Elon Musk. Mission to mars

Photo from another article
When a person tells you that he once planned to break a garden on Mars, you will doubt his mental health. But if the same person has since launched several rockets that are truly capable of reaching Mars, sending them into Bond-style orbit from a tiny island in the Pacific Ocean, you should find another diagnosis. The fact of the matter is extreme entrepreneurship: the line between madness and genius is very thin, and you need a little bit of both to truly change the world.
All entrepreneurs are inclined to take risks, but more importantly, it is their ability to self-deceive. Indeed, psychological research has shown that entrepreneurs risk nothing more than non-entrepreneurs. Simply, they are so able to believe in their ideas about the future that they embark on their realization without realizing the risk. Of course, they are not right, but without being so wrong, without intentionally ignoring all skeptics and all the evidence to the contrary, without such courage, nothing radically new can be started.
')
I have never met an entrepreneur who would fit this model more than Elon Musk. All the entrepreneurs I admire most of all - Musk, Jeff Bezos, Reed Hastings, Jack Dorsey, Sergey Brin and Larry Page, Bill Gates, Steve Jobs and others, sought not only to build a big company, but also to tackle the really significant problems. But even in the class of people who change the world, Musk stands out. After the successful sale of the Internet companies he created, including PayPal, the South African native could simply retire to enjoy his wealth. Instead, he decides to change the most difficult-to-manage industries in the world. At 41, he reinvents the car with Tesla and builds an electric car factory in Detroit. (Wired represented this venture in discussion 18.10) He transforms energy with SolarCity, a startup that leases solar energy systems to homeowners.
And he heads the private space race with SpaceX, capable of replacing the shuttle and leading us into interplanetary space. Musk founded the company in 2002, and developed a series of new-generation missiles that can deliver payload to space for a small fraction of the cost of launching existing missiles. In 2010, SpaceX became the first private company to launch a spacecraft into orbit and bring it back. In 2012, her ship successfully docked to the International Space Station.
Not surprisingly, for the Iron Man movie Musk served as a prototype for the character Tony Stark, played by Robert Downey Jr .: This is a material worthy of a superhero. I met him at the Tesla factory in Fremont, California, to discuss how cheaper and (sooner or later) reusable rockets could someday deliver a man to Mars.

Independent businessman Elon Musk. Photo: Art Streiber
Chris Anderson : You're not a scientist or a space engineer by training.
Elon Musk : That's true. My basic education is physics and economics, but I grew up in a kind of engineering environment — my father is an electrical engineer. And there were a lot of engineering things around me. When I asked, they explained to me how these things actually work and work. I also made, for example, a model of a rocket. But in South Africa there were no ready-made rockets: I had to go to the pharmacy, purchase components for rocket fuel, mix them, put the mixture into the pipe.
Anderson : But then you became an Internet entrepreneur.
Musk : I have never done manual labor. I founded two internet software companies, zip2 and paypal. So it took me several years to study rocket science in part.
Anderson : How did you turn to space, how did your next project come about?
Musk : In 2002, when it became clear that PayPal was being sold, I talked with my friend, entrepreneur Adeo Ressi, who was my college neighbor. I stayed at his house for the weekend, and when we returned on a rainy day, we were stuck in traffic on Long Island. He asked me what I would do after selling PayPal. And I said: well, I have always been interested in space, but I do not think that I can do something there alone. But, I continued, it is already clear that we would like to send people to Mars. Suddenly I asked myself why this has not happened so far. Then I went to the NASA site to see the flight schedule there. [ Laughs ]
Anderson : And, of course, there was nothing.
Musk : At first I thought, damn it, maybe I was just looking in the wrong place! Why is there no plan, no schedule? There was nothing. It seemed insane.
Anderson : NASA has no budget for it.
Musk : Since 1989, when the study showed that a manned flight would cost $ 500 billion, the topic has become very dangerous. Politicians do not want an expensive federal program that would be used as a political weapon against them.
Anderson : Their opponents would call it a worthless effort.
Musk : But the United States is a nation of researchers. America is the concentrated spirit of development.
Anderson : We all went into the unknown to get here.
<b> Star Man </ b>. To see the astronomical goals of Elon Mask in perspective, look at some of the things he has already achieved. - Victoria Tang
1983 - At the age of 12, he develops the video game Star Blast and sells it to a computer magazine for $ 500.
1995 - Drops out of physics at Stanford University, two days after the start, to begin developing zip2, an online publishing platform for the media industry.
1999 - Compaq buys zip2 for $ 307 million.
