Farm SharePoint 2013 in Windows Azure. AD DC

As you know, you can already download and try SharePoint 2013 (at the moment the product is in the Preview status).
In order to work with the new version, it is not necessary to buy a new server or create virtual machines with obviously inappropriate requirements .
- Farm SharePoint 2013 in Windows Azure. AD DC (this article)
- Farm SharePoint 2013 in Windows Azure. SQL Server 2012
- Farm SharePoint 2013 in Windows Azure. SharePoint 2013
Consider how to create a farm with SharePoint 2013 using the capabilities of Windows Azure.
The necessary conditions
- Windows Azure PowerShell Cmdlets
- Subscribe to Windows Azure with the included ability to preview virtual machines - you can register for free here
Get subscription credentials
To perform all further actions, you will need security credentials for your subscription. Windows Azure allows you to load the Publish Settings file with all the information you need to manage your account in your development environment.
Upload and Import Publish Settings File
At this stage, you need to log in to the Windows Azure portal and upload the file with the publish settings. This file contains security credentials and additional information about a Windows Azure subscription that will be used in your development environment. You then need to import this file using Windows Azure cmdlets to install the certificate and get the account information.
Go to https://windows.azure.com/download/publishprofile.aspx and log in using your Microsoft Account credentials that match your Windows Azure account.
Save the publish file to your local PC.
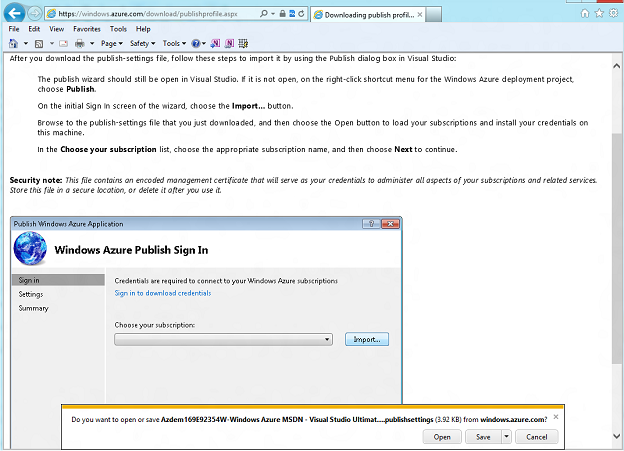
Uploading a file with publish settings
Run Windows Azure PowerShell and as administrator.
Next, you need to import the file with the parameters and generate the XML file with your credentials using PowerShell
Import-AzurePublishSettingsFile '[YOUR-PUBLISH-SETTINGS-PATH]' Run the following commands and note the subscription name and storage account name, we still need them
Get-AzureSubscription | select SubscriptionName Get-AzureStorageAccount | select StorageAccountName[/sourcecode] Run the following commands to assign the current storage account to your subscription
Set-AzureSubscription -SubscriptionName '[YOUR-SUBSCRIPTION-NAME]' -CurrentStorageAccount '[YOUR-STORAGE-ACCOUNT]'[/sourcecode] Let's move on to setting up a virtual network.
')
Configuring a virtual network
To work in an Active Directory domain, clients will need static IP addresses; clients must connect to a DNS server that supports Active Directory. Internal DNS (iDNS), deployed in Windows Azure, will not work because it assigns dynamic IP addresses to virtual machines. For this solution, a virtual network will be created in which you can connect virtual machines to specific subnets
- A virtual network called SP2013-VNET, address prefix: 192.168.0.0/16
- Subnet called SP2013AD-Subnet, address prefix: 192.168.1.0/24
- Subnet called SP2013Farm-Subnet, address prefix: 192.168.2.0/24
Create a territorial group
Open https://manage.windowsazure.com/ . Enter your credentials for Windows Azure when prompted. In the Windows Azure portal, click Networks , Affinity Groups , and click Create at the bottom.
Name the regional group SP2013-AG and select the region. To create a territorial group, click Finish.
