Curiosity identified a volcanic rock
At 43 sol (Martian day) of being on Mars, MSL Curiosity approached a large stone. Many Internet users were attracted by its form, which at first glance seemed to be pyramidal. Although, for NASA, this sample was interesting because it is the largest stone encountered by Curiosity at that time. Rover operators have long been eager to test the functionality of the manipulator in practice, so that the stone turned up very well. Moreover, he did not “turn up”, and the rover purposefully moved towards him for two days.
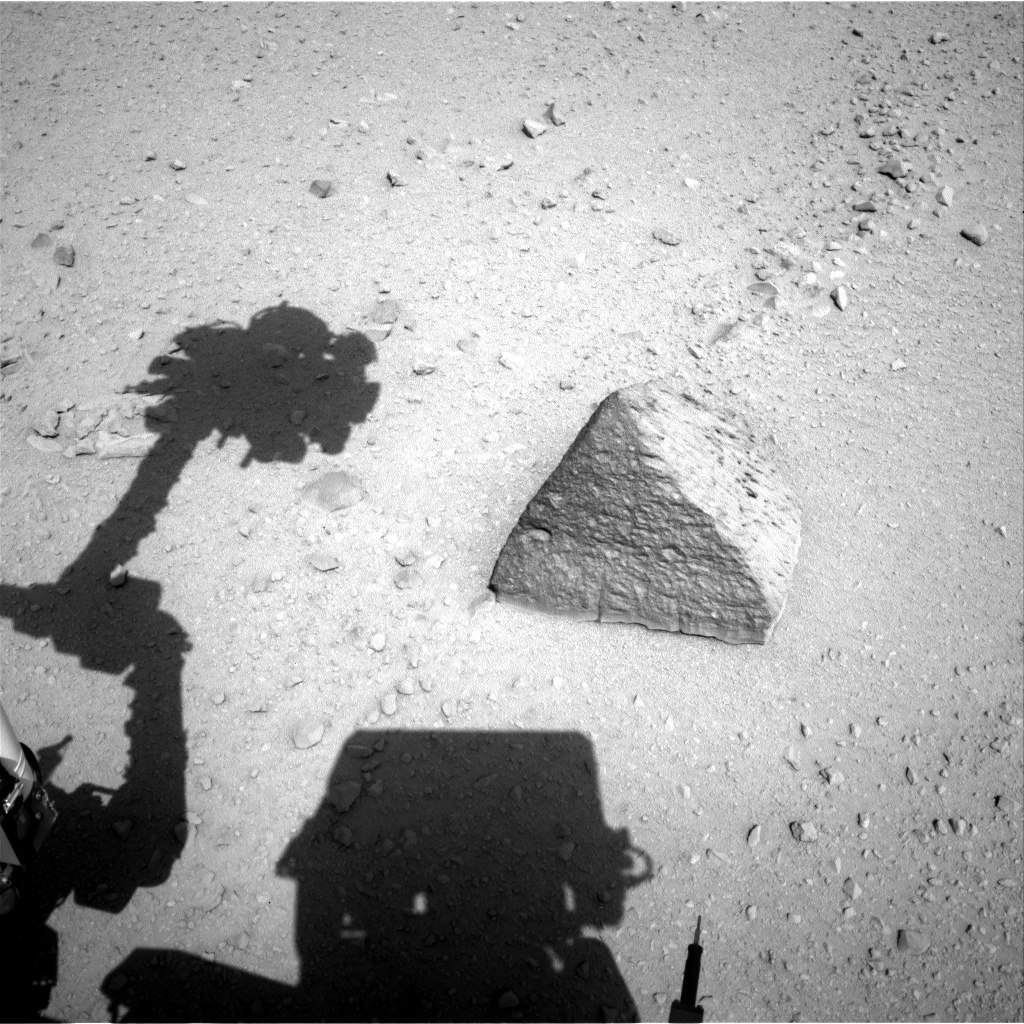

