Setting SMS notifications in zabbix
The issue of SMS notifications in zabbix has already been covered on Habré and the problem was solved using SMS gateways. Also mentioned about sending SMS using Delphi . I want to tell you how to set up SMS notifications using a USB modem.
So, what we have:
1) quite extensive IT infrastructure
2) Zabbix 2.0.3 monitoring system (current version at the time of this writing) operating under Fedora 14 x64
')
3) 3G USB modem ZTE MF100 from the national Ukrainian operator Kyivstar.

4) Prepaid Simka, which was bundled with the modem.
Also, a corporate 3G SIM card was purchased for the modem, but it cannot be used, since it is impossible to call and send SMS from 3G cards, and this does not suit us. So, I put a small amount on the card “for experiments”, stuck the modem into USB and .
First of all, I registered the card in My Kyivstar system. Through it is convenient to watch the rest of the money on the modem's account and order additional. services. Let me remind you that I spend all the actions in Fedora. For other Linux teams may differ, but I think to figure out what to replace for you is not difficult. Also, I will not consider the option of installing the necessary from source, although this can also be done. I will confine myself to installing existing standard packages:
Now we set up SMS Tools. We rule config / etc / smsd.comf. I bring the finished config with comments:
Now we create a script /etc/smsd/trsms.sh, which will write the log of the sent SMS. Moreover, all Cyrillic messages will fall into it in readable encoding. Do not forget to give permissions to execute the script to the user smstool and to write to the log /var/log/smsd/sms.log
SMSTools can handle events using external programs. Our script will help send Russian sms in the correct encoding by checking messages before sending (the prototype was taken from unicode2sms from the standard script package, which can be found in / usr / bin. Similarly, do not forget to give the right to execute script user smstool
Let's write a script that will execute Zabbix for send sms. In Zabbix, these scripts are in the directory defined in the variable AlertScriptsPath .

Next in the user settings (Administration -> Users or Administration -> Users) add the Alert Method (Media):

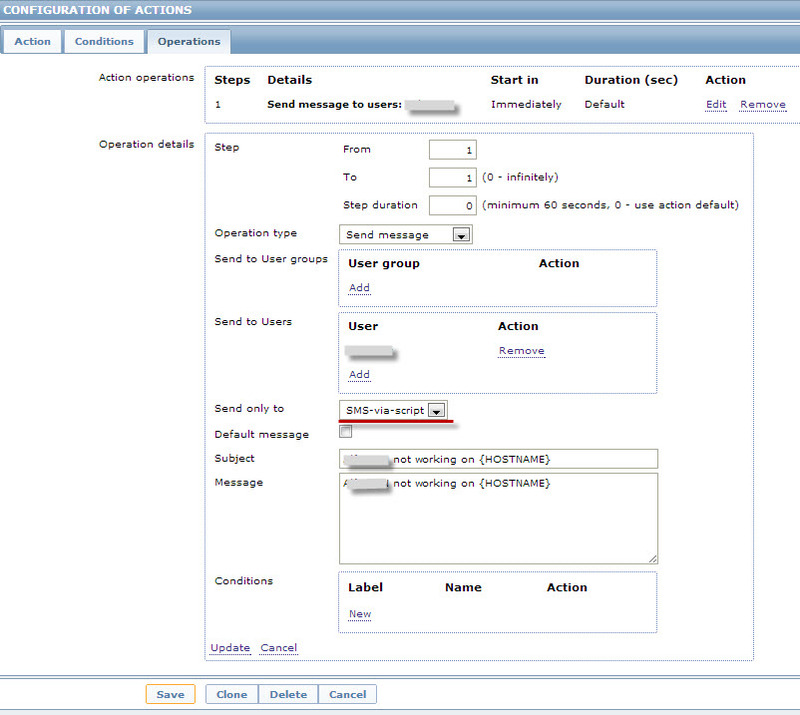
After that, in the Actions settings you will be able to use this Media:
Standard price of one SMS = 0.5 UAH. With a large number of SMS can result in a large penny. What does the operator offer to reduce costs?
first option - Prepaid
Here are two options:
option two - contract
Here are three options:
By the way, the prices are competitive. For example, the internet service smscentre.kiev.ua for our organization offered a price of 15 kopecks. for one SMS when the number of SMS per month is 1-25000 without a subscriber. boards and with free activation package. But when using a modem, we get one indisputable advantage - independence from the Internet. After all, they are not interested in mass SMS-sending, but notices from Zabbix. And when using Internet-based SMS-sending services, I don’t risk receiving an important SMS in the case of, for example, a prolonged switching off of the light in the office or an accident at the provider. Which package to choose is up to you.
