AutoTracker software. Work with routes and schedules
In the previous post, we talked about the main features of the AutoTracker software. But there are specialized software modules that are worth mentioning separately.
City administrations and bus fleets are now trying to actively implement satellite-based transport monitoring systems. In many cases, they are prompted by the legislative acts recently adopted as part of the federal target program for the development of the GLONASS system and the law On Navigation Activities. There were even GOSTs on this topic, in particular GOST R 54024-2010 "Dispatch management systems for urban land passenger transport." In practice, the customers themselves often did not fully understand what functions the system should perform and how it works. In such cases, the developers recommended something ready that could approximately fit their needs. Historically, in the process of such interactions of car fleet representatives and developers, a number of well-established solutions have emerged, one of which is the service of working with routes.
Consider how this service works in the AutoTracker system. The route consists of points - bus stops. All bus stops are entered into the database in the form of graphic objects. The easiest route is, in fact, a collection of graphic objects - bus stops.
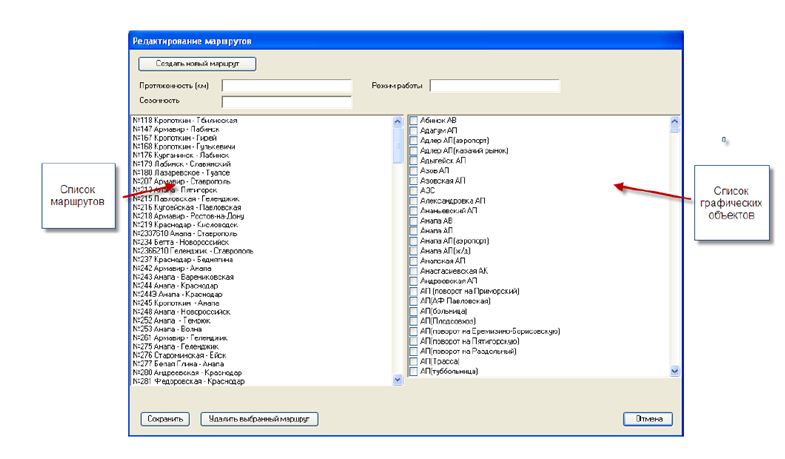
Putting and removing ticks on the objects you can create and edit any route.
But a simple route in the form of a set of objects in practice is required only for the transportation of goods by points. It does not take into account neither the sequence of visits to points, nor the time of delivery. And in some cases it is really not critical. But in passenger traffic routes are always used with the order of the visit. To do this, in the form of creating a route, you can choose the type of route.
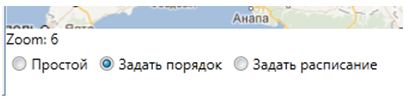
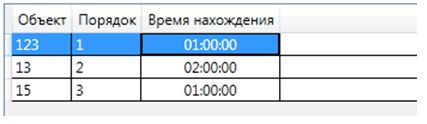
On routes with a given order of visit it is possible to set the time spent on the object (for example, at a bus stop).
For many routes, especially long-distance, necessary binding to the schedule. The route with the schedule is characterized by the fact that for each stopping point the time of entry and exit from the object is specified.
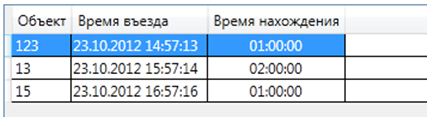
And for one route several schedules can be used. In a special schedule editor, they can be edited and linked to routes.