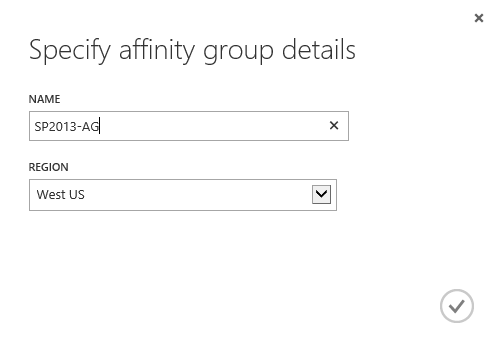
Creation of a territorial group
Create a new virtual network
Create a new virtual network for your subscription.
In the Windows Azure portal, click Networks , then Virtual Networks . At the bottom click Create .
Name the new virtual network SP2013-VNET , enter a description, and click the arrow button to continue.
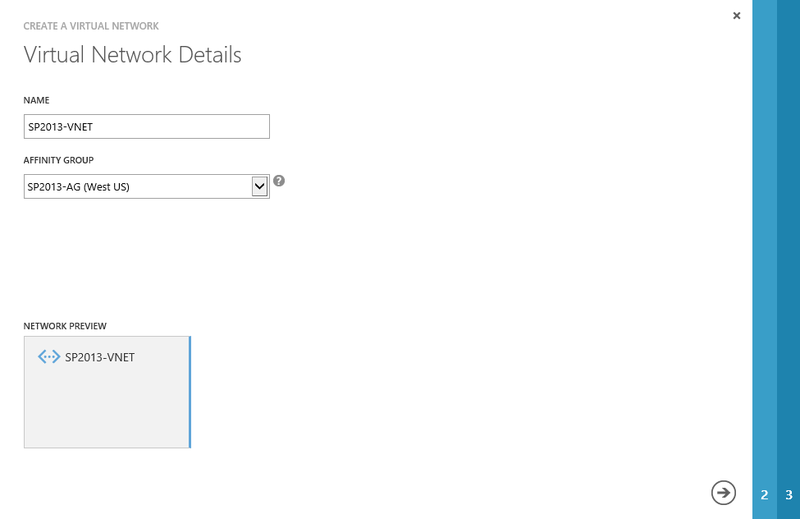
Creating a new virtual network
In the Address Space field, enter 192.168.0.0/16 and add two subnets: SP2013AD-Subnet with the prefix 192.168.1.0/24 and SP2013Farm-Subnet with the prefix 192.168.2.0/24 .
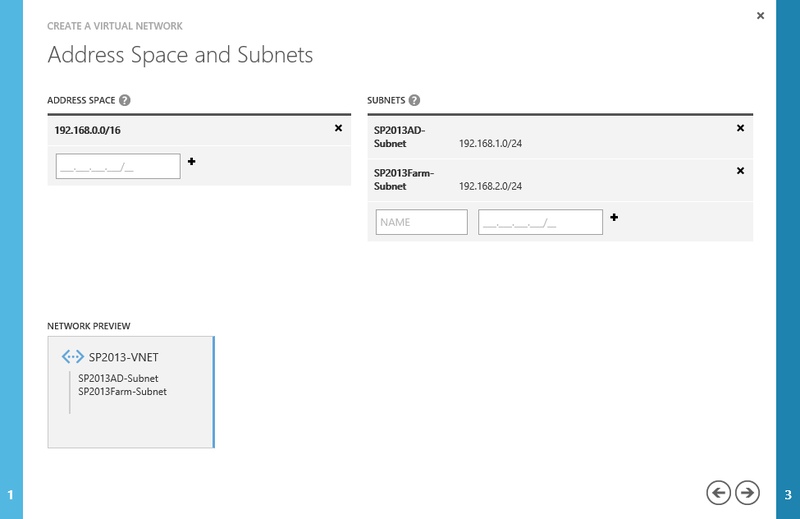
Add address space and subnets
Leave the default DNS settings and click Finish.