2000 - Creates PayPal by merging its new company for online payments X.com and the company Confinity, created by Max Levchin and Peter Tile.
2001 - Establishes the Mask Foundation for research grants in the field of renewable energy, space and medical research, as well as scientific and engineering education.
2002 - PayPal enters the market; stocks rise more than 54 percent on the first day of trading. Eight months later, eBay acquires PayPal for $ 1.5 billion. Musk founds SpaceX.
2004 - Invest in Tesla Motors, a high-performance electric car company.
2006 - Helps create SolarCity, which provides solar energy systems for 33,000 buildings. Becomes the head of the company .
2008 - NASA selects the SpaceX Falcon 9 booster rocket and the Dragon space shuttle to deliver cargo to the International Space Station after the shuttles have retired.
2010 - Plays a cameo role in Iron Man 2 . Director John Favreau says that Musk inspired him to the image of Tony Stark.
2012 - Dragon SpaceX becomes the first commercial spacecraft to dock with the ISS.
1995 - Drops out of physics at Stanford University, two days after the start, to begin developing zip2, an online publishing platform for the media industry.
1999 - Compaq buys zip2 for $ 307 million.
2000 - Creates PayPal by merging its new company for online payments X.com and the company Confinity, created by Max Levchin and Peter Tile.
2001 - Establishes the Mask Foundation for research grants in the field of renewable energy, space and medical research, as well as scientific and engineering education.
2002 - PayPal enters the market; stocks rise more than 54 percent on the first day of trading. Eight months later, eBay acquires PayPal for $ 1.5 billion. Musk founds SpaceX.
2004 - Invest in Tesla Motors, a high-performance electric car company.
2006 - Helps create SolarCity, which provides solar energy systems for 33,000 buildings. Becomes the head of the company .
2008 - NASA selects the SpaceX Falcon 9 booster rocket and the Dragon space shuttle to deliver cargo to the International Space Station after the shuttles have retired.
2010 - Plays a cameo role in Iron Man 2 . Director John Favreau says that Musk inspired him to the image of Tony Stark.
2012 - Dragon SpaceX becomes the first commercial spacecraft to dock with the ISS.
Musk : So, I started with a crazy idea to spur national will. I called it the Mission “Oasis of Mars”. The idea was to send a small greenhouse to the surface of Mars, along with dehydrated nutrient gels that would be moistened after landing. You would finish this project with wonderful photos - green plants on a red background, the first life on Mars, and as far as we know - the farthest place where life has ever penetrated. It would be a big waste of money, but in the black you will get a lot of engineering information about what is needed to keep such a greenhouse, keeping the plants alive on Mars. If I could afford it, I realized that it would be a worthy investment, without the prospect of financial gain.
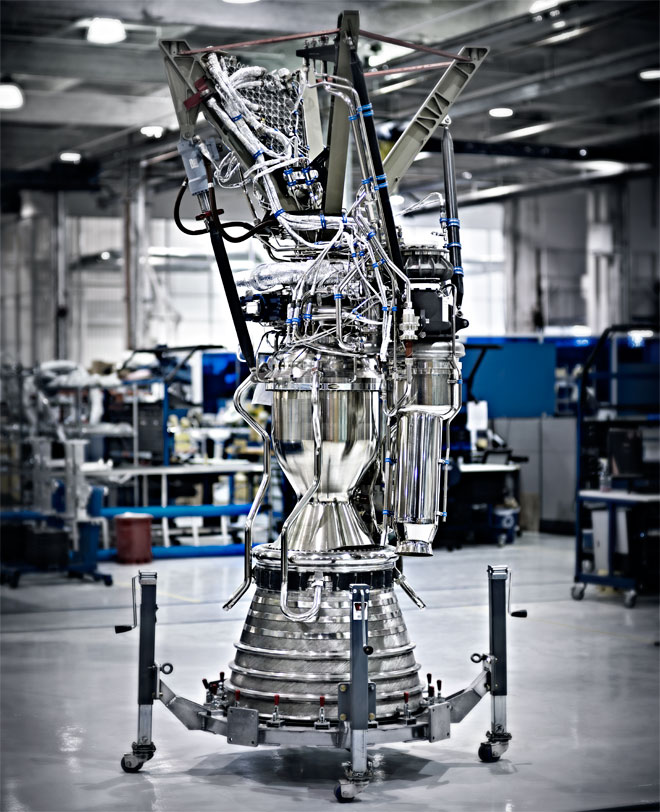

Merlin Engine Photo: Art Streiber
Anderson : In a sense, are you going to buy a trip to Mars?
