Curiosity conducted the most detailed geological research on Mars
X-ray diffraction is one of the most accurate methods of mineralogical analysis. Thanks to this method, it turns out to know exactly the mineral composition, and not chemical. After all, for example, diamond and graphite, from the point of view of chemistry, are identical, but different conditions of formation influenced the structure of the crystal lattice, and radically changed the properties of the mineral. The goal of Curiosity is to determine exactly what conditions led to the emergence of a particular mineral, which means to find out what conditions were on Mars in ancient times.
Read more about the device and the device CheMin: habrahabr.ru/post/154691
On October 17 or at 71 Martian salt, MSL Curiosity scooped up sand for the third time, sifted it on the manipulator in the CHIMRA device, and poured a small pinch into the CheMin soil receiving hopper. The first two buckets of sand did not go into action because of the danger of plastic fragments falling off the rover. (The fragment fell off alone, but the bright stone found in the second excavation resulted in NASA deciding to play it safe and examine it carefully at first. For more information: habrahabr.ru/post/155449 ).
CHIMRA sifted only particles of no more than 150 microns, but NASA did not want to rely on a sieve, so it simply gathered a new bucket of soil. To get a guaranteed local sample, without alien "additives".
The video, shot on Earth, shows how the process of soil extraction takes place.
')
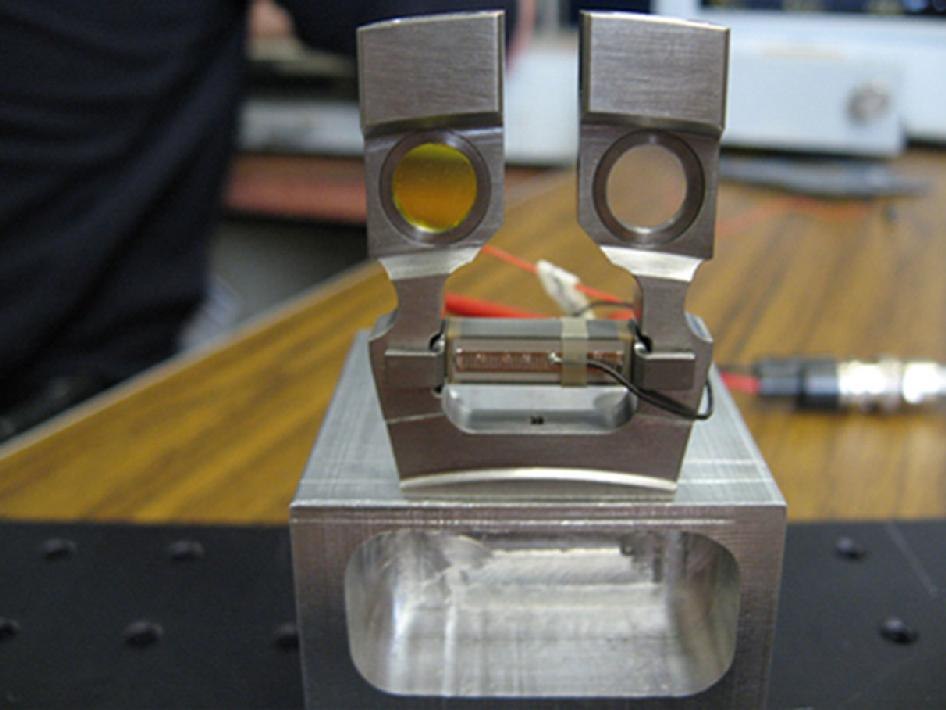
After the CheMin funnel, the sample fell into a round transparent cell with a diameter of 8 mm and a thickness of 175 microns. These cells are located on the petals of the instrument wheel, which, using the revolving principle, provides samples for X-ray irradiation.
When the cell stops in front of the radiation source, it begins to vibrate at a frequency of 2 thousand vibrations per second. Because of this, the sand in the cell acquires the properties of a liquid and begins to circulate inside. Therefore, under the thin, like human hair, the beam hits a lot of the investigated particles.
The process of the device is depicted in the demo animation from 9:08
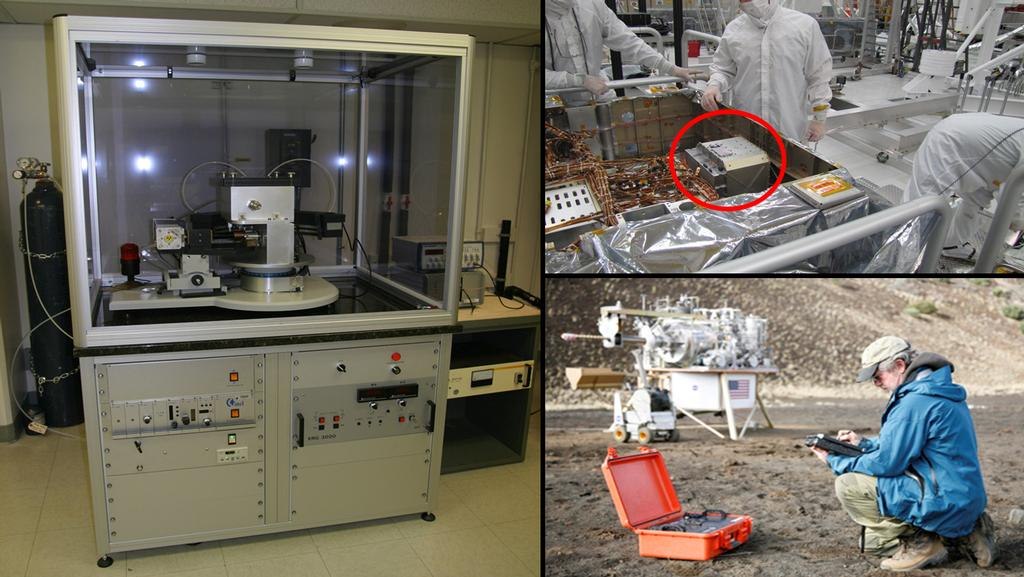
This technology was developed by NASA and it allowed reducing the size of X-ray diffraction devices from the size of two refrigerators to a cube with a side of 25 cm or even to a case. Now it is used by geologists in the fields, as well as found use in the pharmaceutical industry.