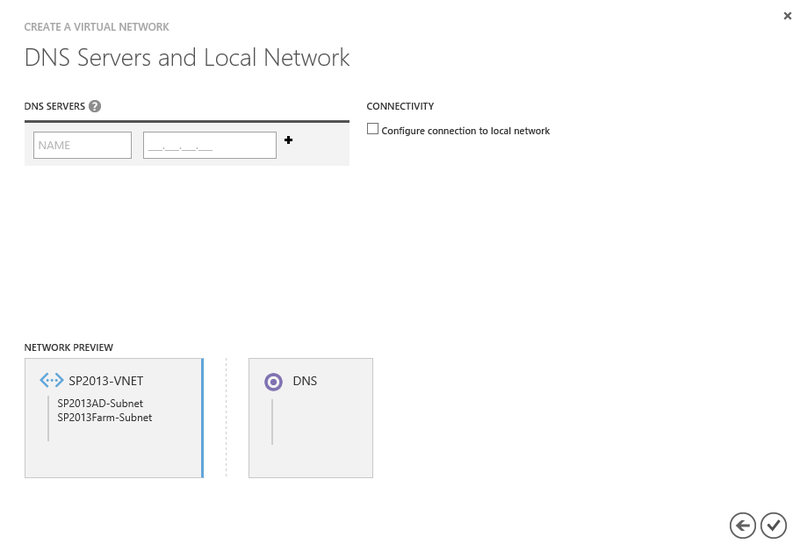
Creating a virtual network
Thus, we have created a virtual network through the management portal.
A similar task can be performed using PowerShell scripts.
Using PowerShell Script
The contents of the script CreateVnet .ps 1
# Azure Get-AzureSubscription | Select SubscriptionName # $subscriptionName = "-" $storageAccount = "--" Select-AzureSubscription $subscriptionName Set-AzureSubscription $subscriptionName -CurrentStorageAccount $storageAccount # Get-AzureLocation | Select Name # $AGLocation = "West US" $AGDesc = "SharePoint 2013 Affinity Group" $AGName = "SP2013-AG" $AGLabel = "SP2013-AG" # New-AzureAffinityGroup -Location $AGLocation -Description $AGDesc -Name $AGName -Label $AGLabel # Set-AzureVNetConfig -ConfigurationPath "C:\SharePoint2013FarmVNET.xml" Content of the SharePoint2013FarmVNET.xml configuration file
<NetworkConfiguration xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ServiceHosting/2011/07/NetworkConfiguration"> <VirtualNetworkConfiguration> <Dns /> <VirtualNetworkSites> <VirtualNetworkSite name="SP2013-VNET" AffinityGroup="SP2013-AG"> <AddressSpace> <AddressPrefix>192.168.0.0/16</AddressPrefix> </AddressSpace> <Subnets> <Subnet name="SP2013AD-Subnet"> <AddressPrefix>192.168.1.0/24</AddressPrefix> </Subnet> <Subnet name="SP2013Farm-Subnet"> <AddressPrefix>192.168.2.0/24</AddressPrefix> </Subnet> </Subnets> </VirtualNetworkSite> </VirtualNetworkSites> </VirtualNetworkConfiguration> </NetworkConfiguration> We expand the domain controller
You can use a Windows Azure portal or PowerShell to prepare a virtual machine that will become a domain controller.
Create a new virtual machine through the portal
In the Windows Azure portal, click New and select Virtual Machine | From Gallery (Virtual Machine | From Gallery) .
New virtual machine from the gallery
Select a Windows Server 2012 image from the list. Click the arrow to continue.
Enter the name of the virtual machine, for example, SP2013-DC1, in the Virtual Machine Name field and set the password for the Administrator user. Click the arrow to continue.