Musk : Right. So I began to evaluate this enterprise. Spacecraft, communications, greenhouse experiment: I understood how to do it all inexpensively. But then it was the turn to calculate the cost of the rockets - what should move all of the above from Earth to Mars. The cheapest US missiles that could do this would have cost $ 65 million, and I figured it would take at least two.
Anderson : So, 130 million dollars.
Musk : Yes, plus spending on everything else, which would mean that I would spend everything I earned on PayPal, and with any price increase I could not cover the cost of the flight. So then I came to Russia three times at the end of 2001 and in 2002 to see if I could agree on the purchase of two ICBMs, obviously, without nuclear weapons.
Anderson : Of course.
Musk : They would cost me from $ 15 million to $ 20 million each. It was certainly a big step forward. But when I thought about it, I realized that the only reason why ICBMs were so cheap is that they have already been made. They just stood idle without being used. You could not make a new one for sale at the same price. I suddenly realized that all my premises to the idea of “Oasis of Mars” are no good. The real reason why we are not going to Mars was not the lack of national will; and the fact that we did not have enough cheap rocket technology to get there with a reasonable budget. This is the perception of the American people, correctly, given the current technology, that there is no financial sense to fly there.
Anderson : Instead of buying rockets for a charity mission, you realized that you need to start a business to make rockets more effective.
Musk : We needed to put rocket technology on the path of rapid improvement. Trying to collect the Mars Oasis, I talked with many people in the space industry and began to figure out which of them are technically astute and who are not. So I put together a team, and for a number of Saturdays, gathering with me, we did a feasibility study for the creation of more efficient rockets. It became clear that there was nothing to prevent us from doing so. Rocket technology has not progressed significantly since the 60s, perhaps they have stepped back! We decided to reverse this trend.
Anderson : And you turned it back.
Musk : Six years after we founded the company, in 2008 we launched our first rocket, the Falcon 1, into orbit. And the price, not the cost price, notice, and the total launch price for customers was about $ 7 million.
Anderson : How did you achieve such a low price?
Musk : I try to approach things based on physics. And physics teaches reasoning based on primary principles, and not by analogy. So I said, okay, let's look at the primary principles. What is the rocket made of? Aluminum alloys of aerospace class, as well as titanium, copper and carbon fiber. And then I asked, what is the cost of these materials in the commodity market? It turned out that the cost of the materials that make up the rocket was about 2% of its price, which is an insane ratio for large mechanical products.
Anderson : How does this compare, say, to cars?
Musk : It depends on the car. For Tesla, this is probably between 20 and 25 percent.
Anderson : The difference is in order.
Musk : Right. So, I thought, we are able to make rockets much cheaper with these materials costs. A lot of pretty stupid things should happen on the market. And so it is!
Anderson : Like what?
Musk : One of them is an incredible aversion to risk in large aerospace firms. Even if advanced technologies are already available, they still use obsolete components, often those developed in the 1960s.
Anderson : I heard that there is a rule that, in fact, you cannot fly with components that have not yet flown.
Musk : The right, which is obviously shown in the movie Trick-22 , is not it? There must be a joke by Groucho Marx about this. So yes, there is a huge bias against risk. Everyone is trying to optimize the cover of his ass.
Anderson : Good phrase.
Musk : The results are pretty crazy. One of our competitors, Orbital Sciences, has a contract to replenish the International Space Station’s reserves, and their rockets, in fact, it sounds like an anecdote, they use Russian rocket engines that were made in the 60s. I do not mean that their design is from the 60s, I mean that they start with engines that were made literally in the 60s and, like, are stored somewhere in Siberia.

Capsule Dragon Photo: Art Streiber
Anderson : Where else are the inefficiencies?
Musk : Secondly, there is a tendency of large aerospace companies to outsource everything. It was fashionable in many industries, but aerospace brought it to the point of absurdity. They give the order for outsourcing to subcontractors, and then the subcontractors outsource to sub-subcontractors, and so on. You have to go four or five levels down to find someone who actually does something useful, actually cuts metal, forms atoms. Each level above requires its own profit - it is overhead in the fifth degree.
Anderson : Is this the result of bureaucracy?
Musk : In many cases, the government was the largest customer, and the government’s contracts were what they called cost plus: the company gets a fixed level of profit no matter how wasteful its execution is. It actually encourages doing everything as expensive as possible, as far as can be justified.
Anderson : This kind of bureaucracy should also play a role in the bidding process.