X-ray diffraction involves the refraction of X-rays in mineral crystals, and the fixation of this refraction on the photomatrix. On the device CheMin placed CCD matrix with a resolution of 600 by 600 pixels.

The optimum mode of its operation requires a temperature of -60 ° C, so the study is conducted at night when the device reaches the required temperature. If it is warmer, then noises from the neutron generator of the DAN instrument will be introduced into the readings of the matrix.
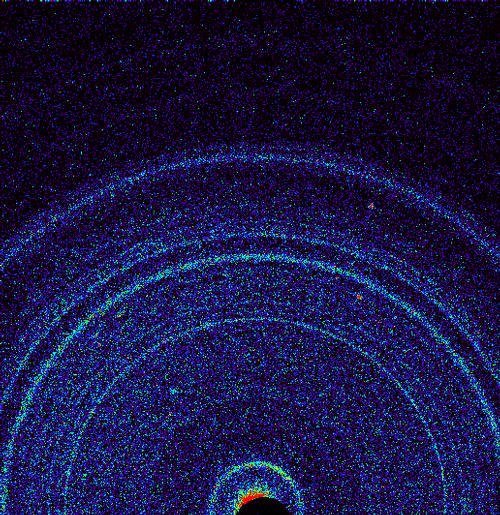
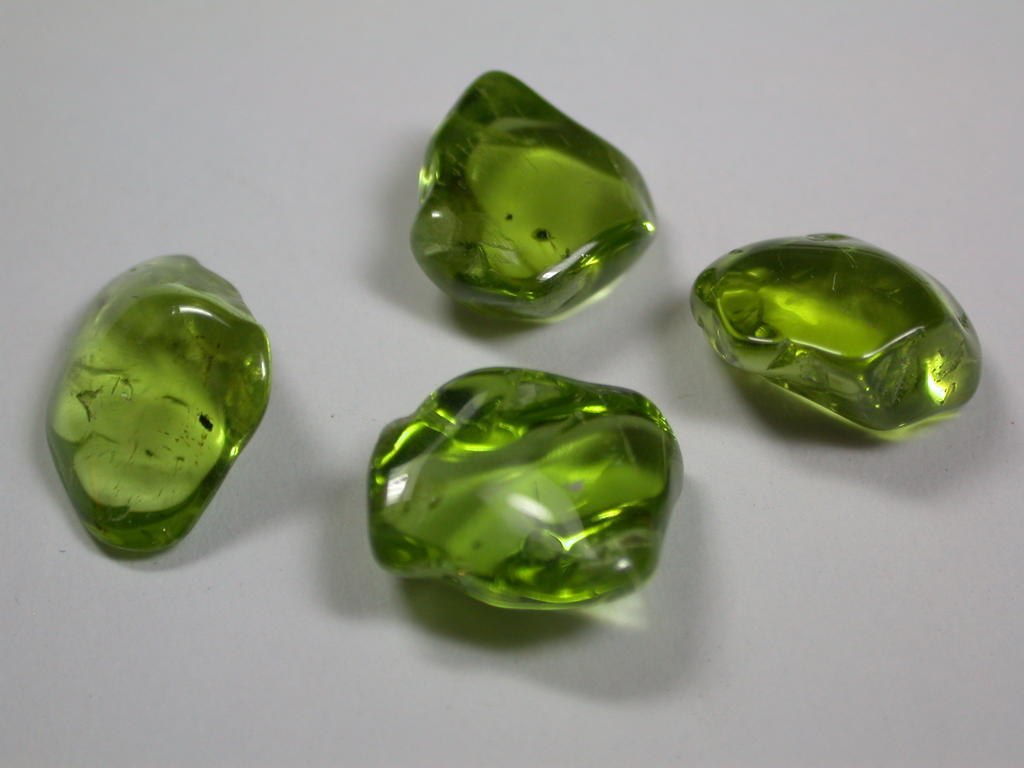
Geologists already know the diffraction patterns that draw certain crystals in such devices, so they need only get a photo from Mars, and determine what the rover has studied. Photo posted at the beginning of the article. The result of the first study showed that sand has a characteristic structure for volcanic soil and contains feldspar, pyroxene and olivine. Photos of earth samples of olivine:

