Messaging between the cloud and the device (Cloud to Device Messaging)
Messaging between the cloud and the Android device (C2DM) is a service that allows developers to send data from servers to applications on Android devices. The service provides a simple and easy mechanism that servers can use to inform mobile applications about communicating with the server directly to receive application updates or user data. The C2DM service manages all aspects of message queuing and delivery to the target application running on the target device.
Messaging between the cloud and the device includes key terms and concepts that can be classified into two divisions. It:
')
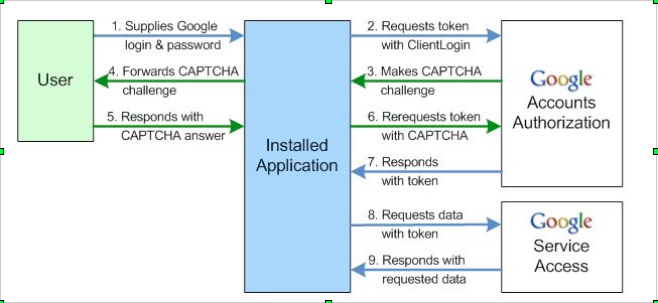
Identifiers and tokens that are used at different stages of C2DM to ensure that all parties are authorized and that the message is sent to the right place.
This is an email account associated with the application developer. The sender ID is used in the registration process to identify the Android application that is allowed to send messages to the device. This identifier is usually based on a role, and not on a personal account, for example, my-app@gmail.com
This is the application ID that is registered to receive messages. An application is identified by the package name from the manifest. This ensures that messages are targeted to the right application.
The identifier given by the C2DM servers of the Android application to allow it to receive messages. Once an application receives a registration ID, it sends it to a third-party application server, which uses it to identify each device that has registered to receive messages for that application. In other words, the registration ID is associated with a specific application running on a specific device. For a Google account for C2DM to work, a mobile device must include at least one authorized Google account.
ClientLoginAuth is a token that is stored on a third-party application server and gives the application server authorized access to Google services. The token is included in the POST header of the requests that send messages.
The main processes used in the exchange of messages between the cloud and the device:
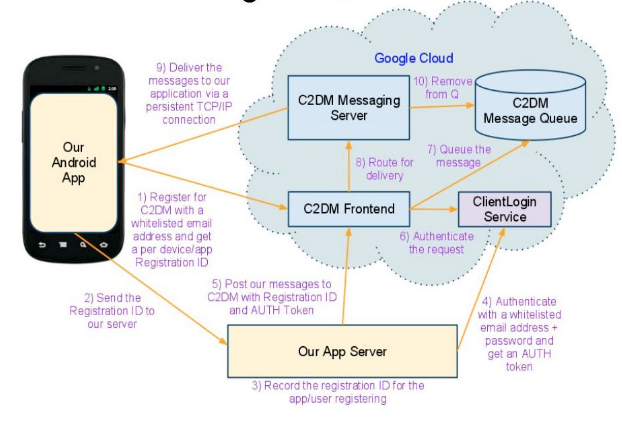
Below is a sequence of events that occur when an Android application running on a mobile device is registered to receive messages:
In order for the application server to send messages, the following conditions must be met:
There is one more condition that is necessary for the application server to send messages: Client Login authorization token. Client Login token authorizes the application server to send messages to a specific Android application. The application server has one Client Login token for a specific third-party application and several registration identifiers. Each registration ID represents a particular device that has registered to use the messaging service for a particular third-party application.
The sequence of events that occur when the application server sends a message:
An application can deregister C2DM if it no longer needs to receive messages.
This is the sequence of events that occurs when an Android application running on a mobile device receives a message:
C2DM Android Features
The main characteristics of C2DM:
- It allows third-party application servers to send small messages to their Android applications. The messaging service is not intended to send large amounts of user data through messages. On the contrary, it should be used to inform the application that there is new data on the server, and that the application can pick it up.
- The application on the Android device does not need to run to receive messages. The system will launch the application through the target broadcast when a message arrives, if the application is installed with the appropriate broadcast receiver and permissions.
- It uses the existing connection for Google services. This requires users to set up a Google account on their mobile devices.
Architecture Overview
Messaging between the cloud and the device includes key terms and concepts that can be classified into two divisions. It:
- Components
- Credentials

')
Credentials
Identifiers and tokens that are used at different stages of C2DM to ensure that all parties are authorized and that the message is sent to the right place.
Sender ID
This is an email account associated with the application developer. The sender ID is used in the registration process to identify the Android application that is allowed to send messages to the device. This identifier is usually based on a role, and not on a personal account, for example, my-app@gmail.com
Application ID
This is the application ID that is registered to receive messages. An application is identified by the package name from the manifest. This ensures that messages are targeted to the right application.
Registration ID
The identifier given by the C2DM servers of the Android application to allow it to receive messages. Once an application receives a registration ID, it sends it to a third-party application server, which uses it to identify each device that has registered to receive messages for that application. In other words, the registration ID is associated with a specific application running on a specific device. For a Google account for C2DM to work, a mobile device must include at least one authorized Google account.
Sender Auth Token Auth Token
ClientLoginAuth is a token that is stored on a third-party application server and gives the application server authorized access to Google services. The token is included in the POST header of the requests that send messages.
C2DM life cycle
The main processes used in the exchange of messages between the cloud and the device:
- Enable C2DM: Android application running on a mobile device is registered to receive messages.
- Send Message: A third-party application server sends messages to the device.
- Receive message: The Android application receives a message from the C2DM server.

Enable C2DM
Below is a sequence of events that occur when an Android application running on a mobile device is registered to receive messages:
- The first time an application needs to use a messaging service, it sends a C2DM registration request to the server.
This registration request includes the sender ID (this is an account authorized to send messages to the application, which is usually the email address of the account configured by the application developer) and the application ID. - The C2DM server transmits a request that gives the application a registration ID.
The application stores this identifier for further use. Google may periodically update the registration ID, so the application is designed taking into account that the registration intent can be invoked several times. - To complete registration, the application sends the registration ID to the application server. The application server typically stores the registration ID in the database.
The registration ID is valid until the application cancels the registration itself or until Google updates the registration ID for your application.
Posting a message
In order for the application server to send messages, the following conditions must be met:
- The presence of the registration ID of the application, which allows it to receive messages for a specific device.
- The registration ID is stored on the application server.
There is one more condition that is necessary for the application server to send messages: Client Login authorization token. Client Login token authorizes the application server to send messages to a specific Android application. The application server has one Client Login token for a specific third-party application and several registration identifiers. Each registration ID represents a particular device that has registered to use the messaging service for a particular third-party application.
The sequence of events that occur when the application server sends a message:
- The application server sends a message to the C2DM servers.
- Google queues and saves a message in case the device is inactive.
- If the device is online, Google sends a message to the device.
- On the device, the system transmits the message to a specific application through the target broadcast with the appropriate permissions, so that only the target application receives the message. This launches the application. The application does not require pre-launch to receive the message.
- The application processes the message. If the application performs non-trivial processing, you may want to use wake lock and do any processing in the service.
An application can deregister C2DM if it no longer needs to receive messages.
Receiving a message
This is the sequence of events that occurs when an Android application running on a mobile device receives a message:
- The system receives the incoming message and extracts the raw key / value pairs from the message.
- The system sends key / value pairs to the target Android application in the request (in a Intent) as a set of additional parameters.
- The Android application extracts the raw data from the request (intent) by key and processes the data.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/156933/
All Articles