Internet acquiring "for dummies"
Good day, habravchane!
With this article I want to shed light on Internet acquiring in general, to tell what it is eaten with.
Purpose of the article: for general development.
E-commerce is an economic area that includes all financial and trade transactions carried out through computer networks and the business processes involved in conducting such transactions.
E-commerce includes:
')
• Electronic Information Interchange (Electronis Data Interchange, EDI),
• Electronic capital flow (Electronic Funds Transfer, EFS),
• Electronic commerce (e-trade),
• Electronic money (e-cash),
• Electronic marketing (e-marketing),
• Electronic banking (e-banking),
• Electronic insurance services (e-insurance).
Business schemes:
1) B2B or business-to-business
The company trades with another company. B2B is one of the most promising and actively developing areas of e-commerce today. An example of a B2B transaction is the sale of templates for a site to companies for later use as the basis for the design of a company's own web resource.
2) B2C or business consumer
In this case, the company is already selling directly with the client (not a legal entity, but an individual). Examples of this type of trade are traditional online stores, social commerce, or the sale of goods and services in social networks.
3) C2C or consumer-to-consumer
Transactions between two consumers, none of which is an entrepreneur in the legal sense of the word. As a rule, C2C commerce is carried out on Internet auction sites.
Internet acquiring is a general term that refers to the acceptance of payments by plastic cards via the Internet using a specially developed web-interface. Internet acquiring, as a component of e-commerce, is the activity of a credit institution (acquiring bank), which includes settlements with e-commerce organizations on transactions performed using bank cards on the Internet. The connection of e-commerce organizations by the acquiring bank is usually carried out with the technical support of Service Providers, which ensure the security of payments using the 3-D Secure and SSL authentication protocol and are responsible for fraud monitoring of transactions conducted in the online store. To pay using this system, you must have a credit card, the account of which is designed specifically to pay for goods and services not only on the Internet, but also in real stores.
Benefits of use:
For organizations:
Global Scale
cost reduction
Improving supply chains
Business is always open (24/7/365)
Personalization
Quick product launch
Low cost distribution of digital products
For consumers:
Ubiquity
Anonymity
Large selection of goods and services
Personalization
Cheaper products and services
Prompt delivery
Electronic socialization
For society:
A wide range of services provided (eg, education, health care, public services)
Improving living standards
Enhance national security
Reducing the “digital” gap
Online sale / order of goods / services reduces car traffic and reduces environmental pollution
Disadvantages:
For organizations:
Possible doubts of the parties about the affiliation of a project to the company (negative anonymity)
Some difficulty in conducting and legitimizing the activities of an enterprise on the Internet
For consumers:
Consumer distrust of services sold through the Internet
The inability to "touch" the goods by hand
Waiting for delivery of purchased products
For society:
Attractive fraud platform (reduced network security)
Displacement from the market of commercial offline enterprises
For the state:
Non-receipt of tax payments to the state budget when maintaining “gray” accounting schemes
Market participants:
1. Buyer - A customer who has a computer with a web browser and Internet access.
2. The issuing bank. Here is the current account of the buyer. The issuing bank issues cards and is the guarantor of the client's financial obligations.
3. Sellers. E-Commerce Servers, where catalogs of goods and services are kept and customer orders for purchase are accepted.
4. Acquiring banks. Each seller has the only bank in which he holds his
settlement account (Alfa-Bank, Rosbank, VTB 24, Raiffeisenbank, TransCreditBank).
Bank Equaire should have its own processing.
5. Payment system Internet. Electronic components that are intermediaries between the other participants.
6. Traditional payment system. A complex of financial and technological tools for servicing cards of this type. Ensuring the use of cards as a means of payment for goods and services, use of banking services, carrying out offsets, etc. (Visa Int., MasterCard WorldWide, Diners Club, Amex, JCB and China Union Pay).
7. Processing center of the payment system. An organization that provides information and technological interaction between members of a traditional payment system.
8. Settlement bank of the payment system. A credit institution that conducts mutual settlements between participants in the payment system on behalf of the processing center.
