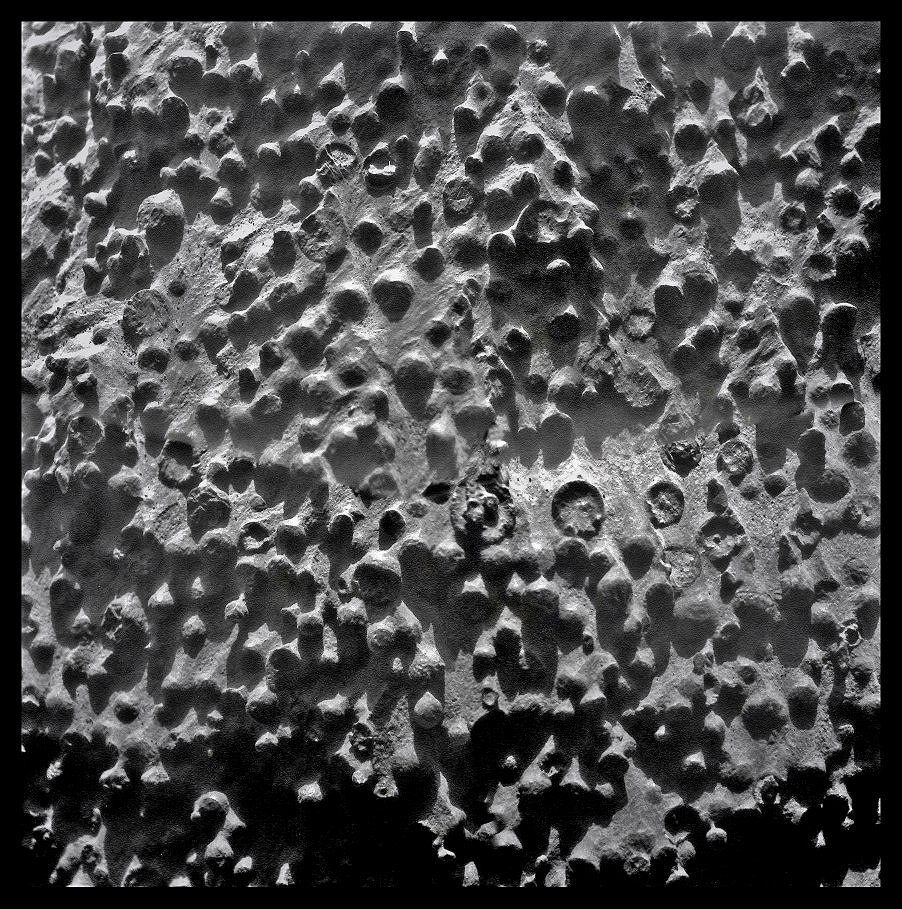

Exposure "Kirkwood" baffled scientists. Analysis of the breed showed a low iron content, so this "grape" is not at all the "blueberry" which is covered with the whole desert. The balls enclosed in the rock have a heterogeneous structure, they have hard shells and soft