The stone was thoroughly examined with the tools Chem Cam, Mast Cam, MAHLI, APXS for five days. On the rover's calendar now it's 66 minutes, and it took NASA twenty days to process the data and prepare it for public release.
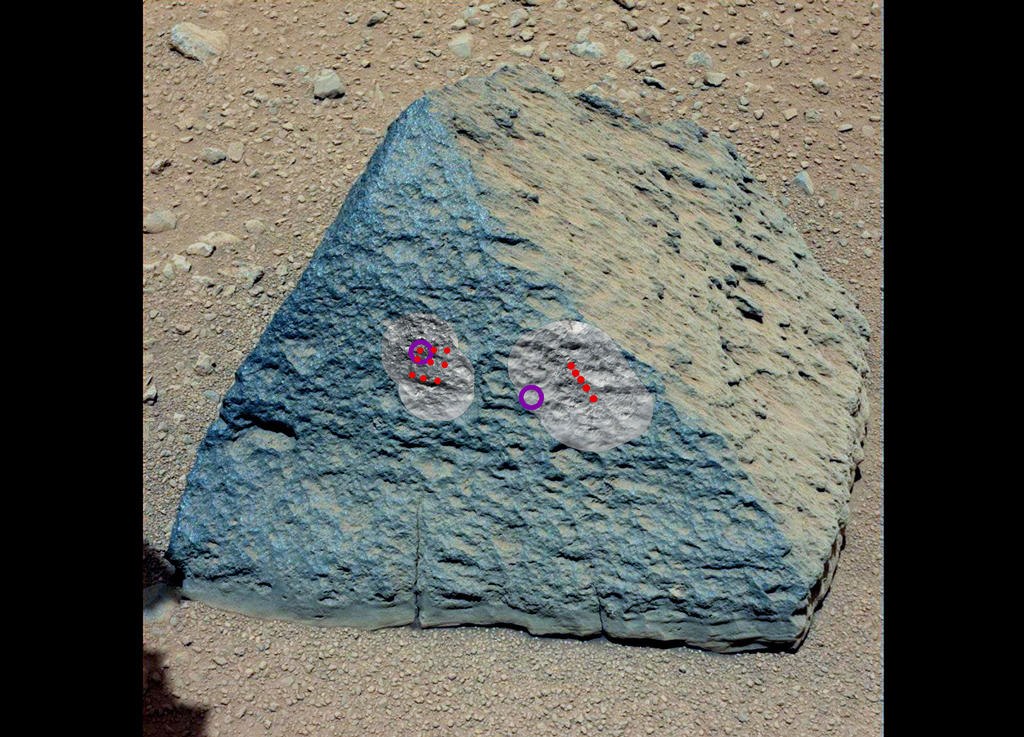