Acquiring scheme:
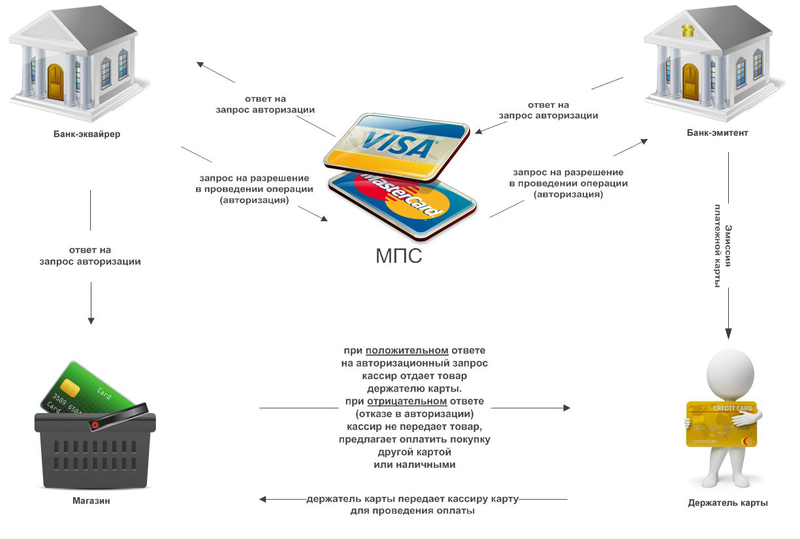
1. The customer makes a purchase in the online store.
2. When choosing to pay for an order with a plastic card, the client is redirected to the Provider authorization page and enters payment details.
3. The provider forms an authentication request and sends the client to the issuing bank's authentication system (ACS).
4. After authentication, the Provider sends the information for the authorization request to the Processor.
5. The processor sends a request for authorization of the operation to the international payment system.
6. Depending on the result of the authorization, the Processor generates a message to the Provider about the operation or refusal.
7. The provider informs the online store and the customer about the results of the operation.
8. Depending on the result of the operation, the online store makes a sale or cancels an order.
9. The processor sends the clearing file for settlement to the Settlement Bank.
10. The settlement bank transfers the reimbursement for the transactions made to the online store account.
11. Sending a final Act on the results of the reporting period.
As part of Internet acquiring service providers offer a wide
range of services for e-commerce enterprises:
- Personal account;
- Virtual terminal - A program for authorizing payments via the Internet in real time, which is installed on the computer of an online store or an offline store.
- A complete set of methods to prevent fraud,
- Formation of an authorization request or transfer of a file of financial transactions to an acquirer for further settlement;
- Formation of chargebacks;
- Internal tools to detect and protect against fraud;
- Multicurrency payments
- Customer and technical support 24/7
- Competitive cost reduction policy
- safety standards;
- High level of service;
- Development of relations with companies providing additional services to increase customer loyalty.
Frode
Fraud (from the English. Fraud) - type of fraud in the field of information technology, in particular, unauthorized actions and unauthorized use of resources and services in communication networks.
Fraud and credit cards
Carding (from the English. Carding) - type of fraud, in which the operation is performed using a payment card or its details, not initiated or not confirmed by its holder. Payment card details are usually taken from hacked servers of online stores, payment and settlement systems, as well as from personal computers (either directly or through Trojans and worms). Responsibility for such fraud lies with the seller if he does not use 3DSecure.
Phishing (English phishing, distorted “fishing” - “fishing”) is the creation by scammers of a site that will be trusted by the user, for example, a site similar to the site of the user's bank, through which the details of payment cards are stolen.
Skimming (from the English. Skim - skim the cream), which uses a skimmer - an attacker's tool for reading, for example, the magnetic track of a payment card. In carrying out this fraudulent operation, a complex of skimming devices is used:
Skimmer - A tool for reading a magnetic track of a payment card - is a device installed in the card reader and a card reader at the entrance door to the customer service area at the bank premises. It is a device with a readout magnetic head, an amplifier - a converter, a memory and an adapter for connecting to a computer. Skimmers can be portable, miniature. The main idea and task of skimming is to read the necessary data (track / track content) of the magnetic strip of the card for later reproduction on a fake one. Thus, when making a transaction with a fake card, the authorization request and the debiting of funds under a fraudulent transaction will be made from the account of the original, “simulated” card. Skimmers can accumulate stolen information about plastic
maps, or remotely transmit it over the radio channel to attackers nearby. After copying information from the card, the fraudsters make a duplicate card and, knowing the PIN, withdraw all the money within the issuance limit, both in Russia and abroad.