filler. But what is NASA is not defined. According to the working version, this is a result of volcanic activity - the structure of the "shell" resembles volcanic glass. It can also be the result of an impact impact - from the explosion that gave rise to the entire crater.
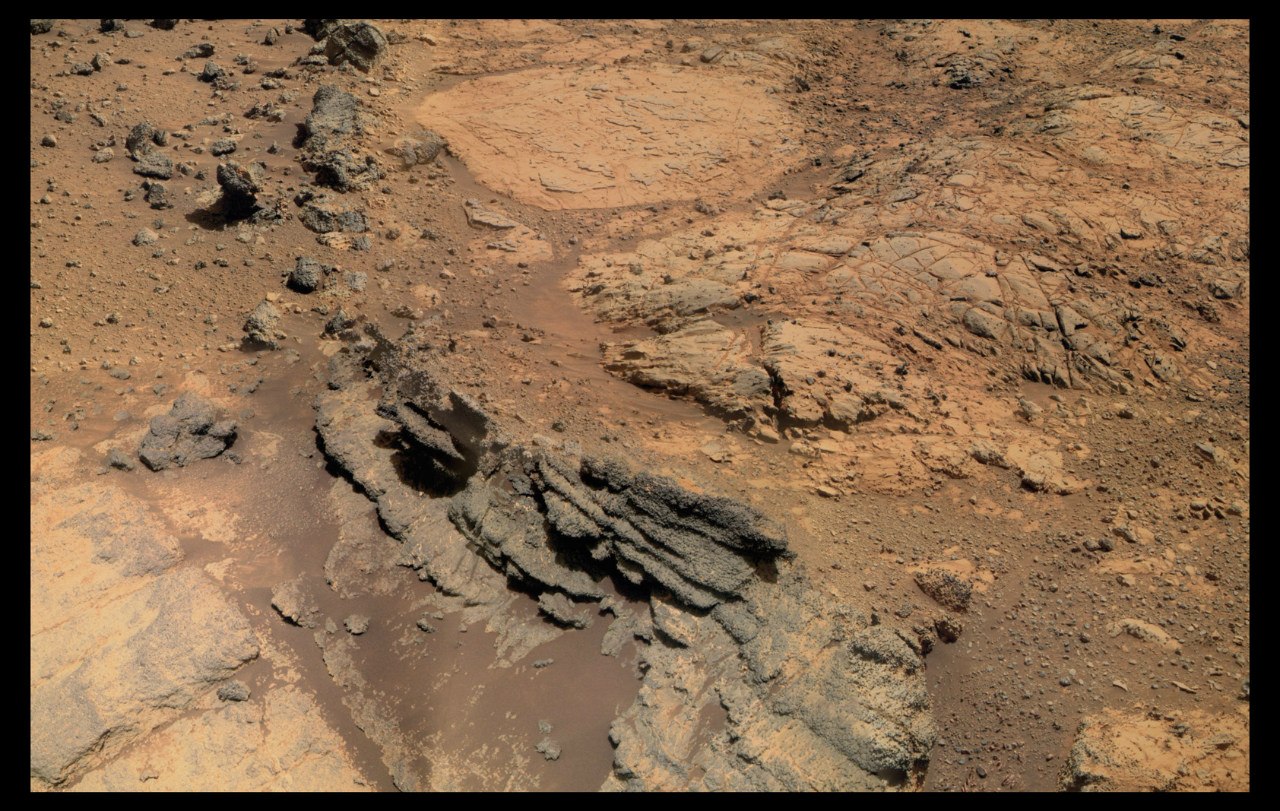