When all the objects are prepared, routes have been created, schedules are set, it remains to tie these routes to specific cars. For this there is a so-called "Planning Center".
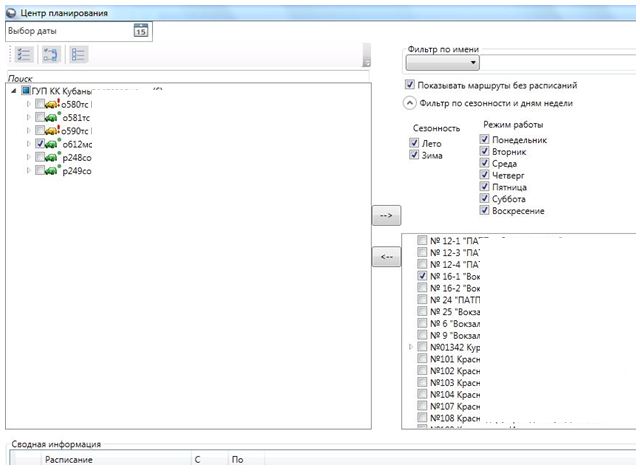
This module allows you to configure all the relationships between specific buses and routes, set the dates, seasonality and weekdays of the bus on the route. The same bus can travel on different routes on different days, so it is possible to set several routes for it at once.
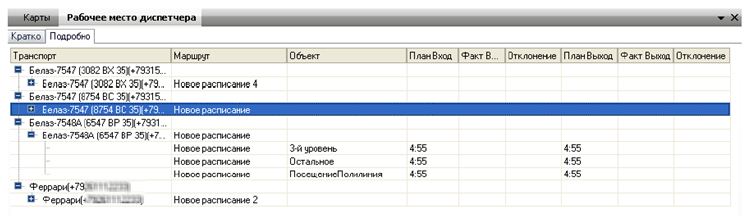
After all the preliminary settings, the dispatcher can start work. For this there is a module "Dispatcher workplace". The main task of the dispatcher is to monitor compliance with the schedule and track the plan / fact. Further actions depend on the rules of the specific fleet, but the plan / fact and deviations are convenient to track, they are highlighted in a separate column of the form. Here you can see the time of deviation in the schedule for visiting each object (stop).
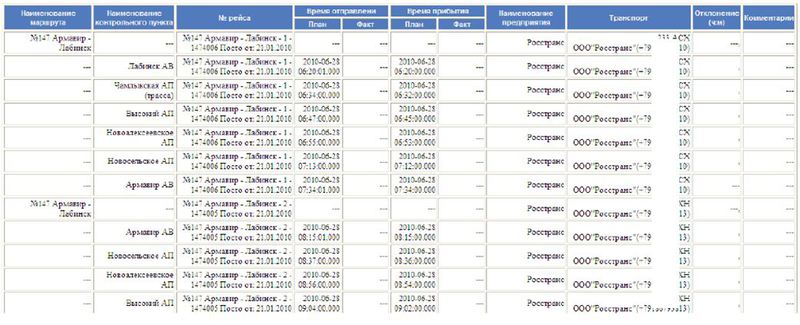
The dispatcher receives this data online. But in most cases it is required to generate a report on the work of transport for a certain period (day, week, month). For this there is a special report on the observance of the route schedule. The report presents data on the implementation of the plan / actual indicators and deviations for all vehicles and for any required period.
Such reports are intended mainly for the management and administration of the fleet when analyzing the work of the automobile enterprise as a whole.
But planning and monitoring compliance with the parameters of the route is not the only component of the solution for bus fleets. If the route service helps dispatchers in the first place to organize and streamline the work of transport, then the “Prediction Service” and “Autoinformer” help passengers directly.
Recently, a lot of talk has been going on about “smart” bus stops, an integral part of which is the LED display, which displays the bus arrival time for each route.

And if the routes of each stop are known in advance, then the arrival time is variable. And it calculates this time Service forecasts. This is done as follows. GPS determines the location of the bus and the current speed. This information is compared with targets and historical data. A special algorithm, taking into account these parameters, calculates the expected time of arrival at the stop. Information is corrected at a specified frequency, which can be configured in the system, for example, 1 time per minute. In accordance with the adjustments are changing data and on the scoreboard.
Another service for passengers has existed since time immemorial, but if earlier the driver himself turned on the recording at each stop, now the system does it automatically. It happens as follows. The informant is equipped with a built-in GLONASS / GPS receiver, which determines the location of the bus. In the memory of the informant is information about the coordinates of all bus stops. Arriving at the appropriate stop, the system generates a command that activates the audio recording corresponding to the given stop. Record is broadcast to passengers at the right time without the participation of the driver. But it is necessary to announce the same, what is the next stop, so that passengers prepare in advance for the exit. This is also done automatically, although the technology in this case is much more simple. The same autoinformer is connected to the driver's door closing button. When the doors close, he warns of this and announces the next stop.
City administrations and bus fleets are now trying to actively implement satellite-based transport monitoring systems. In many cases, they are prompted by the legislative acts recently adopted as part of the federal target program for the development of the GLONASS system and the law On Navigation Activities. There were even GOSTs on this topic, in particular GOST R 54024-2010 "Dispatch management systems for urban land passenger transport." In practice, the customers themselves often did not fully understand what functions the system should perform and how it works. In such cases, the developers recommended something ready that could approximately fit their needs. Historically, in the process of such interactions of car fleet representatives and developers, a number of well-established solutions have emerged, one of which is the service of working with routes.
Consider how this service works in the AutoTracker system. The route consists of points - bus stops. All bus stops are entered into the database in the form of graphic objects. The easiest route is, in fact, a collection of graphic objects - bus stops.