More information about SMS packages can be found at: for the contract and for Prepaid
Installing this application is optional. The application is necessary for mass mailing SMS, which adds to the mysql database. To work, you need the packages httpd, mysql, php, php-pear, php-mysql, php-cli, phpmyadmin. But I have already installed all these packages for Zabbix to work. Create a new user and directory for PlaySMS. Download the latest version of PlaySMS and create a database in mysql:
Check that the correct path is specified in / etc / default / playsms
Links that will push you to thoughts on further improving the idea of sending SMS:
The article with the script-gateway E-mail-> SMS
Detailed manual on AT commands and sending SMS
Description of various AT commands
SMS forwarding using SMSTools
Description of SMS File Headers
UPD: to view the balance on the account and the number of promotional SMS you need to install the gsm-ussd package. Format command and the result is as follows:
So, what we have:
1) quite extensive IT infrastructure
2) Zabbix 2.0.3 monitoring system (current version at the time of this writing) operating under Fedora 14 x64
')
3) 3G USB modem ZTE MF100 from the national Ukrainian operator Kyivstar.

4) Prepaid Simka, which was bundled with the modem.
Also, a corporate 3G SIM card was purchased for the modem, but it cannot be used, since it is impossible to call and send SMS from 3G cards, and this does not suit us. So, I put a small amount on the card “for experiments”, stuck the modem into USB and .
Install the necessary
First of all, I registered the card in My Kyivstar system. Through it is convenient to watch the rest of the money on the modem's account and order additional. services. Let me remind you that I spend all the actions in Fedora. For other Linux teams may differ, but I think to figure out what to replace for you is not difficult. Also, I will not consider the option of installing the necessary from source, although this can also be done. I will confine myself to installing existing standard packages:
sudo yum install usb_modeswitch # USB- Huawei, T-Mobile, Vodafone, Option, ZTE, Novatel sudo yum install minicom # /dev/ttyUSB* sudo yum install smstools # . ls -l /dev/ttyUSB* The result should look something like this. crw-rw----. 1 root dialout 188, 0 Oct 22 12:05 /dev/ttyUSB0 crw-rw----. 1 root dialout 188, 1 Oct 22 15:56 /dev/ttyUSB1 crw-rw----. 1 root dialout 188, 2 Oct 22 12:05 /dev/ttyUSB2 The modem has created 3 virtual USB ports. In my case, ttyUSB1 and ttyUSB2 are available for AT commands. If the modem has created 5 or more virtual ports, then their number can be reduced to 3x. To do this, disable the cdrom and flash-drive modes in it. Turning off is done with the command AT + ZCDRUN = E , turning on AT + ZCDRUN = F. If you want to disable only cd-rom, then AT + ZCDRUN = 8 . If we want to turn it back on - AT + ZCDRUN = 9. I launch the terminal minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB1 I see a greeting Welcome to minicom 2.5 OPTIONS: I18n Compiled on Feb 24 2011, 11:25:55. Port /dev/ttyUSB1 Press CTRL-A Z for help on special keys AT S7=45 S0=0 L1 V1 X4 &c1 E1 Q0 OK turn off the CD-ROM >AT+ZCDRUN=8 Close autorun state result(0:FAIL 1:SUCCESS):1 OK In general, AT commands are quite a lot before, at the time of telephone modems, of the knowledge was mandatory for self-respecting admin. Now everything has changed and remember the forgotten commands can be with the help of Google. For example, here is a good reference article. Let's try to communicate with the modem. Let's look at the modem operation mode >AT+ZSNT? +ZSNT: 1,0,0 OK in my case - = 1,0,0 - Automatic selection of only GSM network. Since I use the usual, rather than 3G SIM, this mode suits me completely. There are also the following options for the mode of operation: AT+ZSNT=0,0,0 () - AT+ZSNT=0,0,1 : GSM+WCDMA, GSM