The upper part of Cape York was named Holm Matievich, in memory of Jake Matievich - an engineer who worked on all NASA rovers. The study of the hill Matievich began in October and continues to this day. Since there are many outcrops of rocks on it, it was decided to go around it in a circle studying each stone, so as to make the most detailed geological picture of the place.
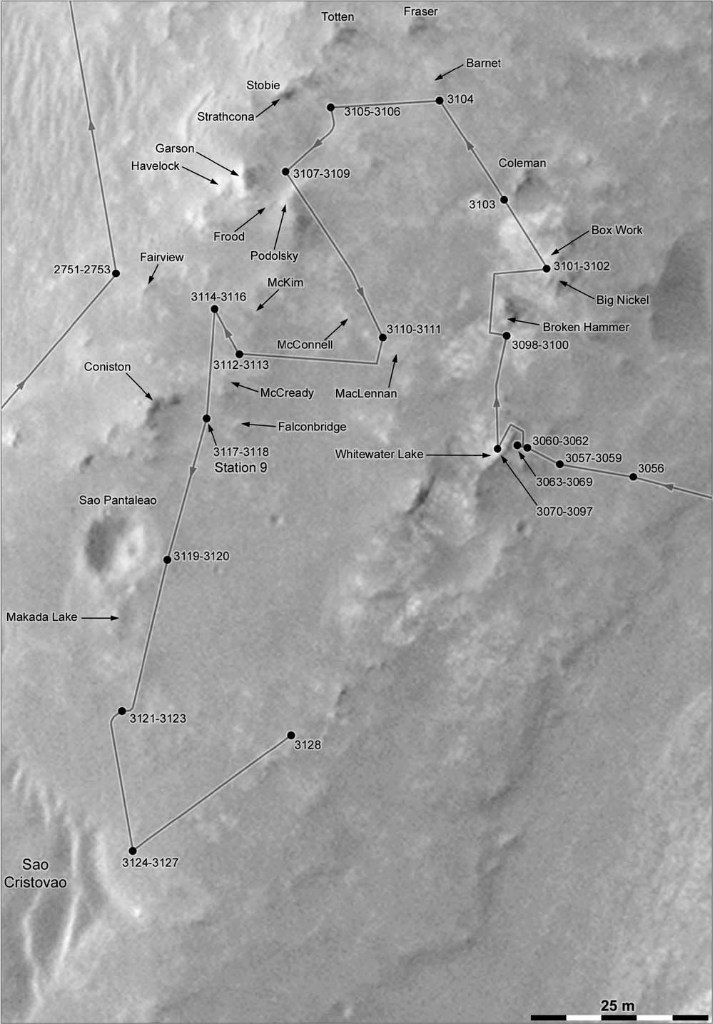
Map © Phil Stooke
NASA stretches pleasure, and consistently examines all oncoming stones, resisting the temptation to rush immediately to the deposits of phyllosilicates. On the hill and without them lack of interesting. For example, studying satellite images, one can notice geometrically regular figures that on Earth, most likely, would have turned out to be some kind of archaeological monument.
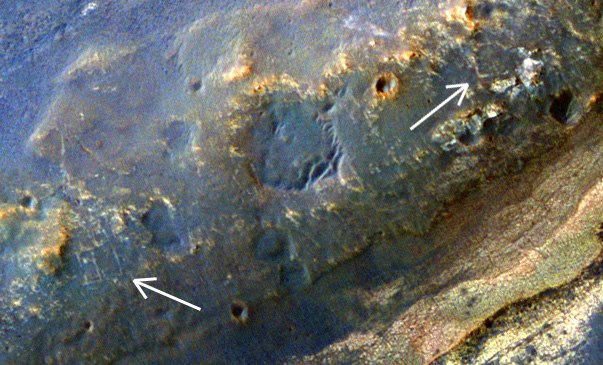
But NASA has no full-time archaeologists, so they provide a geological explanation for such structures. They are called "boxwork", they can be both multimeter scale and centimeter. Such as times were found where a large “boxwork” was seen from the satellite.
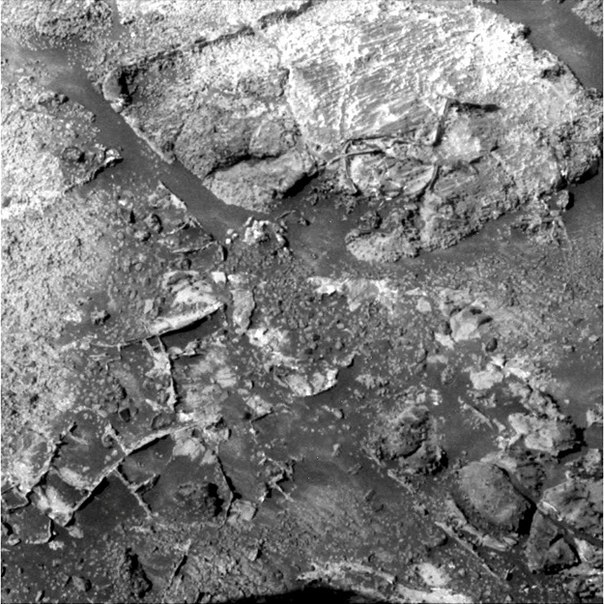