A video camera installed on an ATM and sent to the keyboard of the ATM as a visor or other overlays, for example, advertising materials - is used together with a skimmer to receive a PIN of the holder, which allows you to receive cash in ATMs using a fake card (having the given tracks and the original PIN).
These devices are powered by self-contained energy sources - miniature power supply batteries, and, for the difficulty of detection, as a rule, they are made and masked by the color and shape of the ATM.
Fraud and GSM
GSM fraud options
1) When subscribing to some content, for a conditional fee to the client, the contract includes a very high rate for unsubscribing, and then they do everything possible so that the client decides to unsubscribe.
2) Non-return on SIM-cards of credit tariff plans.
3) Making SIM-cards for lost documents so that the received SIM-cards with roaming be used abroad. At the same time, the local operator sends invoices for calls to the operator who issued the SIM card with some delay, but for the time being it pays for the calls independently.
4) Frank deception, when the caller says that by transferring a small amount to his phone, you are helping your
a relative who has had an accident or other difficult situation.
5) The option of opening a paid service is possible, with the method of payment by SMS. At the same time, it is technically possible to obtain a negative balance on a SIM-card with a debit tariff plan.
6) Exceeding the limit on the number of SMS requests sent, due to the technical capabilities of the OSS platform, leading to the receipt of the ordered services by the subscriber without actual payment.
The International Association of GSM Network Operators has developed its classification for fraud crimes:
Access Fraud - fraudulent access - unauthorized use of cellular services by thinking or inadvertently interfering with, manipulating or reprogramming the numbers of ESN (Electronic Serial Number) and / or MIN (Mobile Identification Number) cellular phones. The method is possible on networks without authentication.
Stolen Phone Froud - unauthorized use of a stolen or lost mobile phone. The method works until the owner notifies the company and she does not block access from the stolen phone.
Subscription Fraud - specifying incorrect data when concluding a contract, use of services on credit with the intention not to pay for them.
Contractual aspect
Acquiring agreement is a legal document, in accordance with which a trade and service company is obliged to operate both in accordance with the current legislation and according to the rules established by payment systems and the acquirer bank. The main requirements for this agreement are defined in the Rules of Payment Systems (for example,
specialized section of the Visa International Operating Regulations), however, acquirers have the right to change both the form and content of such contracts.
Internet acquiring connection:
- Online store refers to the service provider (electronic payment system) - Assist, DengiOnline, etc.
- By choosing one of these providers, the online store is registered on its website, i.e. there is a registration form and indicates that he intends to accept plastic cards for payment and in which bank he will be serviced from the proposed list of banks that offer this service.
- Application for connection is sent to the bank by the service provider.
- The bank processes this application, contacts the online store using the contact information provided in it.
- Online store, passes all stages before signing the contract.
- As a result, the online store signs a contract for online acquiring and begins to accept plastic cards for payment via the Internet.
Security technology of electronic Internet payments
plastic cards.
SSL protocol (Secure Socket Layer) + 3D Secure Protocol
3-D Secure is an XML protocol that is used as an additional level of security for online credit and debit cards, two-factor user authentication. It was developed by Visa in order to improve the security of Internet payments and offered customers the Verified by Visa (VbV) service. Services based on this protocol were also accepted by MasterCard, called MasterCard SecureCode (MCC), and JCB International, as J / Secure. 3-D Secure adds another authentication step for online
payments.
3-D Secure should not be confused with the CVV2 code printed on the back of the card.
3-D Secure is a trademark of VISA Corporation.
3 domain system:
The 3-D Secure model is implemented on the basis of 3 domains in which transactions are generated and verified:
Domain of the Issuer, which includes the Cardholder and the Bank issuing the cards.
The Acquirer Domain, which includes the Acquirer Bank and its customers (online merchants).
Domain interaction contains elements that make it possible to conduct transactions between two other domains. It mainly contains networks and services of card associations.
Domains are independent in their rights and are an important part of the information transfer process in a shared 3-D Secure infrastructure. Each domain has its own responsibility in conducting
transactions:
• In the Issuer's domain, the issuing bank is responsible for authenticating the buyer and providing correct information for the transaction.
• In the Acquirer domain, the online merchant is responsible for the business relationship with the buyer, as well as ensuring that the buyer is sent to the correct issuing bank for verification. In the same domain, the Acquirer is responsible for coordinating the conduct of a transaction through traditional networks of Visa or MasterCard.