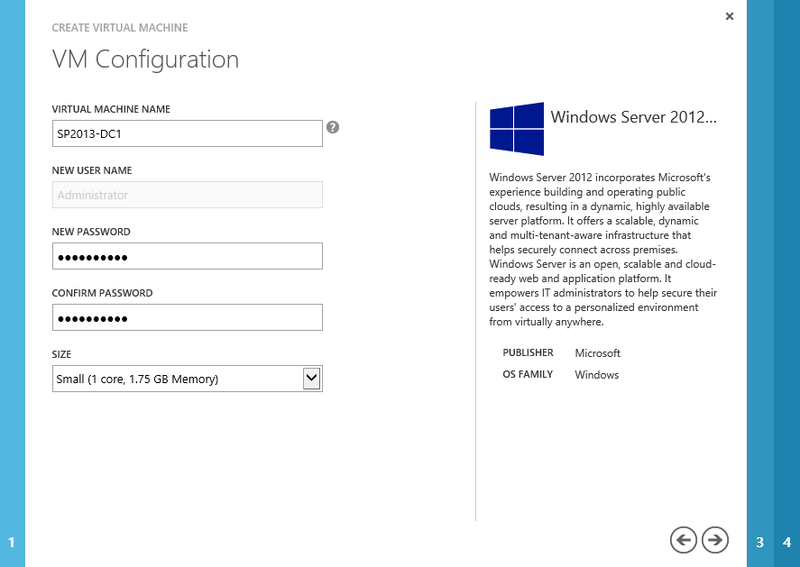
Creating a new virtual machine
DNS name must be unique. You can choose an existing storage account or automatically create a new one. Select your virtual network from the Region / Affinity Group / Virtual Network drop-down list. Click the arrow to continue.

Virtual network selection for a virtual machine
Check the box next to SP2013AD-Subnet in the Virtual Network Subnets list. To create a virtual machine, click Finish.
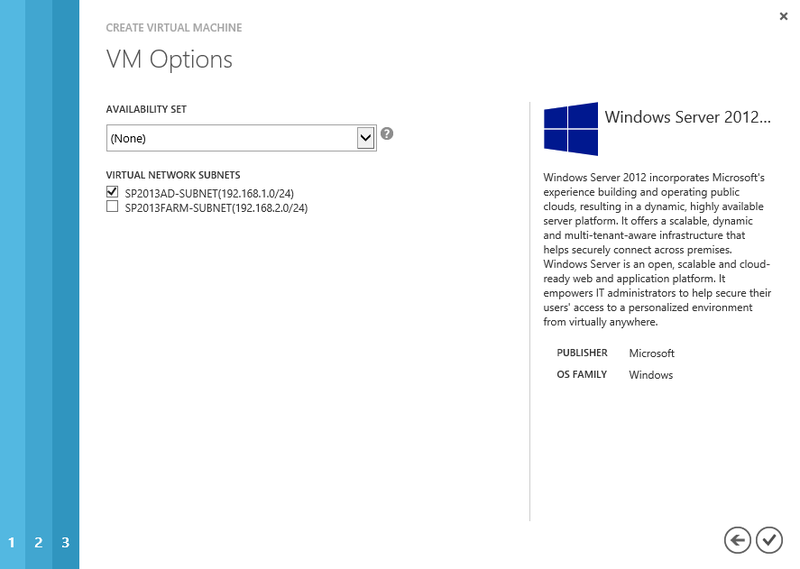
Select Active Directory subnet
Wait for the virtual machine creation process to complete. Click the name of the virtual machine and select Dashboard .
Click Attach in the menu at the bottom of the page and select Attach Empty Disk .
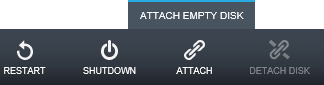
Attaching an empty disk
On the Attach empty disk to virtual machine page, set the Size parameter to “ 20 GB” (20 GB) and click the Finish button to create the disk.
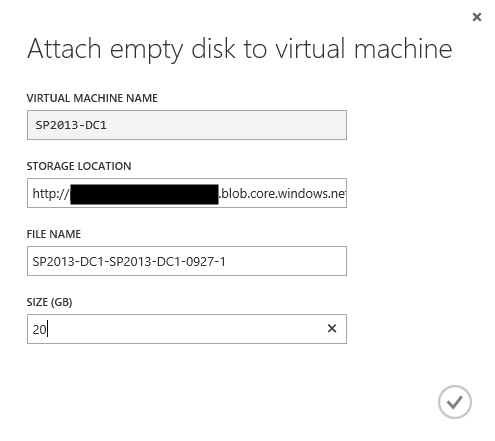
Create a new disk
In addition to the above method for creating new machines through the portal, you can use PowerShell.