AT+ZSNT=0,0,2 : GSM+WCDMA, WCDMA AT+ZSNT=1,0,0 : GSM AT+ZSNT=2,0,0 : WCDMA AT+ZSNT=0,1,0 : GSM+WCDMA AT+ZSNT=1,1,0 : GSM AT+ZSNT=2,1,0 : WCDMA Check whether the protection is set pin-code >AT+CPIN? +CPIN: SIM PIN OK disable PIN >AT+CLCK="SC",0,"1111" enable PIN >AT+CLCK="SC",1,"1111" If it is enabled, then to continue the work we need to enter it. >AT+CPIN=”1234″ OK check again >AT+CPIN? +CPIN: READY OK Now the pin code is accepted. Let's see the signal level >AT+CSQ +CSQ: 21,99 OK get the version of the IMEI module >AT+GSN 359518034903581 OK Let's see the type of registration in the network >AT+CREG? +CREG: 0,1 OK 0 means that there is no message about the change of registration in the network1 - successfully registered in the networkWe look at the information about the operator >AT+COPS? +COPS: 0,0,"Kyivstar",0 OK The first 0 means automatic network selection, a long test name format (the second is 0), and the operator’s name itself is Kyivstar. We’ll check if we have the Service Center Address AT+CSCA? +CSCA: "+380672021111",145 OK For Kyivstar this is the correct number. Now we will try to send a message. Before sending a message, you need to set the message format. This is done with the command AT + CMGF = x . where x is the message format, 0-1.0, is the PDU mode, command code control. Displays a message in the HEX code. The default mode is 1, text mode. Text commands. The message will be displayed in text form. In the first mode, messages will be issued in the form of hexadecimal ascii or unicode codes. This is a very inconvenient mode. SMS sending is done with the AT + CMGS = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" command, where XXXXXXXXXXX is the subscriber number. Sending SMS depends on the message format. After entering the command, it displays the prompt ">" after which you can enter the text of the messages. Ends with the ESC or Ctrl-Z character. Send a message using text mode and pre-forcibly setting SCA: AT+CMGF=1 OK AT+CSCA= "+380672021111" OK AT+CMGS="+38067xxxxxxx" > test message > +CMGS: 110 OK SMS has successfully arrived. You can send SMS before writing to memory: AT+CMGW="91234567"<CR>Sending text messages is easy.<Ctrl+z> AT+CMSS=3 When working with AT commands, things don't always go smoothly. Sometimes commands are executed with errors, returning a three-digit error code. Here is a list of the main error codes: Error code Meaning 0-127 GSM 04.11 Annex E-2 values 128-255 GSM 03.40 section 9.2.3.22 values 300 Phone failure 301 SMS service of phone reserved 302 Operation not allowed 303 Operation not supported 304 Invalid PDU mode parameter 305 Invalid text mode parameter 310 SIM not inserted 311 SIM PIN necessary 312 PH-SIM PIN necessary 313 SIM failure 314 SIM busy 315 SIM wrong 320 Memory failure 321 Invalid memory index 322 Memory full 330 SMSC (message service center) address unknown 331 No network service 332 Network timeout 500 Unknown error 512 Manufacturer specific Smstools setup
Now we set up SMS Tools. We rule config / etc / smsd.comf. I bring the finished config with comments:
# , — devices = GSM1 # incoming=/var/spool/sms/incoming outgoing=/var/spool/sms/outgoing checked=/var/spool/sms/checked sent=/var/spool/sms/sent # , — syslog, = 1, stdout logfile = /var/log/smsd/smsd.log # loglevel = 5 #debug = 7 user = sms # "" smart_logging = yes #, "" . checkhandler = /etc/smsd/check.sh #, . eventhandler = /etc/smsd/trsms.sh [GSM1] # device = /dev/ttyUSB1 #- pin = 1111 #SCA smsc = 380672021111 More information about all the parameters of the config can be found on the official smstool website.Script trsms.sh
Now we create a script /etc/smsd/trsms.sh, which will write the log of the sent SMS. Moreover, all Cyrillic messages will fall into it in readable encoding. Do not forget to give permissions to execute the script to the user smstool and to write to the log /var/log/smsd/sms.log