By the way, about the same geological structure had "Jake Matievich" - a large stone with addiction studied a month earlier: habrahabr.ru/post/154517
About half of the sand particles studied had a crystalline structure, the rest had an amorphous structure and did not leave fingerprints in the photograph.
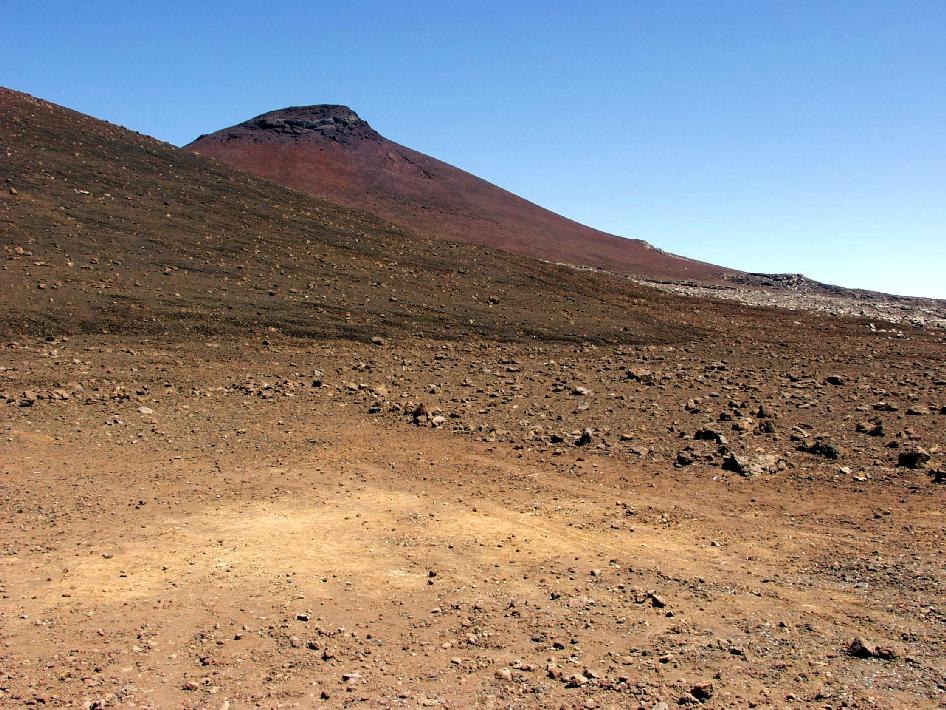
Terrestrial volcanic soils have a similar composition, for example, at the foot of Mauna Kea in Hawaii.