Their origin is explained by the crystallization of salt in the silt of a drying reservoir. For example, the usual NaCl salt has a cubic form of crystals, so they are arranged in rectangular structures. On Earth, a similar effect can be observed on drying salt lakes, such as the famous Groom Lake.
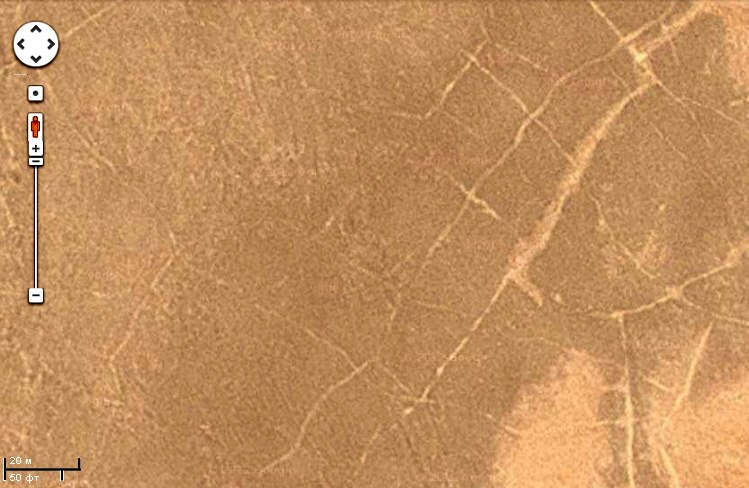

However, it may be calcite, which under the action of water filled cracks in some rock, and then it collapsed due to erosion.
The NASA team says it will go to the phyllosilicate deposits only after it closes the ring around the Matievich hill.

For today the mars rover has problems with the engine of the right wheel; the arm of the manipulator is broken, because of which it is impossible to move the “arm” to the marching position; one heater is faulty; Batteries produce approximately half the energy from the level at the time of landing. But the rover operators are optimistic and are ready to please us more than once with great discoveries that can compete with the results of Curiosity.

Part of the photos borrowed from the Vkontakte group the Best from Mars .
Part of the blog www.planetary.org/blogs/emily-lakdawalla

Opportunity visualization © Nick Sotiriadis 2011
Opportunity continues to work for more than 3,120 solos. He set a new record for the work of the product of human hands on the surface of Mars. The previous record belonged to the stationary Land Viking-1, which transmitted information to 2,245 soloes. Opportunity mileage exceeds 35 kilometers and it continues, with its inherent slowness, to approach the next record - the distance covered by the surface of a human apparatus outside the Earth. The record was set back in 1973 - Lunokhod-2 traveled exactly 37 kilometers. A couple hundred meters separates the Opportunity from the American record, which set the Moonbuggy of Apollo 17 - 35.89 km. The wind is blowing, the sun is shining, the wheels are spinning, and for now there is no reason to fear that both records will not be taken.
')

About the wind - this is a separate story. Mars rovers chose a short century because of the dustiness of solar panels. But Mars presented a gift to NASA in the form of short-term storms and frequent tornadoes - sand demons (dust devils). Together they set about cleaning the solar panels of the rovers and they rushed to the unplanned conquest of Mars.

The reason why interest in Opportunity has practically disappeared is that in the previous three years he was simply moving toward a new goal of his research. After exploring the interesting crater Victoria, there were no targets left for him nearby, and he went to the 19-km marathon along the Meridian Plateau, which he had already thoroughly studied. Three years without news and discoveries - then anyone will be forgotten.

But he has a promising goal - the crater Endeavor. When the rover just landed, its main goal was to find evidence of the existence of periods in the history of Mars when the planet had liquid water and free water. The first months of research have shown that there is the whole desert in this evidence - hematite globules.

