Theory of radio waves: educational program
I think everyone turned the knob of the radio, switching between "VHF", "DV", "SV" and heard a hiss from the speakers.
But apart from decrypting abbreviations, not everyone understands what lies behind these letters.
Let's take a closer look at the theory of radio waves.
Radio wave

')
Wavelength (λ) is the distance between adjacent wave crests.
Amplitude (a) is the maximum deviation from the average value during oscillatory motion.
Period (T) - the time of one full oscillatory movement
Frequency (v) - the number of full periods per second
There is a formula that allows you to determine the wavelength by frequency:

Where: wavelength (m) is equal to the ratio of the speed of light (km / h) to frequency (kHz)
"VHF", "DV", "SV"
Superlong waves — v = 3–30 kHz (λ = 10–100 km).
They have the ability to penetrate deep into the water column up to 20 m and are therefore used to communicate with submarines, and the boat does not have to float to this depth, just throw the radio buoy up to this level.
These waves can propagate up to the rounding of the earth, the distance between the earth's surface and the ionosphere, represents for them the "waveguide" over which they freely propagate.
Long wavelengths (DW) v = 150–450 kHz (λ = 2000–670 m).

This type of radio wave has the property to go around obstacles, it is used for communication over long distances. It also has a weak penetrating power, so if you do not have a remote antenna, you can hardly catch any radio station.
Medium waves (SW) v = 500–1600 kHz (λ = 600–190 m).

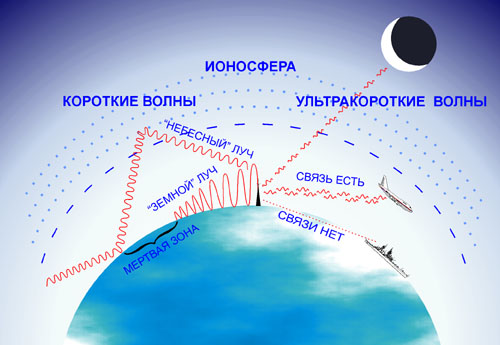
These radio waves are well reflected from the ionosphere, located at a distance of 100-450 km above the earth's surface. The feature of these waves is that during the daytime they are absorbed by the ionosphere and the reflection effect does not occur. This effect is used practically for communication, usually for several hundred kilometers at night.
Short waves (CV) v = 3–30 MHz (λ = 100–10 m).

Like average waves, they are well reflected from the ionosphere, but unlike them, regardless of the time of day. They can spread over long distances (several thousand km) due to re-reflections from the ionosphere and the surface of the earth, such a propagation is called jump. High power transmitters are not required for this.
Ultrashort Waves (VHF) v = 30 MHz - 300 MHz (λ = 10—1 m).

These waves can go around obstacles of several meters in size, and also have good penetrating power. Due to such properties, this range is widely used for radio broadcasts. The disadvantage is their relatively fast attenuation when encountering obstacles.
There is a formula that allows you to calculate the communication range in the VHF range:

So, for example, when transmitting radio from the Ostankino television tower with a height of 500 m to a receiving antenna with a height of 10 m, the communication range under the condition of direct visibility will be about 100 km.
High frequencies (RF centimeter range) v = 300 MHz - 3 GHz (λ = 1—0.1 m).
Do not go around obstacles and have good penetrating power. Used in cellular networks and wi-fi networks.
Another interesting feature of the waves of this range is that water molecules are able to absorb their energy as much as possible and convert it into heat. This effect is used in microwave ovens.
As you can see, wi-fi equipment and microwaves work in the same range and can affect the water, so sleeping in an embrace with a wi-fi router is not worth it for a long time.
Extremely high frequencies (EHF-millimeter range) v = 3 GHz - 30 GHz (λ = 0.1—0.01 m).
Reflected almost all obstacles, freely penetrate through the ionosphere. Due to its properties are used in space communications.
AM - FM
Often, the receiving devices have the position of the switches am-fm, what is it:
AM - amplitude modulation

This change in the amplitude of the carrier frequency under the action of the coding oscillation, for example, voice from a microphone.
AM is the first kind of modulation invented by man. Of the shortcomings, like any analog modulation type, has low noise immunity.
FM - frequency modulation

This change in the carrier frequency under the influence of the coding oscillation.
Although it is also an analog type of modulation, but it has a higher noise immunity than AM and therefore is widely used in the soundtrack of TV broadcasts and VHF broadcasting.
In fact, the modulation described by the modulation has some subspecies, but their description is not included in the material of this article.
More terms
Interference - as a result of reflection of waves from various obstacles, the waves are added. In the case of addition in the same phases, the amplitude of the initial wave may increase, if added in opposite phases, the amplitude may decrease down to zero.
This phenomenon is most pronounced when receiving VHF FM and TV signal.

Therefore, for example, indoors, the reception quality of a TV room antenna strongly “floats”.
Diffraction is a phenomenon that occurs when a radio wave encounters obstacles, as a result of which the wave can change its amplitude, phase and direction.
This phenomenon explains the connection on the HF and SW through the ionosphere, when the wave is reflected from various inhomogeneities and charged particles and thereby changes the direction of propagation.
This phenomenon explains the ability of radio waves to spread without direct visibility, bending around the earth's surface. For this, the wavelength must be commensurate with the obstacle.
PS:
I hope the information described by me will be useful and will bring some understanding on this topic.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/158161/
All Articles