The stone was called Jake Matijevic or, for short, “Jake”, in memory of one of the JPL engineers.
The sample was subjected to biased spectrometers. In the photo, the red dots show where the Chem Cam laser pulses were directed, and the purple circles — which areas were irradiated with APXS alpha particles.
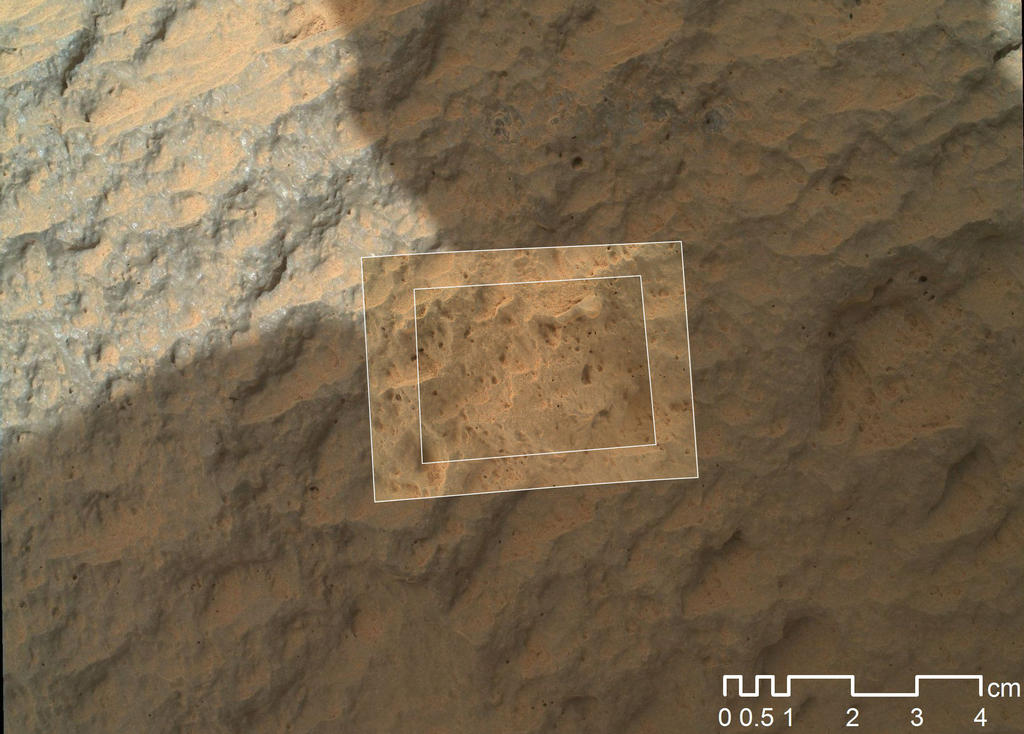
The camera on the MAHLI manipulator was also tested on the Martian object for the first time (before it could only take off the rover).