Create a new virtual machine using PowerShell script
# Azure Get-AzureSubscription | Select SubscriptionName $subscriptionName = "-" $storageAccount = "--" Select-AzureSubscription $subscriptionName Set-AzureSubscription $subscriptionName -CurrentStorageAccount $storageAccount # Get-AzureVMImage | Select ImageName # #1 $vmName = 'SP2013-DC1' $imageName = 'MSFT__Windows-Server-2012-Datacenter-201208.01-en.us-30GB.vhd' $size = "ExtraSmall" $subnet = 'SP2013AD-Subnet' $password = 'pass@word1' # $dc1 = New-AzureVMConfig -Name $vmName -InstanceSize $size -ImageName $imageName Add-AzureProvisioningConfig -Windows -Password $password -VM $dc1 | Add-AzureDataDisk -CreateNew -DiskSizeInGB 20 -DiskLabel 'data' -LUN 0 Set-AzureSubnet -SubnetNames $subnet -VM $dc1 # $serviceName = "SP2013DC-Service" $serviceLabel = "SP2013DC-Service" $serviceDesc = "Domain Controller for SharePoint 2013" $vnetname = 'SP2013-VNET' $ag = 'SP2013-AG' # New-AzureVM -ServiceName $serviceName -ServiceLabel $serviceLabel -ServiceDescription $serviceDesc -AffinityGroup $ag -VNetName $vnetname -VMs $dc1 Create a domain controller
Wait until the virtual machine is ready: this may take several minutes. Log in to the newly created virtual machine in the Windows Azure portal. To do this, go to the Virtual Machines section, select SP2013-DC1 and click Connect at the bottom.
Open the Computer Management panel , expand the Storage node, and select Disk Management .
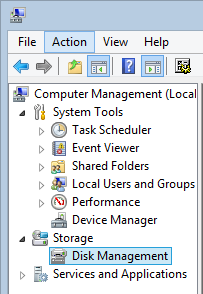
Open Disk Management window
Initialize Disk 2 by clicking OK in the Initialize Disk dialog box.

Disk initialization
Right-click unallocated disk space and select New Simple Volume .
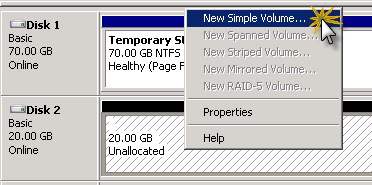
Create a new simple volume
This will launch the New Simple Volume Wizard . Click Next and leave the default values on the Specify Volume Size and Assign Drive Letter or Path screens.
On the Format Partition screen, set the Volume label field to DIT and click Next .
To start the formatting process, click Finish . After this process is complete, the disk will be ready for use.

Formatted disk
In Windows Server 2012, the mechanism for creating a domain controller has changed (DCPROMO is outdated). Open Server Manager , then select Manage and Add Roles and Features
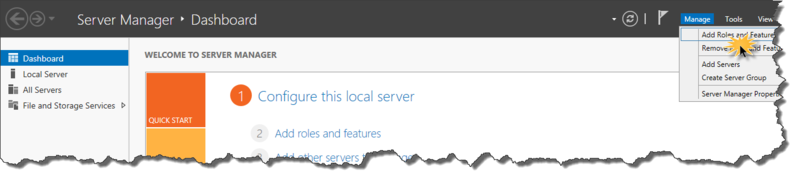
Server manager
In the wizard that opens, click Next , then select the Create a domain in a new forest option and click Next. Next, select Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next.