chown smstools:smstools /etc/smsd/trsms.sh chmod gu+x /etc/smsd/trsms.sh chmod gu+w /var/log/smsd/sms.log The script itself: #!/bin/bash status="$1" file="$2" touch /etc/smsd/ok case "$1" in SENT) FILE=`mktemp /tmp/smsd_XXXXXX` head -5 $file | grep -e "^To: " -e "Alphabet: " -e "^Sent: " >> /var/log/smsd/sms.log if grep "Alphabet: Unicode" $file >/dev/null; then tail -n +6 $file | iconv -f UCS-2BE -t UTF-8 >> /var/log/smsd/sms.log else tail -n +5 $file >> /var/log/smsd/sms.log fi echo >> /var/log/smsd/sms.log echo "========================================" >> /var/log/smsd/sms.log echo >> /var/log/smsd/sms.log ;; esac Example of part of the log: ======================================== To: 38067XXXXXXX Alphabet: Unicode Sent: 12-10-23 21:07:29 test message ======================================== To: 38093XXXXXXX Alphabet: Unicode Sent: 12-10-19 12:16:28 ======================================== Script check.sh
SMSTools can handle events using external programs. Our script will help send Russian sms in the correct encoding by checking messages before sending (the prototype was taken from unicode2sms from the standard script package, which can be found in / usr / bin. Similarly, do not forget to give the right to execute script user smstool
chown smstools:smstools /etc/smsd/check.sh chmod gu+x /etc/smsd/check.sh The script itself: #!/bin/bash # checkhandler for SMS Tools 3 # autoconverts cyrillic messages to UCS-2BE # add checkhandler=/path/to/ucsautoconvert into global part of smsd.conf # written by lexy (lexy@mrlexy.ru), 2008 FILE=`mktemp /tmp/smsd_XXXXXX` if [ ! `grep '[--]' $1 > /dev/null` -o `grep 'Alphabet:\s*U' $1 > /dev/null` ] then exit 0 fi cat $1 | awk '{if(NF==0) {s=1} if(s==0 && NF>0 && $0!~/Alphabet:[ \t]*U/){print}}' > $FILE echo Alphabet: Unicode >> $FILE cat $1 | awk '{if(NF==0) {s=1} if(s==1){print}}' | iconv -t UCS-2BE >> $FILE mv $FILE $1 chmod 664 $1 now everything is ready to launch. >service smsd start Starting smsd: [ OK ] check if it started > ps ax | grep smsd 1345 ? Ss 0:00 /usr/sbin/smsd 1347 ? S 0:00 /usr/sbin/smsd 2322 pts/2 S+ 0:00 grep --color=auto smsd try to send a message. the subscriber's number is indicated in the international format, but without the “+” sign smssend "38067XXXXXXX" "test message" -- Text: test message To: 38067XXXXXXX look at the log. > tail /var/log/smsd/smsd.log lines added 2012-10-23 21:07:08,5, GSM1: SMS sent, Message_id: 112, To: 38067XXXXXXX, sending time 7 sec. 2012-10-23 21:07:21,5, smsd: Moved file /var/spool/sms/outgoing/send_NpoTqX to /var/spool/sms/checked check sent SMS: >cat /var/spool/sms/sent/send_NpoTqX To: 38067XXXXXXX Alphabet: Unicode Modem: GSM1 Sent: 12-10-23 21:07:29 IMSI: 255030837719869 test message Zabbix configuration
Let's write a script that will execute Zabbix for send sms. In Zabbix, these scripts are in the directory defined in the variable AlertScriptsPath .
cat /usr/local/etc/zabbix_server.conf | grep AlertScriptsPath ### Option: AlertScriptsPath AlertScriptsPath=/home/zabbix/bin/ The script itself is called sms_send.sh and it consists of almost one line: #!/bin/bash to=$1 subject="$2" body="$3" smssend $to "$subject" Further configuration is done via the web interface. First go to Administration -> Alert Methods (Administration Media types->) and create a new alert type (Media types). The name of the script must be the same as the name of the script file in the AlertScriptsPath directory
Next in the user settings (Administration -> Users or Administration -> Users) add the Alert Method (Media):

After that, in the Actions settings you will be able to use this Media:

Tariffs
Standard price of one SMS = 0.5 UAH. With a large number of SMS can result in a large penny. What does the operator offer to reduce costs?
first option - Prepaid
Here are two options:
- "Package 30 SMS" with a subscription fee of 4 UAH per week. It turns out that the price is 1 sms = 13.33 kopecks.
