Radio Wave Theory: Analog Modulation

We continue a series of educational articles, under the general title "Theory of Radio Waves."
In previous articles, we met with radio waves and antennas:
Let's take a closer look at the modulation of the radio signal.
Within this article, analog modulation of the following types will be considered:
- Amplitude modulation
- Amplitude modulation with one sideband
- Frequency modulation
- Linear frequency modulation
- Phase modulation
- Differential phase modulation
')
Amplitude modulation
With amplitude modulation, the envelope of the amplitudes of the carrier wave varies according to the law, which coincides with the law of the transmitted message. The frequency and phase of the carrier oscillation does not change.

One of the main parameters of AM is the modulation coefficient (M).
The modulation factor is the ratio of the difference between the maximum and minimum amplitudes of the modulated signal to the sum of these values (%).
Simply put, this coefficient shows how strongly the value of the amplitude of the carrier oscillation currently deviates from the average value.
When the modulation factor is greater than 1, an overmodulation effect occurs, resulting in distortion of the signal.
AM spectrum

This spectrum is peculiar to modulating oscillations of constant frequency.
The graph, along the X axis, represents the frequency, along the Y axis, the amplitude.
For AM, in addition to the amplitude of the fundamental frequency located in the center, the amplitudes are also presented to the right and left of the carrier frequency. These are the so-called left and right sidebands. They are related to the carrier frequency at a distance equal to the modulation frequency.
The distance from the left to the right sideband is called the width of the spectrum .
In the normal case, with a modulation factor of <= 1, the amplitudes of the sidebands are less than or equal to half the amplitude of the carrier.
Useful information is only in the upper or lower sidebands of the spectrum. The main spectral component - carrier, does not carry useful information. The transmitter power with amplitude modulation is mostly spent on “air heating”, due to the non-informativeness of the most basic element of the spectrum.
Amplitude modulation with one sideband
Due to the inefficiency of classical amplitude modulation, amplitude modulation with a single sideband was invented.
Its essence is to remove from the spectrum of the carrier and one of the sidebands, with all the necessary information is transmitted over the remaining sideband.
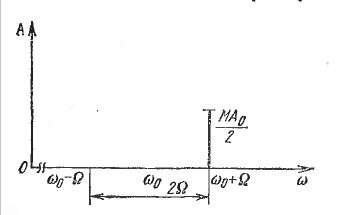
But in its pure form in domestic broadcasting, this species did not take root, because in the receiver you need to synthesize the carrier with very high accuracy. Used in compaction equipment and amateur radio.
Broadcasting often uses AM with one sideband and partially suppressed carrier:
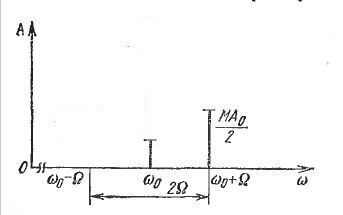
With this modulation, the quality / efficiency ratio is best achieved.
Frequency modulation
A type of analog modulation in which the carrier frequency changes according to the law of the modulating low-frequency signal. The amplitude remains constant.
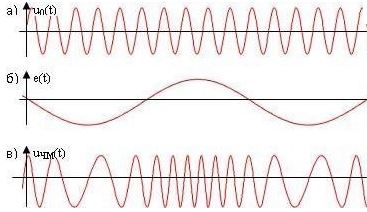
a) - carrier frequency, b) modulating signal, c) modulation result
The largest frequency deviation from the mean is called the deviation .
Ideally, the deviation should be directly proportional to the amplitude of the modulating oscillation.
Spectrum with frequency modulation is as follows:

