Evaluation of information security in the activities of organizations
Introduction
Information security (IB) is now becoming one of the most important aspects of the overall economic security of a modern organization, characterizing the state of security of its business environment. Information protection is a special activity to prevent information leakage, unauthorized changes in its flows and other impacts that adversely affect the stable operation of an organization and its associated economic agents (customers, equipment suppliers, investors, the state, etc.). In this regard, timely, prompt and correct assessment of the risks of reducing or completely losing information security today is a pressing issue in the activities of any organization.

In modern publications dealing with information security issues, 4 types of sources of threats affecting information security are highlighted:
• natural;
• man-made;
• human intentional;
• human unintended.
Thoughts
Given the significant heterogeneity of these sources, the development of methods and algorithms for assessing the risk of reducing or completely losing the information security is quite a laborious and significant task for any information system that requires the fulfillment of a number of conditions.
')
First, it is necessary to build flexible models of an information system, to describe it comprehensively, taking into account software, hardware resources, internal and external threats and vulnerabilities that can be configured in accordance with the characteristics of a particular organization.
Secondly, taking into account a significant number of risk factors, a mathematical model for evaluating information security must allow the development of effective numerical algorithms for information processing in models.
Third, a risk assessment methodology should be extremely transparent so that the information owner can adequately assess the applicability and effectiveness of the methodology to a specific information system.
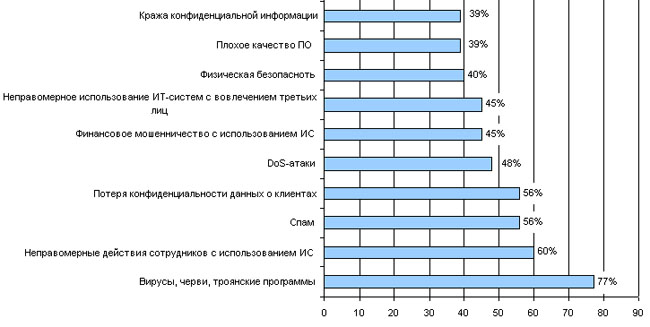
To assess the risks of information security, it is important to identify and analyze, if possible, all or at least the main threats and vulnerabilities through which threats can be realized, and which act on the information system in the sense of refusal or reducing its efficiency. Today, there are a number of information security risk assessment methodologies, the main of which include the following:
1) A risk assessment method based on building a model of threats and vulnerabilities;
2) A risk assessment method based on building a model of information flows.
The first technique is based on using primarily expert and statistical information about threats and vulnerabilities. To assess risks, an organization’s information system determines the security of each valuable resource by assessing the likelihood of threats acting on a specific organization’s resource (for example, the probability of IS system malfunction due to low staff qualifications, lack of or outdated software or hardware, etc. p.), as well as vulnerabilities through which these threats can be implemented. This probability estimate makes it possible to rank threats and vulnerabilities by degree of risk.
Since the risks of information security are closely related to the use of modern information technologies that determine the effectiveness of the organization in its innovative aspect, they can be attributed to a variety of innovative risks. Defining innovative risk as “the probability of losses due to an incorrectly set or unachieved strategic goal,” when characterizing the risks of a system failure, it is advisable to use an indicator such as the level of costs (in material or value terms) to restore the system.

Based on expertly defined data on risks, vulnerabilities and costs for each of the resources, it is possible to build a model of threats and vulnerabilities relevant to the organization’s information system and analyze the functioning of the information system in terms of minimizing the risks of failure or reducing system performance and, therefore, maximizing its effectiveness by the criterion of information security.
We give below a brief description of the steps of the algorithm for solving the described problem. At the first stage, the most important for the organization activities are identified, which determine (from the point of view of its management) the level of information security. At the second stage, in selected areas of the organization, based on an expert assessment of the likelihood of an IS threat, the significance of each threat is calculated, and the level of costs in terms of restoring the system is assessed. Next, the total risk of system failure is calculated as the sum of risks for each of the areas.
Result
The result of solving the described problem will be the distribution of the financial resource in the selected areas of the organization, minimizing the risks of system failure according to the criterion of information security.

Conclusion
In conclusion, we note that many small and medium-sized businesses, being in the information environment, do not pay attention to the various threats to which their information system is exposed, thereby putting themselves at risk of financial losses. That is why it is necessary to develop models of IS risk analysis, as well as create algorithms and methods for analyzing them in order to create decision support systems for managing the organization’s information security.
More detailed information about the algorithm and the algorithm itself will be presented in the next post.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/158143/
All Articles