Musk : This is going out. The Pentagon’s preferred approach is to enter into long-term contracts with a single counterparty, which means closing the entire business into one company! We tried to bid on the primary contract for the Air Force, but this is practically impossible, because the United Launch Alliance, owned by Boeing and Lockheed Martin, currently has an exclusive contract with the Air Force to launch satellites. This is completely inappropriate.
Anderson : Wow, really?
Musk : Even if we save taxpayers at least a billion dollars a year, this is still a conservative estimate.
Anderson : It sounds as if the essence of the proposal is not to surpass its competitors, but simply to compete on price.
Musk : Listen, the speed of the rocket will always be about the same. Convenience and comfort will be about the same. Reliability must be at least the same as what has been done before, otherwise people will not use rockets to launch satellites costing hundreds of millions of dollars, but there are not many opportunities for improvement. Thus, you really have one key parameter by which you need to judge the improvement of technology, and this is the price.
Anderson : So how do you do it? What is your process?
Musk : Now I have to say something to you, and I speak about it in the best and most harmless way possible: I do not believe in processes. In fact, when I interview a potential employee, and he or she says that “it's all about the process,” I see it as a bad sign.
Anderson : Oh, no. I'm fired.
Musk : The problem is that in many large companies the process becomes a substitute for thinking. You were called to behave like a little gear in a complex car. Honestly, it allows you to save people who are not so smart and devoid of creativity.
Anderson : So what did all your creative people come up with? What has changed in your base technology from what it was 50 years ago?
Musk : I can't tell you much. We have practically no patents in SpaceX. Our main long-term competition in China, and our published patents would become a farce, because the Chinese simply use them as a book of recipes. But I can give you one example.
Anderson : What?
Musk : This is the design of the aircraft. If you think about it, rockets are actually just a container for liquid oxygen and fuel, it is a combination of a fuel tank and an aircraft.
Traditionally, an aircraft rocket is made of an aluminum plate about two inches thick, from which everything unnecessary is cut off ( to get an element of a future cylinder arched in a profile from a flat plate? - Cholga’s note ). Then you fold what is left into the desired shape, usually in cylindrical segments, since the rockets are usually cylindrical in shape. This is how Boeing and Lockheed rockets are made, and most other rockets too. But this is a very expensive production method, because you use a small part of the initial mass of the plate. You start with a huge slab of material, and then you mill everything that is not needed, and you have huge material losses. In addition, the processing and removal of excess metal takes a long time, and all this is very expensive.
Anderson : What is the alternative?
Musk : This is similar to the way most airplanes are made: strength is ensured by fastening longitudinal and transverse stiffeners.
Anderson : It's like aluminum origami - it requires very precise cutting of the grooves in them so that they fold into a rigid form.
Musk : But there is one catch, because you can't rivet a rocket, as you can rivet a plane. The pressure drop for an aircraft — the difference between internal and external pressure during flight — is perhaps between 7 and 10 pounds per square inch. But in the case of a rocket, it is likely to be 80 pounds per square inch. It is much harder to rivet so as to resist leakage at this pressure.
Anderson : Right.
Musk : Thus, the approach used for aircraft is not quite suitable for missiles. But there is another way to do this - using advanced welding technology, which is called rotation welding. Instead of riveting the longitudinal and transverse stiffening ribs, you can use a special machine that softens the metals on both sides at the same time, without hobbling or melting them. Unlike traditional welding, which melts and potentially endangers certain metals, this process works well with high-strength aluminum alloys. You get the structure harder and easier than it was before. And your loss of material, maybe 10%, only when trimming the edges. And the ratio of material purchased to fly, as they call the ratio “bought / flew”, which used to be 10-20, you get much better - 1.1-1.2.
Anderson : Wow! Why aren't you afraid to tell us about this method?
