For the first time broadband information was transmitted via the laser channel to the ground station from the ISS
On October 2, 2012, for the first time, broadband information was transmitted to the ground station from the Russian segment of the International Space Station via a laser channel.
In the framework of the space experiment (SLS) to develop the equipment and demonstrate the Russian technology of creating space laser information transmission systems, conducted by OAO NPK SPP together with RSC Energia, a session of information transmission from the communication terminal installed onboard the ISS RS , to the laser terminal of the ground station of the Arkhyz optical observation station in the North Caucasus (branch of NPK SPP).
Information was transmitted totaling 2.8 GB with a speed of 125 Mbit / s.
This step opens the way to the widespread introduction of laser communication lines into space technology of Russia, which, with smaller weight and size parameters of onboard equipment, can potentially provide an extremely high speed of information flow (up to tens of gigabits per second).
Federal Space Agency News
Internet on ISS
Hmm, I thought, in the same place (on the ISS) there is definitely already Internet. Webcams work, you can not watch TV at home during dinner. Why do we need a laser system? After all, it requires accurate guidance, and the weather here, on Earth, is not always happy. And when it pleases us humans, the lasers do not have much joy anyway. Got to search.
Internet, yes, there really is on the ISS. They can use astronauts, he is there on board, even on Wi-Fi is distributed. But he is there, it turns out, not so long ago. Total since 2010 . And at dial speeds . The problem, they say, is not with a bad link, but with a huge relative speed of movement of the station. Data does not have time. Pictures with cats arrive in space, and the astronauts have already caught a trace.
“You can call from the ISS via satellite phone to anywhere in the world. The main thing is the availability of free time and satellite communications. Unfortunately, not all the time there is such an opportunity. Also via this communication channel (KU-band) we can work with the Internet. The speed is small, but you can view the news. For convenience, there is a postal program on board. Before the start, we submit lists of email addresses, the mail from which we will receive during the flight to a special NASA address. Lists can be adjusted during the mission. This mail is thrown to us during the so-called synchronization, about 3-4 times a day, ”noted Shkaplerov.
www.ria.ru 20/02/2012
')
Radio communication
Is it really that bad with radio?
Information from the Voyager to Earth is transmitted by a parabolic antenna with a diameter of 3.65 meters rigidly bonded to the body, which should be oriented precisely to the home planet. Through it, at frequencies of 2295 MHz and 8418 MHz, two 23-watt radio transmitters send signals. For reliability, each of them is duplicated. Most of the data is transmitted to Earth at a speed of 160 bit / s - it is only three or four times faster than the typing speed of a professional typist and 300 times slower than a telephone modem. To receive the signal on Earth, 34-meter antennas of the NASA long-distance network are used, but in some cases the largest 70-meter antennas are used, and then the speed can be raised to 600 and even 1400 bit / s. As the station moves away, its signal weakens, but more importantly, the power of radioisotope generators that power the transmitters gradually decreases. It is expected that the station will be able to transmit scientific data for at least another 10 years, after which the connection with it will cease.
" Cosmic Radio Links " ("Around the World", №10 (2805) | October 2007)
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, which entered Mars orbit on March 10, 2006, can boast the highest interplanetary data transfer speed today. It is equipped with a 100-watt transmitter with a three-meter parabolic antenna and can transmit information at speeds of up to 6 megabits per second. It is still difficult to deliver a larger and larger transmitter to Mars.
" Cosmic Radio Links " ("Around the World", №10 (2805) | October 2007)
Lasers
The only difference between laser radiation and radio emission is frequency. The light frequency is ~ 6 * 10 ^ 14 Hz, 1.5 micron laser - 2 * 10 ^ 14 Hz. Radio transmitters on spacecraft operate at a frequency of GHz units. Radio Ultra in Moscow was broadcasting at 100.5 MHz.
High frequency and, accordingly, a small wavelength - this is both a gift and a curse of laser radiation. Using electromagnetic radiation of such a frequency for communication, we receive into the load and all its diseases - low penetrating power, narrow focus (this, of course, may not be a disease, if the task of hiding the communication channel is solved), etc. The laser beam has a Gaussian shape:
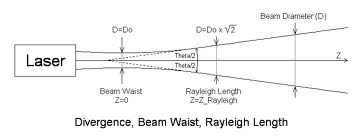
Those. the farther from the ground, the greater will be the area of the laser spot and, accordingly, the smaller part of the photons will take part in the actual transmission of information. Those. the interstellar communication facility the laser, even considering the absence of an obstacle to the propagation of radiation in space, will still not. And interplanetary?
The first laser communication in space was carried out on November 21, 2002. The European Earth remote sensing satellite SPOT 4, which is in orbit at an altitude of 832 kilometers, established contact with an experimental spacecraft Artemis, orbiting at an altitude of 31,000 kilometers, and transmitted images of the earth's surface. And recently, the Lincoln Laboratory at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), together with NASA, has begun to develop a laser system for remote space communications. The first test communication laser is scheduled to be sent to Mars in 2009. It is expected that this 5-watt transmitter during the period of convergence of the planets will provide data transfer rates of up to 30 megabits per second.
" Cosmic Radio Links " ("Around the World", №10 (2805) | October 2007)
More recent news, however, talk about testing the Mars-Earth laser channel in 2012 .
The system that the second day made the data exchange with the Earth from the ISS, is being built by NPK SPP. Quite a bit of information about the system (either the one onboard the ISS, or similar) can be found on their website . Let me duplicate this information here:
Intersatellite laser information transmission systems with speeds up to 600 Mbit / s and range from 1 to 6 thousand km (NKA-NKA line) from 30 to 46 thousand km (NKA-GKA line):
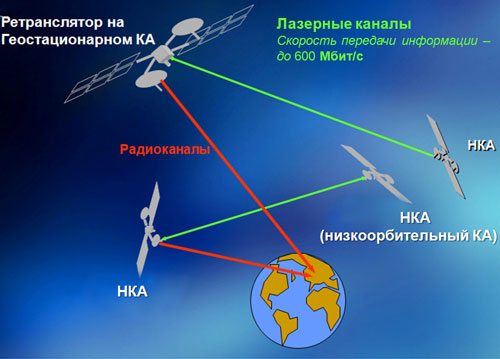
Terminal for space experiments on laser communications on the Bort-Earth route for the ISS:

The length of the route - up to 2000 km
Terminal weight with transport frame - 80 kg
Power consumption - 150 W
Data transfer rate - up to 600 Mbps
Transmitter wavelength - 1550 nm
Beacon wavelength - 810 nm
Transmitter diagram - 50 ang. sec
Guidance accuracy - 10 ang. sec
At the end of the speech. Sorry for the large number of copy-paste and links, I hope that the information is interesting. And yet, I am outraged: GLONASS is a separate hub, but astronautics (as I understand it, this is such a hub-hodgepodge for everything that has to do with space) - hub-offtopic. Disorder, guys. I would change places.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/153555/
All Articles