Putting and removing ticks on the objects you can create and edit any route.
But a simple route in the form of a set of objects in practice is required only for the transportation of goods by points. It does not take into account neither the sequence of visits to points, nor the time of delivery. And in some cases it is really not critical. But in passenger traffic routes are always used with the order of the visit. To do this, in the form of creating a route, you can choose the type of route.

On routes with a given order of visit it is possible to set the time spent on the object (for example, at a bus stop).

For many routes, especially long-distance, necessary binding to the schedule. The route with the schedule is characterized by the fact that for each stopping point the time of entry and exit from the object is specified.

And for one route several schedules can be used. In a special schedule editor, they can be edited and linked to routes.

When all the objects are prepared, routes have been created, schedules are set, it remains to tie these routes to specific cars. For this there is a so-called "Planning Center".

This module allows you to configure all the relationships between specific buses and routes, set the dates, seasonality and weekdays of the bus on the route. The same bus can travel on different routes on different days, so it is possible to set several routes for it at once.
After all the preliminary settings, the dispatcher can start work. For this there is a module "Dispatcher workplace". The main task of the dispatcher is to monitor compliance with the schedule and track the plan / fact. Further actions depend on the rules of the specific fleet, but the plan / fact and deviations are convenient to track, they are highlighted in a separate column of the form. Here you can see the time of deviation in the schedule for visiting each object (stop).

The dispatcher receives this data online. But in most cases it is required to generate a report on the work of transport for a certain period (day, week, month). For this there is a special report on the observance of the route schedule. The report presents data on the implementation of the plan / actual indicators and deviations for all vehicles and for any required period.

Such reports are intended mainly for the management and administration of the fleet when analyzing the work of the automobile enterprise as a whole.
But planning and monitoring compliance with the parameters of the route is not the only component of the solution for bus fleets. If the route service helps dispatchers in the first place to organize and streamline the work of transport, then the “Prediction Service” and “Autoinformer” help passengers directly.
Recently, a lot of talk has been going on about “smart” bus stops, an integral part of which is the LED display, which displays the bus arrival time for each route.

And if the routes of each stop are known in advance, then the arrival time is variable. And it calculates this time Service forecasts. This is done as follows. GPS determines the location of the bus and the current speed. This information is compared with targets and historical data. A special algorithm, taking into account these parameters, calculates the expected time of arrival at the stop. Information is corrected at a specified frequency, which can be configured in the system, for example, 1 time per minute. In accordance with the adjustments are changing data and on the scoreboard.
Another service for passengers has existed since time immemorial, but if earlier the driver himself turned on the recording at each stop, now the system does it automatically. It happens as follows. The informant is equipped with a built-in GLONASS / GPS receiver, which determines the location of the bus. In the memory of the informant is information about the coordinates of all bus stops. Arriving at the appropriate stop, the system generates a command that activates the audio recording corresponding to the given stop. Record is broadcast to passengers at the right time without the participation of the driver. But it is necessary to announce the same, what is the next stop, so that passengers prepare in advance for the exit. This is also done automatically, although the technology in this case is much more simple. The same autoinformer is connected to the driver's door closing button. When the doors close, he warns of this and announces the next stop.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/156295/
All Articles