Musk : I can safely talk about it, because no one knows how to build a rocket in this way. [ Laughs ]
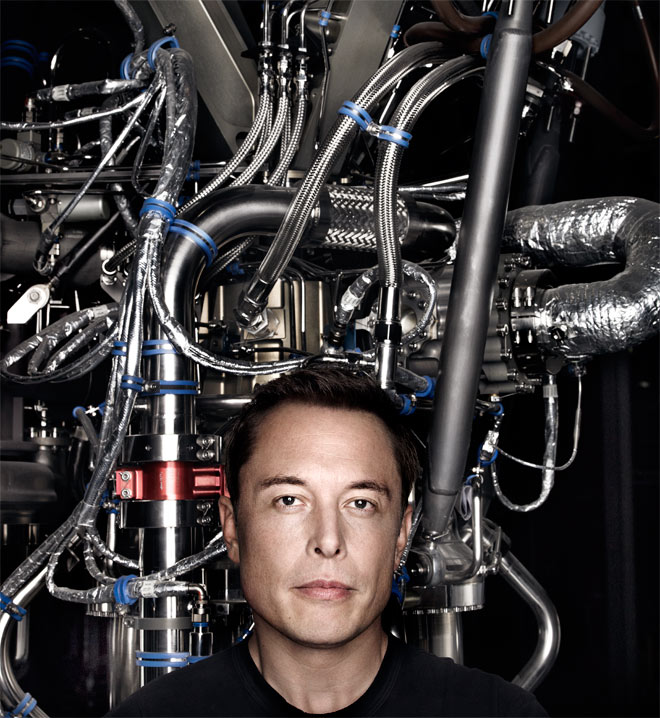
Mask on the background of the engine Merlin. Photo: Art Streiber
Anderson : Let's talk about where it all goes. You have reduced the cost of rocket launches 10 times. Suppose you can reduce it even more. How will this change the game? It seems that when you drastically reduce the price, you can open up a whole new market. This is in itself a form of research.
Musk : Right.
Anderson : Where do you see the prospects for the new market?
Musk : A huge market for satellites. There are many uses for satellites that suddenly begin to make sense if transportation costs are small: more telecommunications, more broadcasting, better weather forecasting, more scientific experiments.
Anderson : That is, the traditional segments of the satellite market are becoming cheaper.
Musk : There are also likely to be a lot more private space flights.
Anderson : You mean tourism.
Musk : Yes, but I think tourism is too derogatory. It can be argued that most of our state space flights were tourism. But the main goal, in which I still believe in the long term, is the settling of other planets.
Anderson : And the Dragon ship, which you docked to the ISS in May, has features that can ultimately prepare it for a manned mission to Mars.
Musk : Over time, yes. Shunting engines on the Dragon are large enough to provide emergency rescue at launch. That means the ability to move away from the rocket with an overload of about 6g. This is the same level of thrust, which is also suitable for supersonic drag when landing on Mars.
Anderson : Could you send the Dragon to Mars and not to the ISS?
Musk : Well, he would fly very slowly, and when he arrived, he could not sit down and leave a crater.
Anderson : So the problem is how to stop when you get there?
Musk : Dragon of the second version, which should be ready for three years, will be able to do it. But in fact, if humanity wants to become multi-planetary, the fundamental breakthrough that should occur in the rocket industry is fast and fully reusable rockets. While they are not, space transport will remain two orders of magnitude more expensive than it should be.
Anderson : Really?
Musk : Imagine that you need a new aircraft for each flight. Very few people will fly with it.
Anderson : Doesn't fuel account for most of the costs?
Musk : The cost of fuel on the Falcon 9 is only about 0.3 percent of the total price. So, if a vehicle costs $ 60 million, the fuel maybe a couple hundred thousand dollars. It is jet fuel for missiles, which is three times the cost of a normal jet fuel. This is due to the use of helium for pressurization, which is a very expensive supercharger. Next-generation missiles could use cheaper fuel and also be fully reused.
Anderson : What would you announce right now?
Musk : I hope that we could present the architecture next year. I would like to emphasize that this is the ambition of SpaceX, I am not saying that we will do it. But I believe this can be done. And I believe that this achievement would be equivalent to what the Wright brothers have done. This is the basic thing that is necessary for humanity to become a space civilization. America would never have been colonized if the ships could not be reused.
Anderson : But wasn't the space shuttle reusable?
Musk : Many people think that it was reusable, but the main fuel level was thrown away every time. Even the parts that were actually returning were so difficult to upgrade that the shuttle cost four times as much as the equivalent payloads would have required.
Anderson : It's like sending the ships to Columbus, and returning the lifeboat back.
Musk : We started testing the re-use of rockets from the Grasshopper project - this is a Falcon 9 with a first stage with a chassis that can take off and land vertically.
Anderson : Huge rockets landing on their feet? Holy shit.
Musk : Yes, Holy shit. When it goes into orbit, the first stage turns around, restarts the engine, returns back to the launch site, reorients, deploys the chassis, and lands vertically.
Anderson : It looks like something from a movie or my old books about Tentin ( Tintin ). This is the way to space, which was supposed to be.
Musk : Exactly.
Chris Anderson (@ chr1sa) is the editor-in-chief of Wired and the author of Figures: The New Industrial Revolution (Makers: The New Industrial Revolution)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/157487/
All Articles