Curiosity sent the first soil sample for internal research
Curiosity has 10 scientific instruments, but only two of them are located in the body of the rover. One of them - Chemistry and Mineralogy instrument or CheMin for the first time during the expedition received a portion of Martian soil, and began the first research. Samples in the device are delivered using the CHIMRA device on the manipulator of the rover.
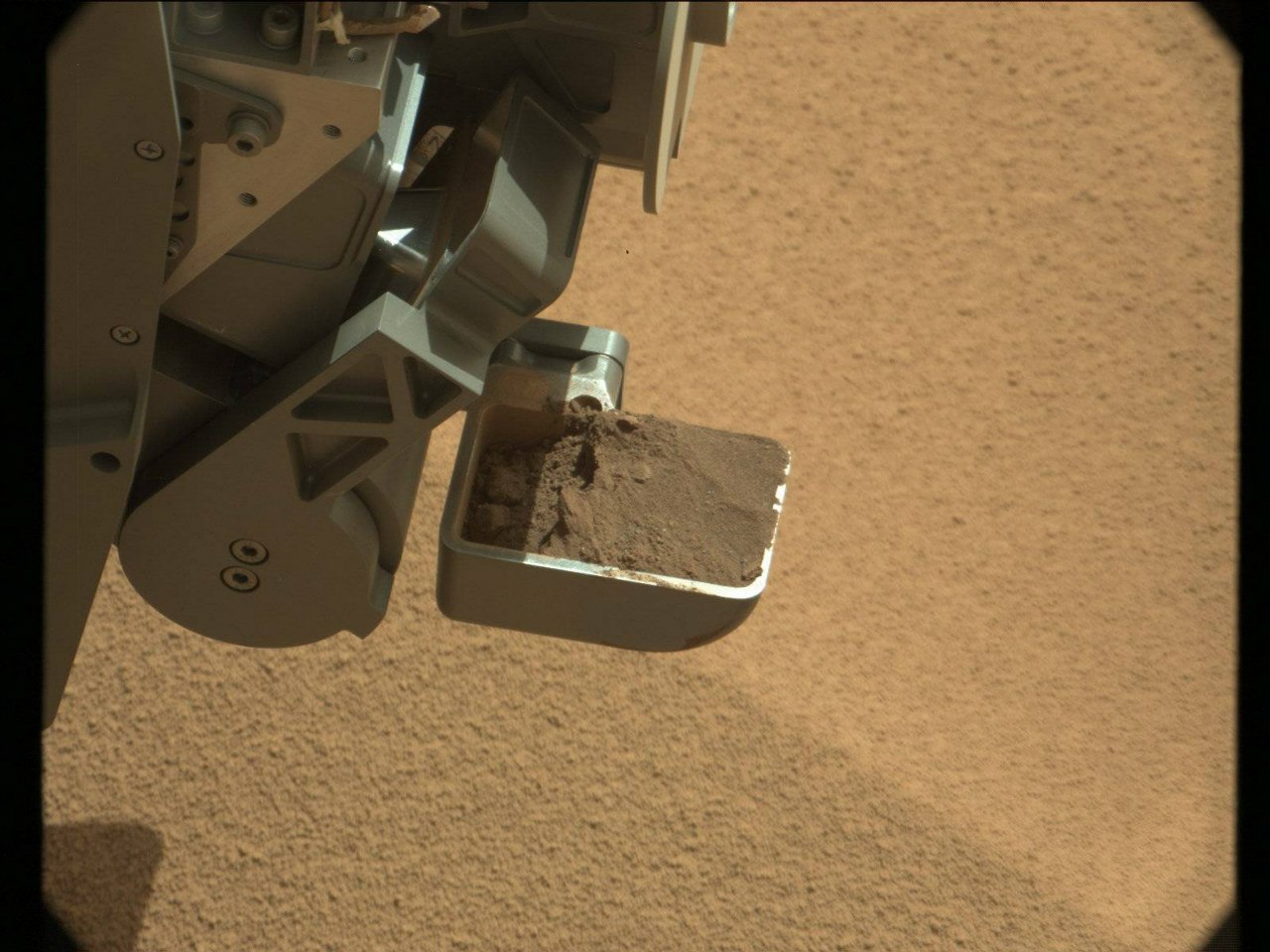

CHIMRA is a small bucket of 4x7 cm for soil sampling, and several cavities connected to each other, for sifting the gathered soil and preparing for loading into CheMin. This device requires particles no larger than 150 microns, so you have to try.