Consists of a carrier and symmetrically lagging behind it to the right and left of the harmonics of the side bands, a frequency multiple of the frequency of the modulating oscillation.
This spectrum represents harmonic oscillation. In the case of real modulation, the spectrum has more complex outlines.
There are broadband and narrowband FM modulation.
In broadband - the frequency spectrum significantly exceeds the frequency of the modulating signal. Used in FM broadcasting.
Radio stations mainly use narrowband FM modulation, which requires more precise tuning of the receiver and, accordingly, is more protected from interference.
Spectra of broadband and narrowband FM are shown below.
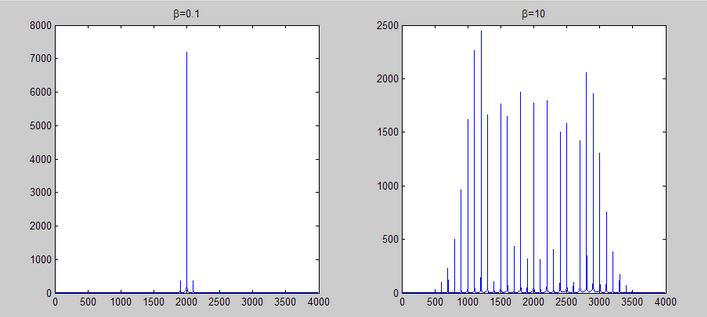
The narrowband FM spectrum resembles amplitude modulation, but if we consider the phase of the sidebands, it turns out that these waves have a constant amplitude and a variable frequency, and not a constant frequency and variable amplitude (AM). With broadband FM, the carrier amplitude can be very small, which causes high efficiency of the FM; This means that most of the transmitted energy is contained in side frequencies that carry information.
The main advantages of the FM, before AM - energy efficiency and noise immunity.
As a kind of FM, emit linear frequency modulation.
Its essence lies in the fact that the frequency of the carrier signal varies linearly.
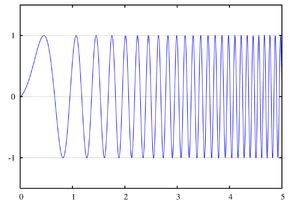
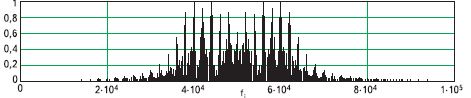
The practical significance of linear-frequency-modulated (chirp) signals is the possibility of significant compression of the signal when received with an increase in its amplitude above the noise level.
Chirp are used in radar.
Phase modulation
In reality, the term phase shift keying is more commonly used. mainly produce modulation of discrete signals.
The meaning of the FM is that the phase of the carrier, changes in steps, with the arrival of the next discrete signal that is different from the previous one.
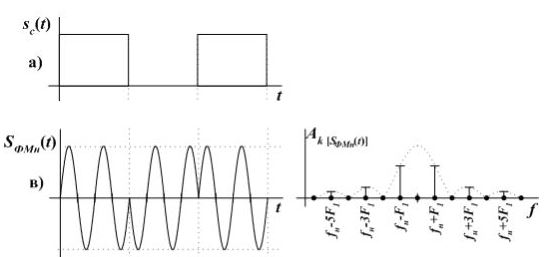
From the spectrum you can see the almost complete absence of carrier, which indicate high energy efficiency.
The disadvantage of this modulation is that an error in one symbol can lead to incorrect reception of all subsequent ones.
Differential phase shift keying
In the case of this modulation, the phase does not change with each change in the value of the modulating pulse, but with a change in the difference. In this example, the arrival of each "1".
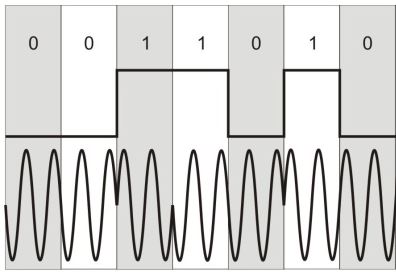
The advantage of this type of modulation is that in the event of a random error in one symbol, this does not entail a further chain of errors.
It is worth noting that there are also phase manipulations such as quadrature, where a phase change within 90 degrees is used and higher order FMs, but their consideration is beyond the scope of this article.
PS: I want to note once again that the purpose of the articles is not to replace the textbook, but to tell “on the fingers” about the basics of radio.
Only the main types of modulations are considered to create an idea of the topic for the reader.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/158493/
All Articles