In addition to the basic mineralogical study, Curiosity continued the usual work: he shot panoramas, shot the surrounding stones and sand with a ChemCam laser.
At the sand spit, called Rocknest, the rover is already more than three weeks.
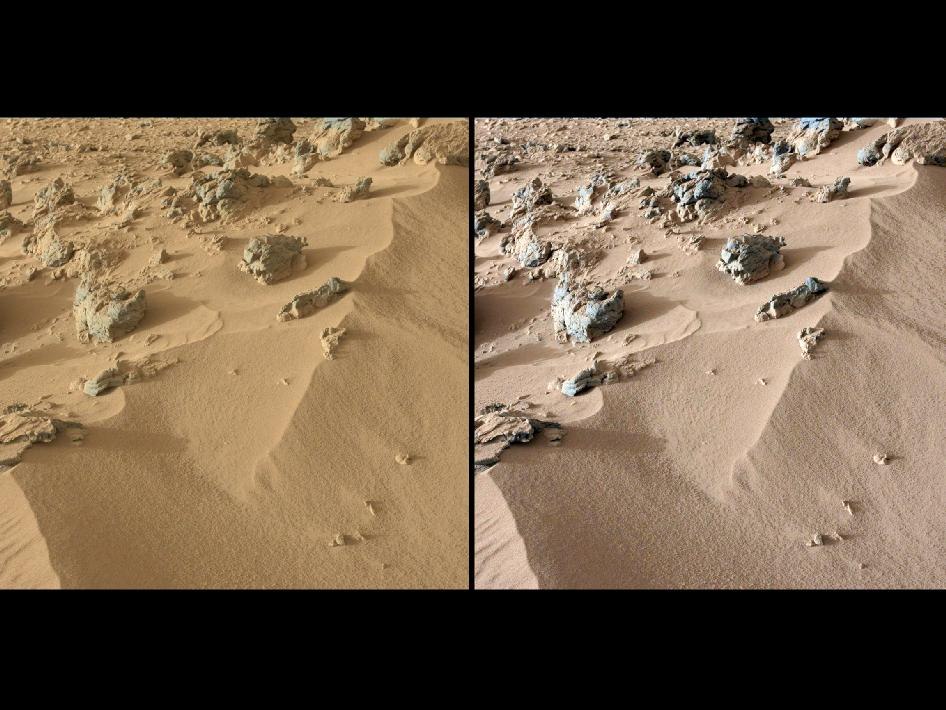

(on the left is the original color, on the right is the NASA balance adjusted for terrestrial lighting)
But during the time he spent there, he shot many panoramas with the Mast Cam Right camera.
For example, a fragment with traces of Curiosity

3735 × 791px 1.3 mb
The color was not adjusted.
And this is a look at the Northwest

2927 × 800px 1.2 mb
Curiosity usually just shoots stones with a laser:

or sand

But one day he became very interested in an unusual stone:

He didn't just shoot him

He shot it with seven frames of Mast Cam Right through different color filters, eight frames of ChemCam with different depth of field, so that we managed to collect a picture with high details
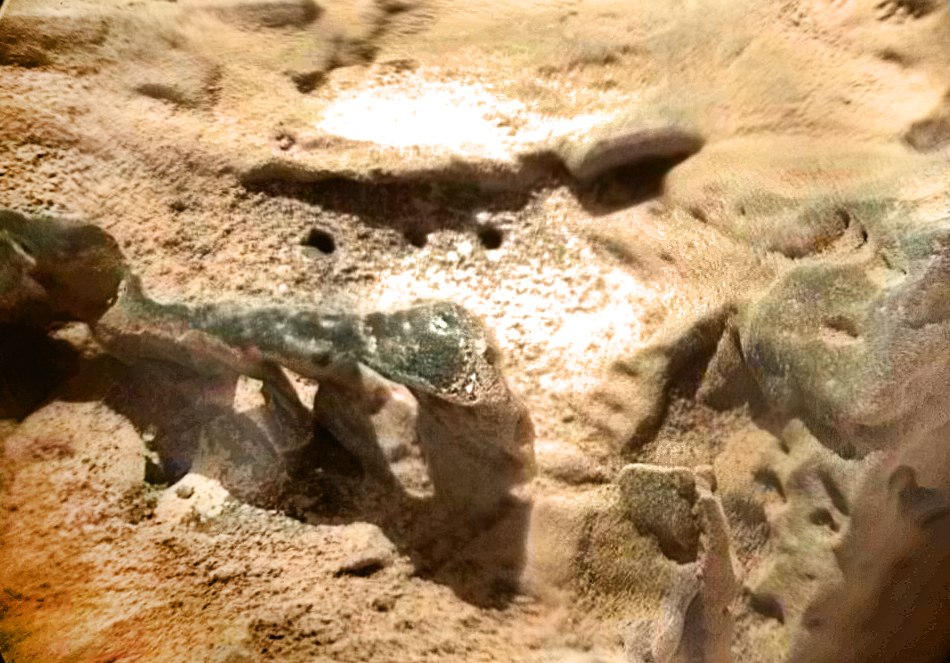