- "Package 60 SMS" with a subscription fee of 6 UAH per week. It turns out that the price is 1 sms = 10 kopecks.
- In both cases, unused at the end of the week SMS “burn”.
- You need to regularly go to My Kyivstar's profile and re-order the service, otherwise you can remain without notice at the most important moment.
option two - contract
Here are three options:
- "SMS Package -50%" with a subscription fee of 3 UAH per month. The package includes 500 sms at a discount. It turns out that the price is 1 sms = 25 kopecks.
- "SMS package -70%" with a subscription fee of UAH 7 per month. The package includes 500 sms at a discount. It turns out that the price is 1 sms = 15 kopecks.
- "Package 1000 SMS" with a subscription fee of 120 UAH per month. The package includes 1000 free sms. It turns out that the price is 1 sms = 12 kopecks.
By the way, the prices are competitive. For example, the internet service smscentre.kiev.ua for our organization offered a price of 15 kopecks. for one SMS when the number of SMS per month is 1-25000 without a subscriber. boards and with free activation package. But when using a modem, we get one indisputable advantage - independence from the Internet. After all, they are not interested in mass SMS-sending, but notices from Zabbix. And when using Internet-based SMS-sending services, I don’t risk receiving an important SMS in the case of, for example, a prolonged switching off of the light in the office or an accident at the provider. Which package to choose is up to you.
More information about SMS packages can be found at: for the contract and for Prepaid
PlaySMS setup
Installing this application is optional. The application is necessary for mass mailing SMS, which adds to the mysql database. To work, you need the packages httpd, mysql, php, php-pear, php-mysql, php-cli, phpmyadmin. But I have already installed all these packages for Zabbix to work. Create a new user and directory for PlaySMS. Download the latest version of PlaySMS and create a database in mysql:
adduser playsms mkdir -p /var/www/playsms mkdir -p /var/spool/playsms mkdir -p /var/log/playsms chown -R apache /var/www/playsms chown -R apache /var/spool/playsms chown -R apache /var/log/playsms chmod -a -G smstools playsms wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/playsms/playsms/Version%200.9.7.1/playsms-0.9.7.1.tar.gz tar -zxvf playsms-0.9.7.1.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src cd /usr/local/src/playsms-0.9.7.1/web/ cp -rR * /var/www/playsms cp playsmsd* sendsmsd* /usr/local/bin/ chown -R apache /var/www/playsms mysqladmin -u root -p create playsms We import into the created database: mysql -u root -p playsms < /usr/local/src/playsms-0.9.7.1/db/playsms.sql We copy the config by editing the password in it to connect to the database (and login, if you are not root) cp /var/www/playsms/config-dist.php /var/www/playsms/config.php vi /var/www/playsms/config.php $core_config['db']['pass'] = ' '; // database password Configuring automatic launch of the program: cd /usr/local/src/playsms-0.9.7.1/bin cp playsmsd playsmsd.php playsmsd_start /usr/local/bin/ cp playsms /etc/default/ In /etc/rc.d/rc.local add the line - / usr / local / bin / playsmsd_start. PlaySMS control panel is available via htpp: //ip.address.your.server/playsms. Login admin \ admin.Check that the correct path is specified in / etc / default / playsms
PLAYSMS_PATH=/var/www/html/playsms useful links
Links that will push you to thoughts on further improving the idea of sending SMS:
The article with the script-gateway E-mail-> SMS
Detailed manual on AT commands and sending SMS
Description of various AT commands
SMS forwarding using SMSTools
Description of SMS File Headers
UPD: to view the balance on the account and the number of promotional SMS you need to install the gsm-ussd package. Format command and the result is as follows:
>gsm-ussd -m /dev/ttyUSB2 '*115#' Bonusy 55.0 SMS na nomery po Ukraini (dijsni do 2012-11-06 23:59:59). Zamovlennia Paketu SMS za tel. 477*030* >gsm-ussd -m /dev/ttyUSB2 '*111#' Na rahunku: 17.14 grn. Nomer die do 24-10-2013. Bonusy: 0 grn (dijsni do 14-10-2022); 104810496 bytes Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/155321/
All Articles