• In the interaction domain, the Visa or MasterCard payment system is responsible for the safety of information on each issuer (cardholder's bank, issuer's Internet address) and the provision of this information for decision making in case of conflict situations.
• The 3-D Secure model provides a standard inter-domain communication protocol for exchanging and verifying transactions. It does not cause the necessity of changes in relations between participants of one domain:
• Merchant and Acquirer are free to choose any way to conduct their transactions and to manage relationships in their domains.
• Issuers are free to choose any mechanisms they prefer for cardholder authentication.
The 3-D Secure architecture implements a set of dedicated servers for
servicing the transaction flow during its life cycle:

• In the Issuer's domain, the Access Management Server (Access Control Server or ACS) is responsible for managing the authentication processes between the Buyer and the Issuer and ensures that payment transactions are conducted for the Merchant.
• In the Acquirer's domain, the Merchant Plug-In (or MPI) server controls the flow of transactions between the Visa / MasterCard infrastructures, the cardholder infrastructure and the payment infrastructure created by the Acquirer.
• In the Server Directory Directory (Directory) interaction domain, Visa / MasterCard keeps information about the process participants. In the same domain, the Authentication History Server Visa / MasterCard (Authentication History Server or AHS) reliably stores information on all transactions and ensures its availability in the event of a conflict.
• In the Issuer and Acquirer domains. Host systems are involved in the process of reconciliation of transactions in the back office of the bank to provide clearing netting between participants for the purpose of further transfer of funds.
• 3-D Secure !
3D Secure :
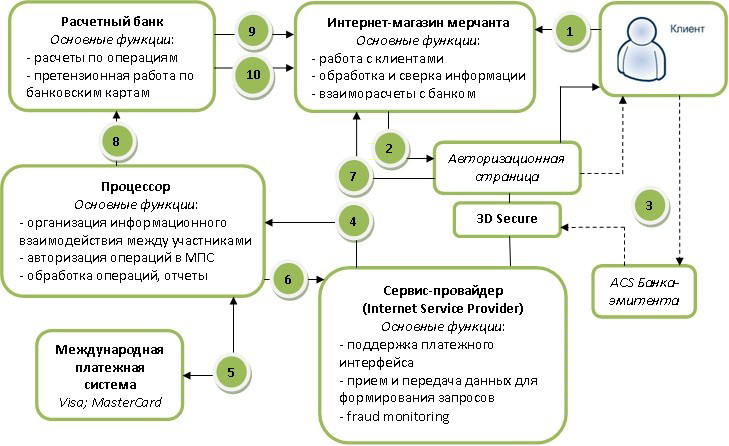
— , - , «».
— , .
— , 3D Secure, - . 3D Secure, MIA SET.
— , 3D Secure. , -, , -.
— - , , - .
— MIA SET.
SET
SET (Secure Electronic Transaction) — , Visa MasterCard .
, . SET- . SET- . SET- - .
SET — Secure Electronic Transaction — , , . .
SET — on-line — , (, .) , ( SET). . , SET, .
SET — — , ( , ... .) , SET.
MIA SET
SET — , , . MIA SET (Merchant Initiated Authorization). MIA SET, RBS . — - — , .
, 3D Secure - . , , -. , ,
.
PCI DSS, : http://habrahabr.ru/post/130652/
:
http://habrahabr.ru/post/30321/
http://habrahabr.ru/post/49254/ —
http://habrahabr.ru/post/124668/ —
— PCI DSS
With this article I want to shed light on Internet acquiring in general, to tell what it is eaten with.
Purpose of the article: for general development.
E-commerce is an economic area that includes all financial and trade transactions carried out through computer networks and the business processes involved in conducting such transactions.
E-commerce includes:
')
• Electronic Information Interchange (Electronis Data Interchange, EDI),
• Electronic capital flow (Electronic Funds Transfer, EFS),
• Electronic commerce (e-trade),
• Electronic money (e-cash),
• Electronic marketing (e-marketing),
• Electronic banking (e-banking),
• Electronic insurance services (e-insurance).
Business schemes:
1) B2B or business-to-business
The company trades with another company. B2B is one of the most promising and actively developing areas of e-commerce today. An example of a B2B transaction is the sale of templates for a site to companies for later use as the basis for the design of a company's own web resource.