')
The results obtained using a Chem Cam laser spectrograph revealed the crystal structure of the rock, where the chemical composition readings changed depending on which crystal the laser beam fell into. In accordance with these differences, several graphs were compiled.
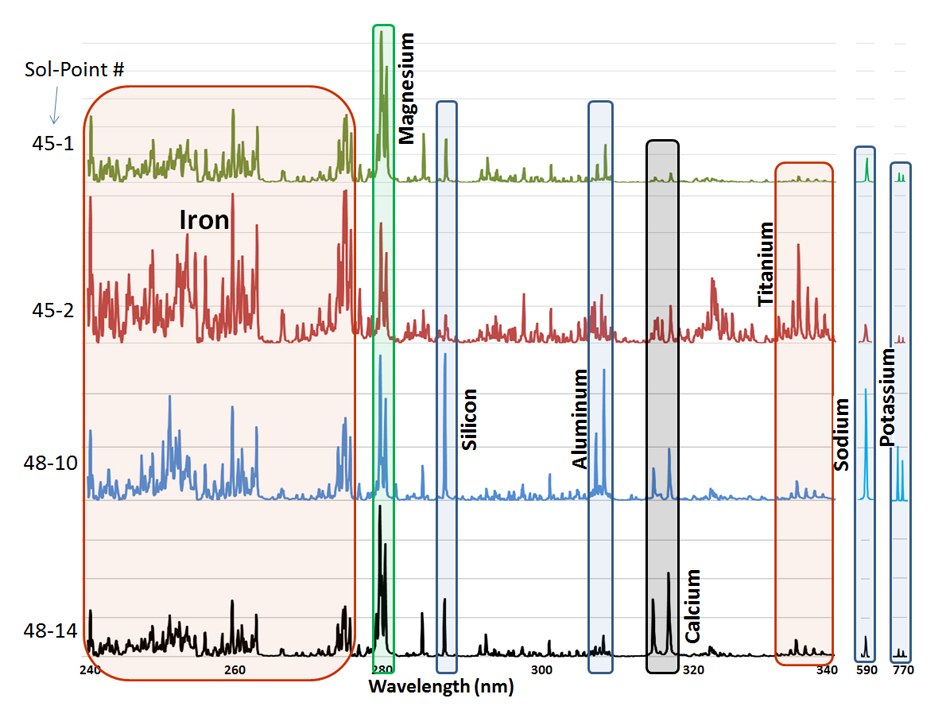
So, the sample rich in magnesium and iron corresponds to the mineral olivine. Enriched with iron and titanium corresponds to ilmenite. A point rich in silicon, aluminum, sodium and potassium corresponds to feldspar. The content of potassium and magnesium indicates pyroxene.
Studies of the chemical composition, as well as the appearance and structure of the stone, showed its relationship to terrestrial minerals, which crystallize under the crust of the planet at high pressure in the mantle layers rich in water. Although conditions on Mars may differ, scientists are inclined to believe that the processes of formation of such rocks on Earth and Mars are very close.
In general, "Jake" surprised researchers with its uniqueness, they expected a less interesting, from a geological point of view, sample.
Leaving this place, Curiosity made photos of the stone from a different angle and they finally destroyed the illusions of its pyramidality.
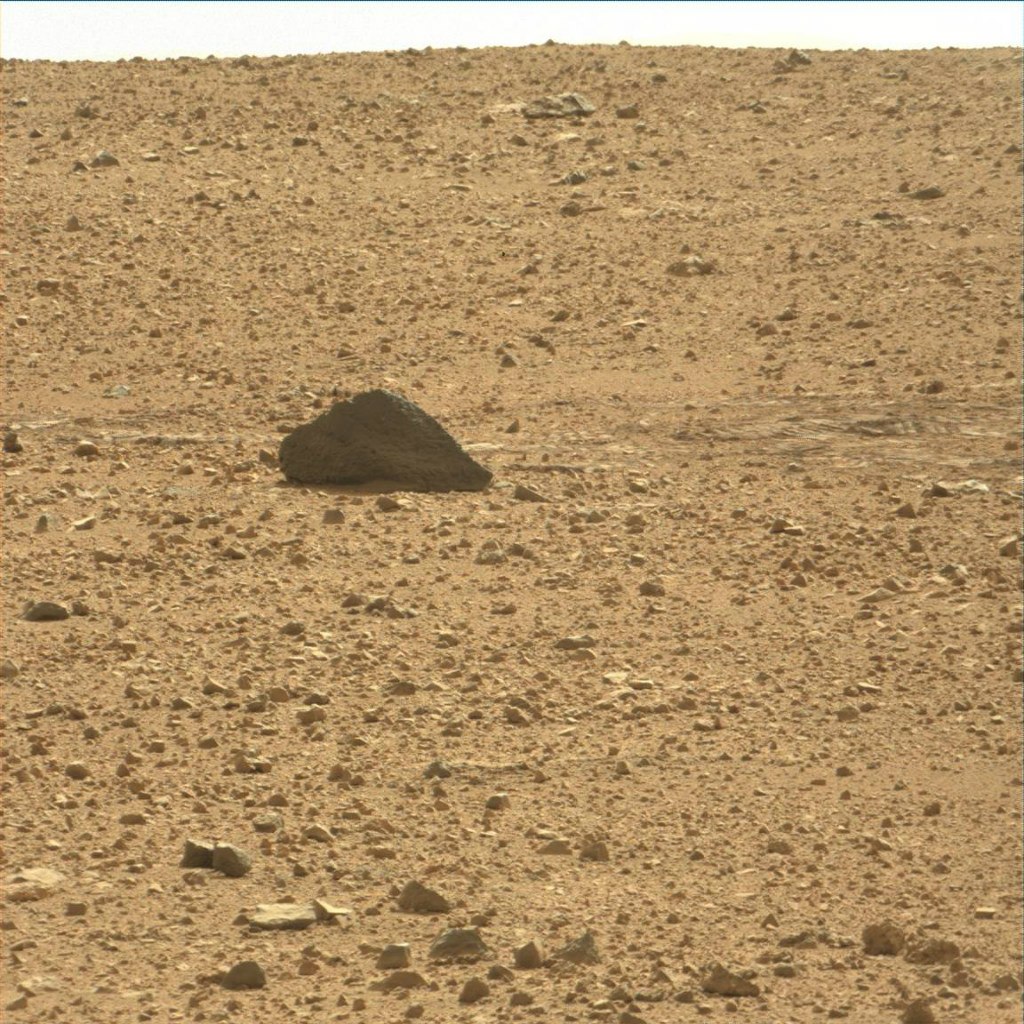