This is a kind of iron ore, which is formed at the bottom of shallow reservoirs. But the prospects for the Martian life, this discovery did not promise. In addition to hematite, called "blueberries", the soil had a high content of sulphates - substances that form in a very acidic aqueous medium. Some terrestrial extremophiles can survive in such an environment, but in such water, life does not self-organize (NASA does not seriously consider options for a non-carbon life form and does not deal with searches).
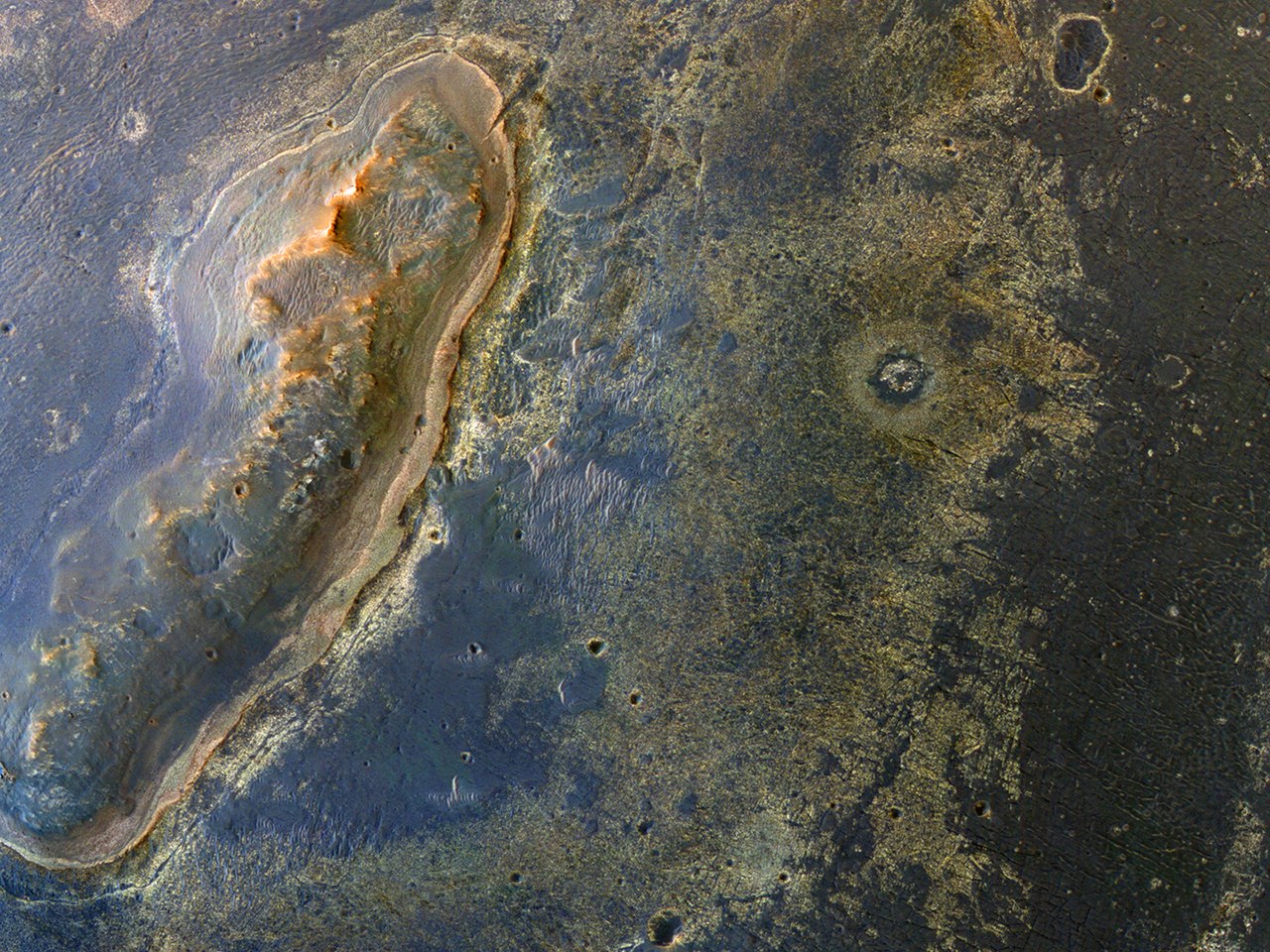
On the other hand, observations of the CRISM satellite spectrometer showed that phyllosilicates, olivine-pyroxene clays, can be deeper.

Cape York Hill. Red color - phyllosilicates, blue - sulfates.
The conditions of their formation are much more comfortable for life, the more they can save the remnants of representatives of the ancient fauna much better. Olivine and pyroxene are volcanic rocks that are practically ubiquitous on Mars. To get phyllosilicate you just need to add water. But such clays are very rare for the surface of Mars. Here we come to explaining why the Endeavor crater is interesting.

