Ipv6 configuration in proxmox and lvm notes

In many places I see questions about how to configure ipv6 for containers in proxmox, as well as why online backup does not work.
I myself have been using proxmox for virtualization of openvz for quite some time now (sharing services, tests, dev. Environments) and all this is going on hetzner.
')
About how to install and configure proxmox - I will not write, on Habre in particular, and on the Internet as a whole - this information is complete. Despite the fact that the best source of such information is the official wiki.
But what's not on the wiki is how to set proxmox correctly on debian.
Lvm
In this moment there is a small nuance: the installer on the C-disk marks the hard disk automatically, creating a physical lvm volume and 2 logical ones on it. Moreover, 2 logical volumes do not fill the entire physical volume by 100%, but leave some 10-20 percent free. This is done in order for online backup to work properly (i.e., backup without stopping the operation of virtual machines).
The fact is that online backup is performed using the snapshot method of the working volume. For this purpose, a temporary logical volume is created just in unallocated space.
And the two volumes are installed by the installer on the C-disk in order to use the 2nd as a backup storage, since the current volume cannot be backed up onto the current volume, this is some kind of recursion coming out.
Therefore, when installing Debian, you need to take into account that there should be 2 logical lvm volumes (1 for the containers themselves, 2 for backups), which fill the physical lvm volume for about 80-90%.
How to create lvm volumes and how to do this from the recovery hetzner environment is either in the documentation for debian, or in the hetzner wiki, there is even in Russian.
Attention. There is another point related to the regression in lvm. During the snapshot - the recording on the logical volume that is being backed up is very tight. Somewhere I saw a ticket, but I can not remember where. If you have information about this moment - please share.
IP V6
About ipv6 there is also a lot of questions.
Many people do not use ipv6 at proxmox at all simply because they cannot configure it, which, in the light of panic on the ipv4 market, is depressing.
And this is done quite easily.
Well, first of all, let's configure ipv4 (once again I remind you how to do it) you need to create a bridge to the physical interface
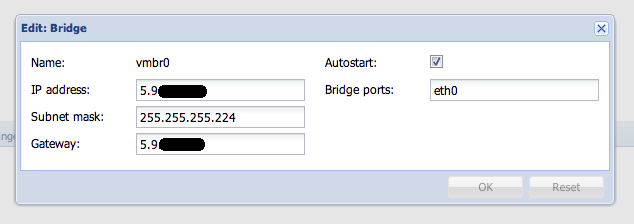
Fill the IP address, mask and gateway as you gave hetzner.
If you ordered a subnet, enter the subnet data there.
If, like me, I ordered several separate ip addresses, enter the main ip that you received when ordering the server.
Then - restart the server or network.
Further, when creating a container, select the bridge and the bridge you created as the network interface interface.
Now is an important point for hetzner. It is necessary to order a virtual mac address for each additional ip address.
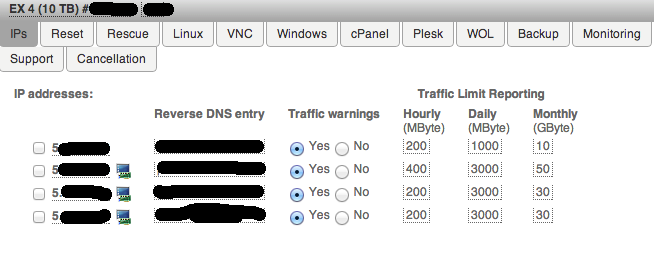
Click on the icon near the ip-address - and you will see your mac address. Copy it and paste it into the MAC field in the edit box of the network interface of your virtual machine (not the Host MAC address, but simply the MAC)
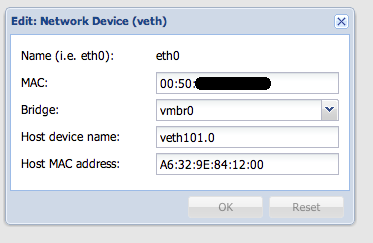
Save, reboot the virtual machine.
Now, a little fix the grid of the physical machine.
Create the file /etc/network/if-up.d/ipv6
Make it executable.
Put there such content
#!/bin/sh ifconfig vmbr0 add 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff:xxxx::1/80 ip -6 route add 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff::1 dev vmbr0 ip -6 route add default via 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff::1 dev vmbr0 Where ffff is to replace it with your data, and xxxx - create your own sub-subnet from the subnet given to you (well, you can use all that issued to you)
80 is a mask of my sub-subnet. (if you set 64 - note that 2a01: ffff: ffff: ffff :: 1 is the gateway, therefore, for the ip address use 2a01: ffff: ffff: ffff :: 2)
Well, the appointment of routes. This is understandable.
Distort server or network and check ifconfig
We go into the virtual machine through the console and vzctl enter 100 (or your number).
We edit / etc / network / interfaces (this is for debian, as I do not remember on other systems)
auto eth0 iface eth0 inet static address 5.5.5.5 netmask 255.255.255.224 gateway 5.5.5.1 iface eth0 inet6 static address 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff:xxxx::1/80 up ip -6 address add 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff:xxxx::2 dev eth0 up ip -6 address add 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff:xxxx::3 dev eth0 up ip -6 route add 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff::/64 dev eth0 up ip -6 route add default via 2a01:ffff:ffff:ffff::1 dev eth0 here - in the ipv4 block: address, netmask, gateway - the data of your additional ipv4 address or subnet
in the ipv6 block: ffff - data of the network issued to you
xxxx - subnet for this Wirth. cars (attention, xxxx here is not equal to xxxx from the previous step)
lines up ip -6 address add 2a01: ffff: ffff: ffff: xxxx :: 3 dev eth0 repeat as many ipv6 addresses you need for this wirth. cars (well, naturally, increasing the last tsiferku by 1 in the hexadecimal system counts). For example, I assign an individual ipv6 address to each site.
The last 2 lines are the gateways: the internal network and the default for everything that is outside.
We overload the car or network. Pinging ipv6.google.com.
Thanks for attention.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/158141/
All Articles