On the combination of two photos before and after loading, it is clear that a bit of sand has woken past the mouth of the CheMin soil receiver.
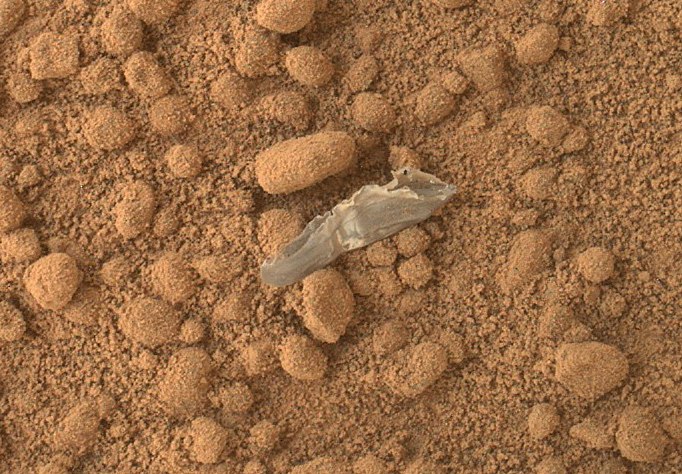
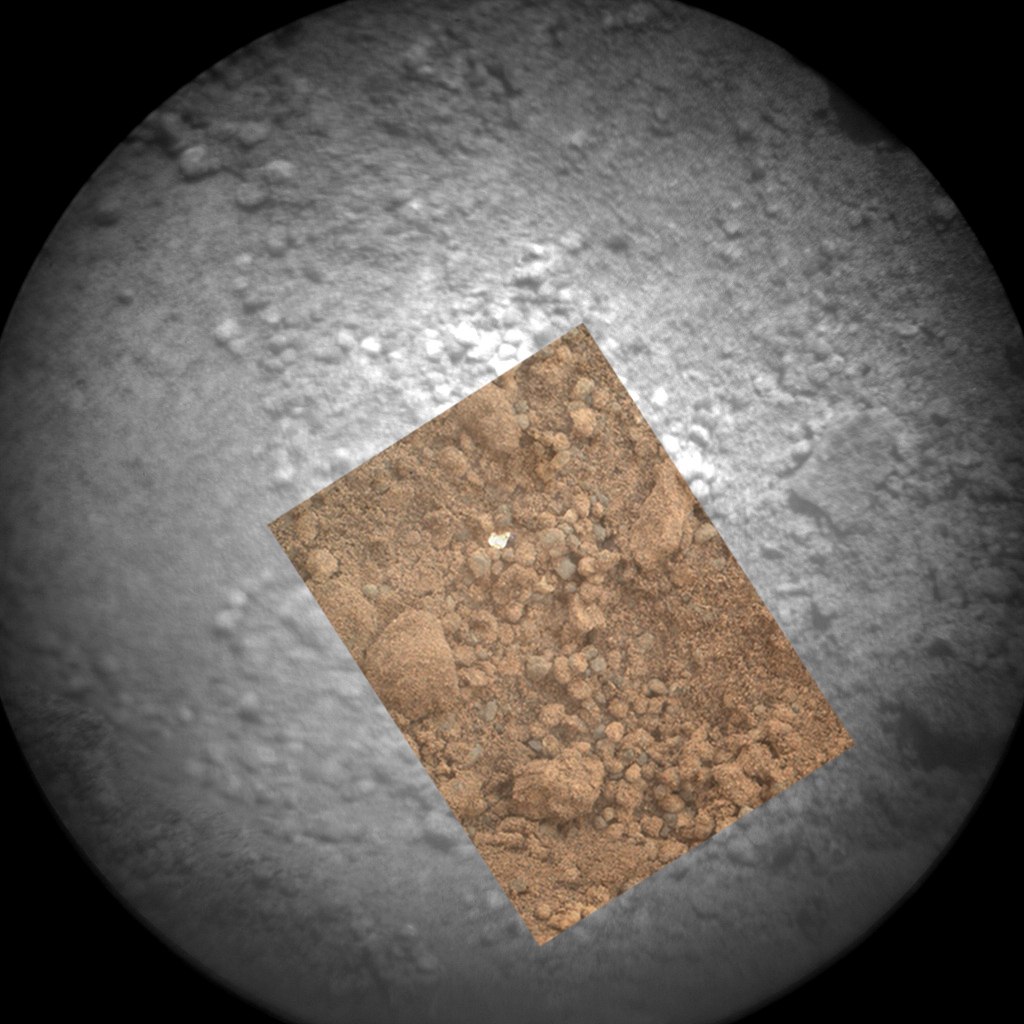
In just the past eleven days that Curiosity spent at the Rocknest site, three soil intakes have been produced. After the first, before the rover, a small bright object of clearly non-Martian origin was found.