This is a very ancient 22 km crater - it is more than a billion years old. At a later time, when the plain was formed, it was sucked in with sulphates and hematite, as well as the entire plateau of Meridiani. But there were ring shafts! The impact of the meteorite lifted the edges of the crater over the surrounding landscape, revealing ancient layers. According to NASA, rocks that are much older than the surrounding plateaus, including the desired clays, can be found in them. Therefore, Opportunity embarked on a long journey, which diversified only small craters, but meteorites coming across.

In the summer of 2011, he finally arrived at the first elevation related to the ring shaft of the crater. In fact, his second life began, as there was an object ahead that was geologically different from everything that the rover had encountered before. Tasks have changed: now, like Curiosity, the rover is looking for evidence of geological periods that were good for life. NASA representatives compared the arrival to the crater with the second landing.

The oblong hill from which they decided to begin exploring the crater was called Cape York. As soon as Opportunity approached him, discoveries began. At the foot of the hill there was a gypsum vein. This was another proof of the water past of Mars, but it was still not the kind of water that NASA would have liked, and carbon life forms.

Phyllosilicates were waiting at the top, but it should still be reached. But the ascent had to be postponed for six months - it was wintering time. Rover, though metallic, but much of the animal is not alien to him. At night, he sleeps to save energy, and uses it only for heating. In winter, almost all the energy goes to heating and the rover is immobilized during the entire cold season. It is placed at an optimum angle to the winter sun and it hibernates.

From January to May 2012, he did not move, but he took off and passed on a full color 360-degree panorama of the place, called Greeley Haven. In August, after the landing of Curiosity, this panorama dispersed on social networks, and often attributed authorship to a novice.
In the summer, Opportunity continued bypassing Cape York, and began climbing in September.
And almost immediately came across a sensation.

Exposure "Kirkwood" baffled scientists. Analysis of the breed showed a low iron content, so this "grape" is not at all the "blueberry" which is covered with the whole desert. The balls enclosed in the rock have a heterogeneous structure, they have hard shells and soft filler. But what is NASA is not defined. According to the working version, this is a result of volcanic activity - the structure of the "shell" resembles volcanic glass. It can also be the result of an impact impact - from the explosion that gave rise to the entire crater.

The upper part of Cape York was named Holm Matievich, in memory of Jake Matievich - an engineer who worked on all NASA rovers. The study of the hill Matievich began in October and continues to this day. Since there are many outcrops of rocks on it, it was decided to go around it in a circle studying each stone, so as to make the most detailed geological picture of the place.

Map © Phil Stooke
NASA stretches pleasure, and consistently examines all oncoming stones, resisting the temptation to rush immediately to the deposits of phyllosilicates. On the hill and without them lack of interesting. For example, studying satellite images, one can notice geometrically regular figures that on Earth, most likely, would have turned out to be some kind of archaeological monument.

But NASA has no full-time archaeologists, so they provide a geological explanation for such structures. They are called "boxwork", they can be both multimeter scale and centimeter. Such as times were found where a large “boxwork” was seen from the satellite.

Their origin is explained by the crystallization of salt in the silt of a drying reservoir. For example, the usual NaCl salt has a cubic form of crystals, so they are arranged in rectangular structures. On Earth, a similar effect can be observed on drying salt lakes, such as the famous Groom Lake.

However, it may be calcite, which under the action of water filled cracks in some rock, and then it collapsed due to erosion.
The NASA team says it will go to the phyllosilicate deposits only after it closes the ring around the Matievich hill.

For today the mars rover has problems with the engine of the right wheel; the arm of the manipulator is broken, because of which it is impossible to move the “arm” to the marching position; one heater is faulty; Batteries produce approximately half the energy from the level at the time of landing. But the rover operators are optimistic and are ready to please us more than once with great discoveries that can compete with the results of Curiosity.

Part of the photos borrowed from the Vkontakte group the Best from Mars .
Part of the blog www.planetary.org/blogs/emily-lakdawalla
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/158565/
All Articles