2) B2C or business consumer
In this case, the company is already selling directly with the client (not a legal entity, but an individual). Examples of this type of trade are traditional online stores, social commerce, or the sale of goods and services in social networks.
3) C2C or consumer-to-consumer
Transactions between two consumers, none of which is an entrepreneur in the legal sense of the word. As a rule, C2C commerce is carried out on Internet auction sites.
Internet acquiring is a general term that refers to the acceptance of payments by plastic cards via the Internet using a specially developed web-interface. Internet acquiring, as a component of e-commerce, is the activity of a credit institution (acquiring bank), which includes settlements with e-commerce organizations on transactions performed using bank cards on the Internet. The connection of e-commerce organizations by the acquiring bank is usually carried out with the technical support of Service Providers, which ensure the security of payments using the 3-D Secure and SSL authentication protocol and are responsible for fraud monitoring of transactions conducted in the online store. To pay using this system, you must have a credit card, the account of which is designed specifically to pay for goods and services not only on the Internet, but also in real stores.
Benefits of use:
For organizations:
Global Scale
cost reduction
Improving supply chains
Business is always open (24/7/365)
Personalization
Quick product launch
Low cost distribution of digital products
For consumers:
Ubiquity
Anonymity
Large selection of goods and services
Personalization
Cheaper products and services
Prompt delivery
Electronic socialization
For society:
A wide range of services provided (eg, education, health care, public services)
Improving living standards
Enhance national security
Reducing the “digital” gap
Online sale / order of goods / services reduces car traffic and reduces environmental pollution
Disadvantages:
For organizations:
Possible doubts of the parties about the affiliation of a project to the company (negative anonymity)
Some difficulty in conducting and legitimizing the activities of an enterprise on the Internet
For consumers:
Consumer distrust of services sold through the Internet
The inability to "touch" the goods by hand
Waiting for delivery of purchased products
For society:
Attractive fraud platform (reduced network security)
Displacement from the market of commercial offline enterprises
For the state:
Non-receipt of tax payments to the state budget when maintaining “gray” accounting schemes
Market participants:
1. Buyer - A customer who has a computer with a web browser and Internet access.
2. The issuing bank. Here is the current account of the buyer. The issuing bank issues cards and is the guarantor of the client's financial obligations.
3. Sellers. E-Commerce Servers, where catalogs of goods and services are kept and customer orders for purchase are accepted.
4. Acquiring banks. Each seller has the only bank in which he holds his
settlement account (Alfa-Bank, Rosbank, VTB 24, Raiffeisenbank, TransCreditBank).
Bank Equaire should have its own processing.
5. Payment system Internet. Electronic components that are intermediaries between the other participants.
6. Traditional payment system. A complex of financial and technological tools for servicing cards of this type. Ensuring the use of cards as a means of payment for goods and services, use of banking services, carrying out offsets, etc. (Visa Int., MasterCard WorldWide, Diners Club, Amex, JCB and China Union Pay).
7. Processing center of the payment system. An organization that provides information and technological interaction between members of a traditional payment system.
8. Settlement bank of the payment system. A credit institution that conducts mutual settlements between participants in the payment system on behalf of the processing center.
Acquiring scheme:

1. The customer makes a purchase in the online store.
2. When choosing to pay for an order with a plastic card, the client is redirected to the Provider authorization page and enters payment details.
3. The provider forms an authentication request and sends the client to the issuing bank's authentication system (ACS).
4. After authentication, the Provider sends the information for the authorization request to the Processor.
5. The processor sends a request for authorization of the operation to the international payment system.
6. Depending on the result of the authorization, the Processor generates a message to the Provider about the operation or refusal.
7. The provider informs the online store and the customer about the results of the operation.
8. Depending on the result of the operation, the online store makes a sale or cancels an order.
9. The processor sends the clearing file for settlement to the Settlement Bank.
10. The settlement bank transfers the reimbursement for the transactions made to the online store account.
11. Sending a final Act on the results of the reporting period.
As part of Internet acquiring service providers offer a wide
range of services for e-commerce enterprises:
- Personal account;
- Virtual terminal - A program for authorizing payments via the Internet in real time, which is installed on the computer of an online store or an offline store.
- A complete set of methods to prevent fraud,
- Formation of an authorization request or transfer of a file of financial transactions to an acquirer for further settlement;
- Formation of chargebacks;
- Internal tools to detect and protect against fraud;
- Multicurrency payments
- Customer and technical support 24/7
- Competitive cost reduction policy
- safety standards;
- High level of service;
- Development of relations with companies providing additional services to increase customer loyalty.