')
Fearing that Curiosity is starting to fall apart, NASA stopped all scientific work for two days, until the subject was properly studied and found out that it was by some miracle that a piece of packing material of the rover or SkyCrane reached this place.
When the bucket made the next hole, some bright object 1.5-2 mm in size was again found in it.

And again the ground did not go to destination, but was poured out. NASA decided to eliminate the possibility that a piece of plastic, brought from Earth and falling off at the wrong moment, would be sent for research. The new discoveries involved a camera on the MAHLI manipulator, which allows it to act as a microscope. Thanks to her, it was determined that the bright subject is a local material.
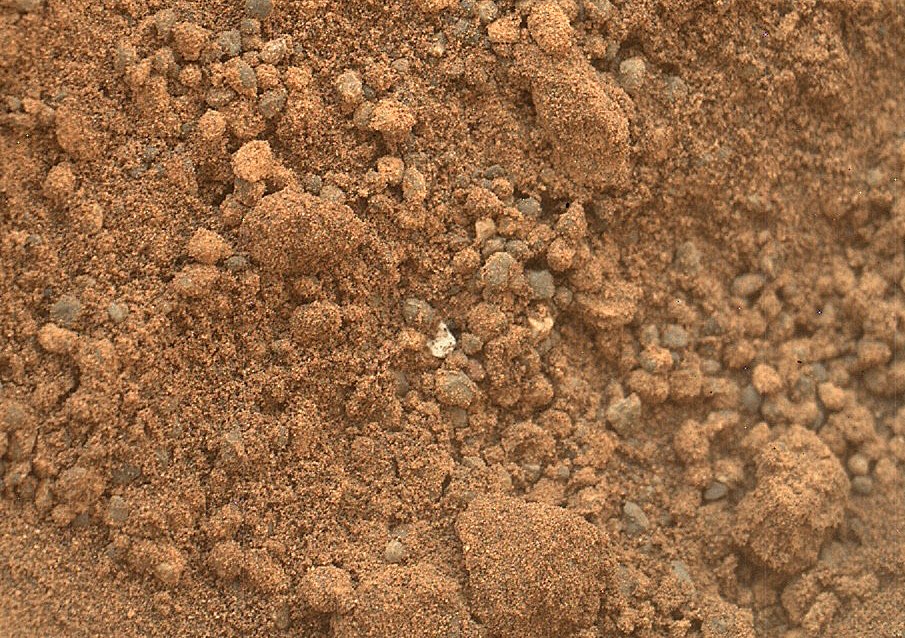