Ahead the rover was waiting for many more similar and unlike stones

Panorama 2445x500 1.5 mb
Formats more VKontakte
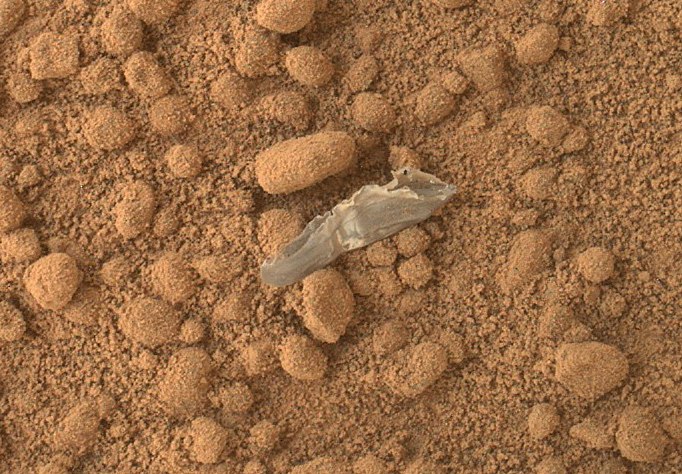
PS A piece of plastic that has fallen off three days ago from a rover is recognized as not dangerous, and all scientific work continues as before.


The stone was thoroughly examined with the tools Chem Cam, Mast Cam, MAHLI, APXS for five days. On the rover's calendar now it's 66 minutes, and it took NASA twenty days to process the data and prepare it for public release.

The stone was called Jake Matijevic or, for short, “Jake”, in memory of one of the JPL engineers.
The sample was subjected to biased spectrometers. In the photo, the red dots show where the Chem Cam laser pulses were directed, and the purple circles — which areas were irradiated with APXS alpha particles.
The camera on the MAHLI manipulator was also tested on the Martian object for the first time (before it could only take off the rover).

')
The results obtained using a Chem Cam laser spectrograph revealed the crystal structure of the rock, where the chemical composition readings changed depending on which crystal the laser beam fell into. In accordance with these differences, several graphs were compiled.

So, the sample rich in magnesium and iron corresponds to the mineral olivine. Enriched with iron and titanium corresponds to ilmenite. A point rich in silicon, aluminum, sodium and potassium corresponds to feldspar. The content of potassium and magnesium indicates pyroxene.
Studies of the chemical composition, as well as the appearance and structure of the stone, showed its relationship to terrestrial minerals, which crystallize under the crust of the planet at high pressure in the mantle layers rich in water. Although conditions on Mars may differ, scientists are inclined to believe that the processes of formation of such rocks on Earth and Mars are very close.
In general, "Jake" surprised researchers with its uniqueness, they expected a less interesting, from a geological point of view, sample.
Leaving this place, Curiosity made photos of the stone from a different angle and they finally destroyed the illusions of its pyramidality.

Ahead the rover was waiting for many more similar and unlike stones

Panorama 2445x500 1.5 mb
Formats more VKontakte
PS A piece of plastic that has fallen off three days ago from a rover is recognized as not dangerous, and all scientific work continues as before.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/154517/
All Articles