Frode
Fraud (from the English. Fraud) - type of fraud in the field of information technology, in particular, unauthorized actions and unauthorized use of resources and services in communication networks.
Fraud and credit cards
Carding (from the English. Carding) - type of fraud, in which the operation is performed using a payment card or its details, not initiated or not confirmed by its holder. Payment card details are usually taken from hacked servers of online stores, payment and settlement systems, as well as from personal computers (either directly or through Trojans and worms). Responsibility for such fraud lies with the seller if he does not use 3DSecure.
Phishing (English phishing, distorted “fishing” - “fishing”) is the creation by scammers of a site that will be trusted by the user, for example, a site similar to the site of the user's bank, through which the details of payment cards are stolen.
Skimming (from the English. Skim - skim the cream), which uses a skimmer - an attacker's tool for reading, for example, the magnetic track of a payment card. In carrying out this fraudulent operation, a complex of skimming devices is used:
Skimmer - A tool for reading a magnetic track of a payment card - is a device installed in the card reader and a card reader at the entrance door to the customer service area at the bank premises. It is a device with a readout magnetic head, an amplifier - a converter, a memory and an adapter for connecting to a computer. Skimmers can be portable, miniature. The main idea and task of skimming is to read the necessary data (track / track content) of the magnetic strip of the card for later reproduction on a fake one. Thus, when making a transaction with a fake card, the authorization request and the debiting of funds under a fraudulent transaction will be made from the account of the original, “simulated” card. Skimmers can accumulate stolen information about plastic
maps, or remotely transmit it over the radio channel to attackers nearby. After copying information from the card, the fraudsters make a duplicate card and, knowing the PIN, withdraw all the money within the issuance limit, both in Russia and abroad.
A video camera installed on an ATM and sent to the keyboard of the ATM as a visor or other overlays, for example, advertising materials - is used together with a skimmer to receive a PIN of the holder, which allows you to receive cash in ATMs using a fake card (having the given tracks and the original PIN).
These devices are powered by self-contained energy sources - miniature power supply batteries, and, for the difficulty of detection, as a rule, they are made and masked by the color and shape of the ATM.
Fraud and GSM
GSM fraud options
1) When subscribing to some content, for a conditional fee to the client, the contract includes a very high rate for unsubscribing, and then they do everything possible so that the client decides to unsubscribe.
2) Non-return on SIM-cards of credit tariff plans.
3) Making SIM-cards for lost documents so that the received SIM-cards with roaming be used abroad. At the same time, the local operator sends invoices for calls to the operator who issued the SIM card with some delay, but for the time being it pays for the calls independently.
4) Frank deception, when the caller says that by transferring a small amount to his phone, you are helping your
a relative who has had an accident or other difficult situation.
5) The option of opening a paid service is possible, with the method of payment by SMS. At the same time, it is technically possible to obtain a negative balance on a SIM-card with a debit tariff plan.
6) Exceeding the limit on the number of SMS requests sent, due to the technical capabilities of the OSS platform, leading to the receipt of the ordered services by the subscriber without actual payment.
The International Association of GSM Network Operators has developed its classification for fraud crimes:
Access Fraud - fraudulent access - unauthorized use of cellular services by thinking or inadvertently interfering with, manipulating or reprogramming the numbers of ESN (Electronic Serial Number) and / or MIN (Mobile Identification Number) cellular phones. The method is possible on networks without authentication.
Stolen Phone Froud - unauthorized use of a stolen or lost mobile phone. The method works until the owner notifies the company and she does not block access from the stolen phone.
Subscription Fraud - specifying incorrect data when concluding a contract, use of services on credit with the intention not to pay for them.
Contractual aspect
Acquiring agreement is a legal document, in accordance with which a trade and service company is obliged to operate both in accordance with the current legislation and according to the rules established by payment systems and the acquirer bank. The main requirements for this agreement are defined in the Rules of Payment Systems (for example,
specialized section of the Visa International Operating Regulations), however, acquirers have the right to change both the form and content of such contracts.
Internet acquiring connection:
- Online store refers to the service provider (electronic payment system) - Assist, DengiOnline, etc.