Finally, after making sure that nothing else interferes with the research, a third soil sampling was carried out, and he went to the CheMin study. Before placing the prepared and sifted sample inside, part of it was spilled on the “sample table” - a special protrusion on the rover’s body, where a metal disk 7.8 cm (3 inches) in diameter was placed.
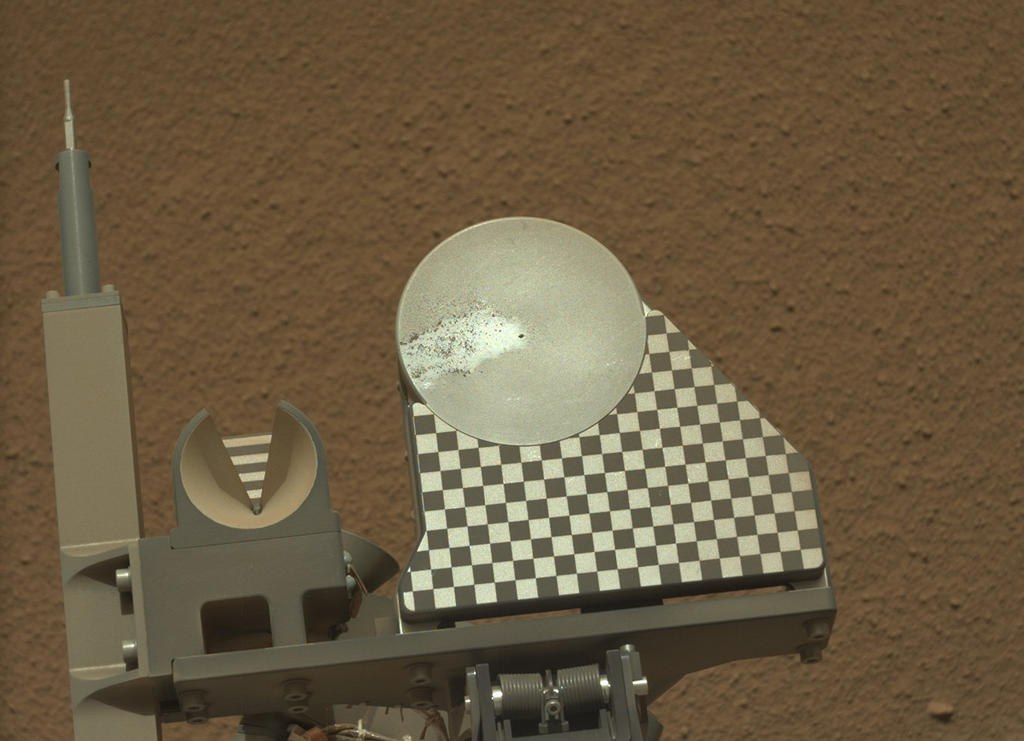

There are not many sand grains left on the “table”, but they dispersed the dust lying on it, and the difference in the surface covered with dust and without it became visible.
A bright stone, found in the excavation, Curiosity shot by a laser, due to numerous requests from ustream-viewers
Some Internet users are interested in the difference in the color of sand on the surface and at shallow depth. It seems that this is the usual sand bar somewhere on the earth's beach, and under a layer of light dry sand lies wet - dark. The physical conditions on Mars in Gale's crater are such that the presence of water both in the liquid and in the crystalline state is excluded: the liquid form is impossible due to low pressure, and the ice would evaporate due to the positive temperature, which has already been fixed by Curiosity.
But a comparison of the 61 and 69 sol excavations shows that the color of the sand has not changed in a few days, which would have happened with wet sand even on Earth, even on Mars.