In fact, Curiosity did everything he could do at such a distance. I already suspected something was amiss: the shape of the stone is strange: whether it looks like a giant ant, or sticking on its ribs; and NASA's interest is not normal ... But it seems they were just practicing in the creation of three-dimensional models

Although about the chemical composition has not yet been told, but it seems there were no sensations. There are many fancy stones.
PS If anyone wants to learn more news from Mars, I suggest to subscribe to twitter: Curiosity_live_ru

Read more about the device and the device CheMin: habrahabr.ru/post/154691
On October 17 or at 71 Martian salt, MSL Curiosity scooped up sand for the third time, sifted it on the manipulator in the CHIMRA device, and poured a small pinch into the CheMin soil receiving hopper. The first two buckets of sand did not go into action because of the danger of plastic fragments falling off the rover. (The fragment fell off alone, but the bright stone found in the second excavation resulted in NASA deciding to play it safe and examine it carefully at first. For more information: habrahabr.ru/post/155449 ).
CHIMRA sifted only particles of no more than 150 microns, but NASA did not want to rely on a sieve, so it simply gathered a new bucket of soil. To get a guaranteed local sample, without alien "additives".
The video, shot on Earth, shows how the process of soil extraction takes place.
')
After the CheMin funnel, the sample fell into a round transparent cell with a diameter of 8 mm and a thickness of 175 microns. These cells are located on the petals of the instrument wheel, which, using the revolving principle, provides samples for X-ray irradiation.

When the cell stops in front of the radiation source, it begins to vibrate at a frequency of 2 thousand vibrations per second. Because of this, the sand in the cell acquires the properties of a liquid and begins to circulate inside. Therefore, under the thin, like human hair, the beam hits a lot of the investigated particles.
The process of the device is depicted in the demo animation from 9:08
This technology was developed by NASA and it allowed reducing the size of X-ray diffraction devices from the size of two refrigerators to a cube with a side of 25 cm or even to a case. Now it is used by geologists in the fields, as well as found use in the pharmaceutical industry.

X-ray diffraction involves the refraction of X-rays in mineral crystals, and the fixation of this refraction on the photomatrix. On the device CheMin placed CCD matrix with a resolution of 600 by 600 pixels.

The optimum mode of its operation requires a temperature of -60 ° C, so the study is conducted at night when the device reaches the required temperature. If it is warmer, then noises from the neutron generator of the DAN instrument will be introduced into the readings of the matrix.
Geologists already know the diffraction patterns that draw certain crystals in such devices, so they need only get a photo from Mars, and determine what the rover has studied. Photo posted at the beginning of the article. The result of the first study showed that sand has a characteristic structure for volcanic soil and contains feldspar, pyroxene and olivine. Photos of earth samples of olivine:

By the way, about the same geological structure had "Jake Matievich" - a large stone with addiction studied a month earlier: habrahabr.ru/post/154517
About half of the sand particles studied had a crystalline structure, the rest had an amorphous structure and did not leave fingerprints in the photograph.
Terrestrial volcanic soils have a similar composition, for example, at the foot of Mauna Kea in Hawaii.

In addition to the basic mineralogical study, Curiosity continued the usual work: he shot panoramas, shot the surrounding stones and sand with a ChemCam laser.
At the sand spit, called Rocknest, the rover is already more than three weeks.

(on the left is the original color, on the right is the NASA balance adjusted for terrestrial lighting)
But during the time he spent there, he shot many panoramas with the Mast Cam Right camera.
For example, a fragment with traces of Curiosity

3735 × 791px 1.3 mb
The color was not adjusted.
And this is a look at the Northwest

2927 × 800px 1.2 mb
Curiosity usually just shoots stones with a laser:

or sand

But one day he became very interested in an unusual stone:

He didn't just shoot him

He shot it with seven frames of Mast Cam Right through different color filters, eight frames of ChemCam with different depth of field, so that we managed to collect a picture with high details

In fact, Curiosity did everything he could do at such a distance. I already suspected something was amiss: the shape of the stone is strange: whether it looks like a giant ant, or sticking on its ribs; and NASA's interest is not normal ... But it seems they were just practicing in the creation of three-dimensional models

Although about the chemical composition has not yet been told, but it seems there were no sensations. There are many fancy stones.
PS If anyone wants to learn more news from Mars, I suggest to subscribe to twitter: Curiosity_live_ru
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/156771/
All Articles