- By choosing one of these providers, the online store is registered on its website, i.e. there is a registration form and indicates that he intends to accept plastic cards for payment and in which bank he will be serviced from the proposed list of banks that offer this service.
- Application for connection is sent to the bank by the service provider.
- The bank processes this application, contacts the online store using the contact information provided in it.
- Online store, passes all stages before signing the contract.
- As a result, the online store signs a contract for online acquiring and begins to accept plastic cards for payment via the Internet.
Security technology of electronic Internet payments
plastic cards.
SSL protocol (Secure Socket Layer) + 3D Secure Protocol
3-D Secure is an XML protocol that is used as an additional level of security for online credit and debit cards, two-factor user authentication. It was developed by Visa in order to improve the security of Internet payments and offered customers the Verified by Visa (VbV) service. Services based on this protocol were also accepted by MasterCard, called MasterCard SecureCode (MCC), and JCB International, as J / Secure. 3-D Secure adds another authentication step for online
payments.
3-D Secure should not be confused with the CVV2 code printed on the back of the card.
3-D Secure is a trademark of VISA Corporation.
3 domain system:
The 3-D Secure model is implemented on the basis of 3 domains in which transactions are generated and verified:
Domain of the Issuer, which includes the Cardholder and the Bank issuing the cards.
The Acquirer Domain, which includes the Acquirer Bank and its customers (online merchants).
Domain interaction contains elements that make it possible to conduct transactions between two other domains. It mainly contains networks and services of card associations.
Domains are independent in their rights and are an important part of the information transfer process in a shared 3-D Secure infrastructure. Each domain has its own responsibility in conducting
transactions:
• In the Issuer's domain, the issuing bank is responsible for authenticating the buyer and providing correct information for the transaction.
• In the Acquirer domain, the online merchant is responsible for the business relationship with the buyer, as well as ensuring that the buyer is sent to the correct issuing bank for verification. In the same domain, the Acquirer is responsible for coordinating the conduct of a transaction through traditional networks of Visa or MasterCard.
• In the interaction domain, the Visa or MasterCard payment system is responsible for the safety of information on each issuer (cardholder's bank, issuer's Internet address) and the provision of this information for decision making in case of conflict situations.
• The 3-D Secure model provides a standard inter-domain communication protocol for exchanging and verifying transactions. It does not cause the necessity of changes in relations between participants of one domain:
• Merchant and Acquirer are free to choose any way to conduct their transactions and to manage relationships in their domains.
• Issuers are free to choose any mechanisms they prefer for cardholder authentication.
The 3-D Secure architecture implements a set of dedicated servers for
servicing the transaction flow during its life cycle:

• In the Issuer's domain, the Access Management Server (Access Control Server or ACS) is responsible for managing the authentication processes between the Buyer and the Issuer and ensures that payment transactions are conducted for the Merchant.
• In the Acquirer's domain, the Merchant Plug-In (or MPI) server controls the flow of transactions between the Visa / MasterCard infrastructures, the cardholder infrastructure and the payment infrastructure created by the Acquirer.
• In the Server Directory Directory (Directory) interaction domain, Visa / MasterCard keeps information about the process participants. In the same domain, the Authentication History Server Visa / MasterCard (Authentication History Server or AHS) reliably stores information on all transactions and ensures its availability in the event of a conflict.
• In the Issuer and Acquirer domains. Host systems are involved in the process of reconciliation of transactions in the back office of the bank to provide clearing netting between participants for the purpose of further transfer of funds.
• 3-D Secure !
3D Secure :

— , - , «».
— , .
— , 3D Secure, - . 3D Secure, MIA SET.
— , 3D Secure. , -, , -.
— - , , - .
— MIA SET.
SET
SET (Secure Electronic Transaction) — , Visa MasterCard .
, . SET- . SET- . SET- - .
SET — Secure Electronic Transaction — , , . .
SET — on-line — , (, .) , ( SET). . , SET, .
SET — — , ( , ... .) , SET.
MIA SET
SET — , , . MIA SET (Merchant Initiated Authorization). MIA SET, RBS . — - — , .
, 3D Secure - . , , -. , ,
.
PCI DSS, : http://habrahabr.ru/post/130652/
:
http://habrahabr.ru/post/30321/
http://habrahabr.ru/post/49254/ —
http://habrahabr.ru/post/124668/ —
— PCI DSS
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/157565/
All Articles