And the light color of the outer layer of sand is caused by the omnipresent light-red dust, which covers almost everything that it can hold onto.
The Rocknest location will remain a Curiosity point of business for a few more days. NASA intends to implement at least two more soil intakes.
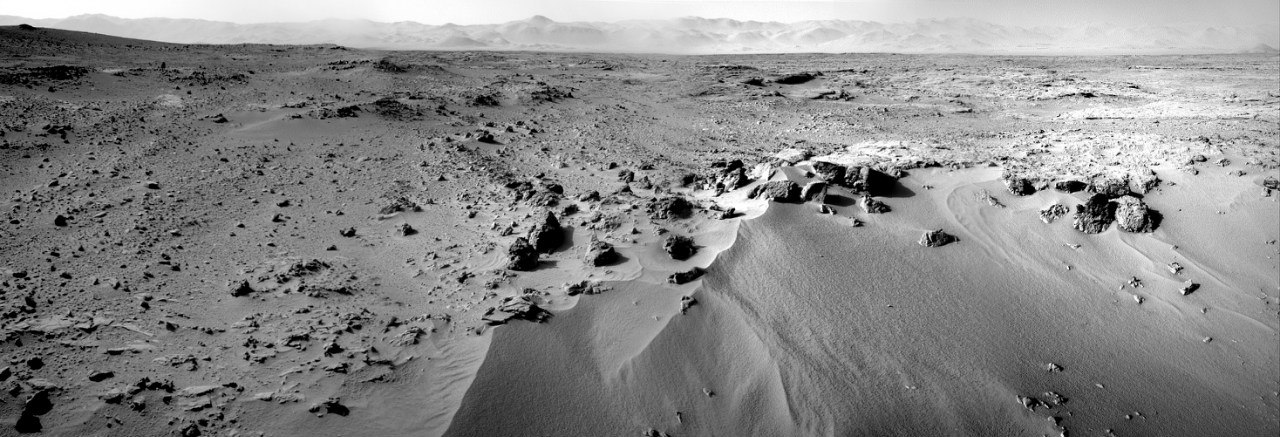

Meanwhile, in the district, you can already see a lot of objects that should be carefully studied. What are some deposits of limestone in a couple of tens of meters:

2538px × 400px 1.1 mb (color corrected for the earth white balance)
Formats larger than VK
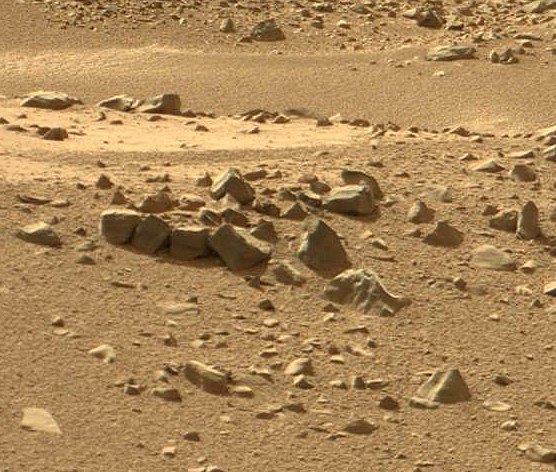
Or another “pyramid”, obviously flown from somewhere else

2370px × 400px 1.2 mb (color source)
Formats larger than VK
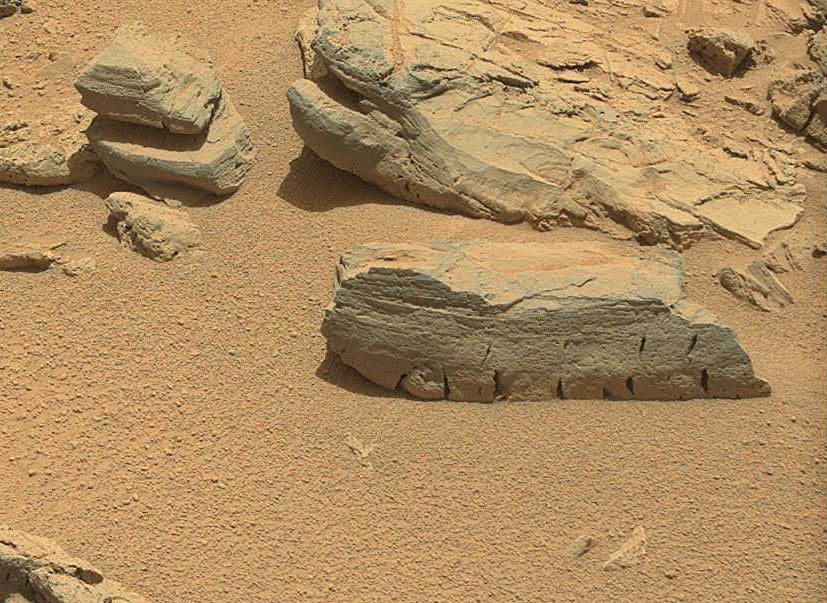
PS Already after the publication of the article on the second panorama, a “brickwork” was found, which will probably excite more than a dozen conspiracy theorists around the world.

Of course, even such a find has a natural origin. “Billets” for such “bricks” were met before


CHIMRA is a small bucket of 4x7 cm for soil sampling, and several cavities connected to each other, for sifting the gathered soil and preparing for loading into CheMin. This device requires particles no larger than 150 microns, so you have to try.

On the combination of two photos before and after loading, it is clear that a bit of sand has woken past the mouth of the CheMin soil receiver.
In just the past eleven days that Curiosity spent at the Rocknest site, three soil intakes have been produced. After the first, before the rover, a small bright object of clearly non-Martian origin was found.

')
Fearing that Curiosity is starting to fall apart, NASA stopped all scientific work for two days, until the subject was properly studied and found out that it was by some miracle that a piece of packing material of the rover or SkyCrane reached this place.
When the bucket made the next hole, some bright object 1.5-2 mm in size was again found in it.

And again the ground did not go to destination, but was poured out. NASA decided to eliminate the possibility that a piece of plastic, brought from Earth and falling off at the wrong moment, would be sent for research. The new discoveries involved a camera on the MAHLI manipulator, which allows it to act as a microscope. Thanks to her, it was determined that the bright subject is a local material.

Finally, after making sure that nothing else interferes with the research, a third soil sampling was carried out, and he went to the CheMin study. Before placing the prepared and sifted sample inside, part of it was spilled on the “sample table” - a special protrusion on the rover’s body, where a metal disk 7.8 cm (3 inches) in diameter was placed.

There are not many sand grains left on the “table”, but they dispersed the dust lying on it, and the difference in the surface covered with dust and without it became visible.
A bright stone, found in the excavation, Curiosity shot by a laser, due to numerous requests from ustream-viewers

Some Internet users are interested in the difference in the color of sand on the surface and at shallow depth. It seems that this is the usual sand bar somewhere on the earth's beach, and under a layer of light dry sand lies wet - dark. The physical conditions on Mars in Gale's crater are such that the presence of water both in the liquid and in the crystalline state is excluded: the liquid form is impossible due to low pressure, and the ice would evaporate due to the positive temperature, which has already been fixed by Curiosity.
But a comparison of the 61 and 69 sol excavations shows that the color of the sand has not changed in a few days, which would have happened with wet sand even on Earth, even on Mars.

And the light color of the outer layer of sand is caused by the omnipresent light-red dust, which covers almost everything that it can hold onto.
The Rocknest location will remain a Curiosity point of business for a few more days. NASA intends to implement at least two more soil intakes.

Meanwhile, in the district, you can already see a lot of objects that should be carefully studied. What are some deposits of limestone in a couple of tens of meters:

2538px × 400px 1.1 mb (color corrected for the earth white balance)
Formats larger than VK
Or another “pyramid”, obviously flown from somewhere else

2370px × 400px 1.2 mb (color source)
Formats larger than VK
PS Already after the publication of the article on the second panorama, a “brickwork” was found, which will probably excite more than a dozen conspiracy theorists around the world.

Of course, even such a find has a natural origin. “Billets” for such “bricks” were met before

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/155449/
All Articles