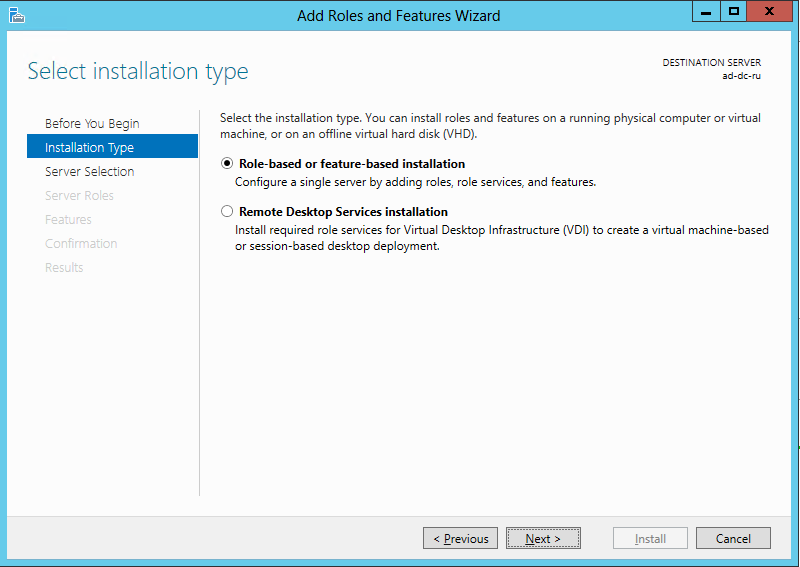
Choosing a way to add roles
Select a server to add roles and click Next

Choosing a server to add roles
In the next step, select Active Directory Domain Services . After that, in the window that appears, select Add Features
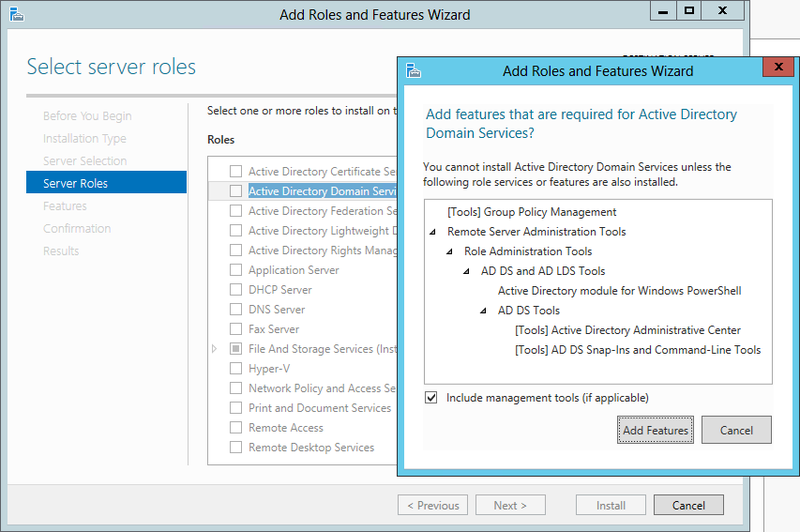
Add AD DS Role
In all the next steps of the wizard, click on Next .

The final step of installing the AD DS role
The server now has the AD DS role, but it is not yet a domain controller. To make our server DC, open Server Manager

Making the server a domain controller from Server Manager
Select Add a new forest , give the root domain ( Root Domain Name ) the name contoso.com and click Next
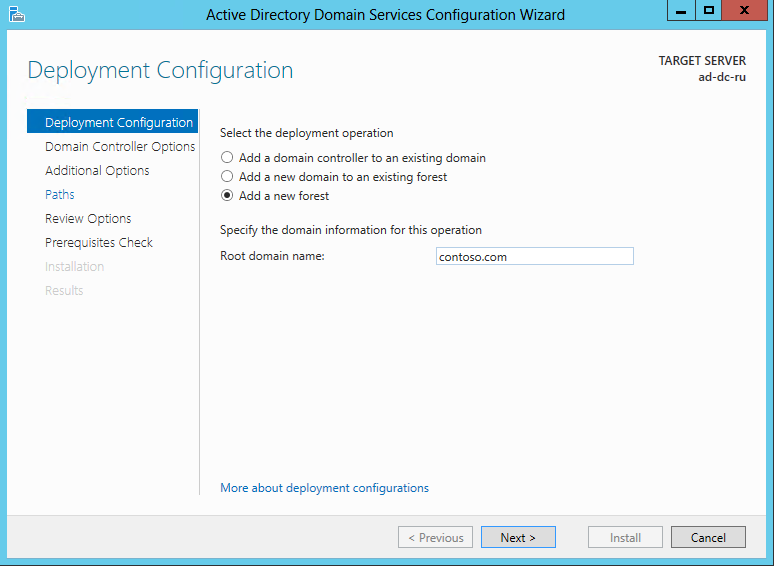
Select Deployment Type
Select the mode of operation of Windows Server 2012, use the default settings to create a DNS server and set the domain administrator password (preferably different from the administrator password on the created server). Click Next
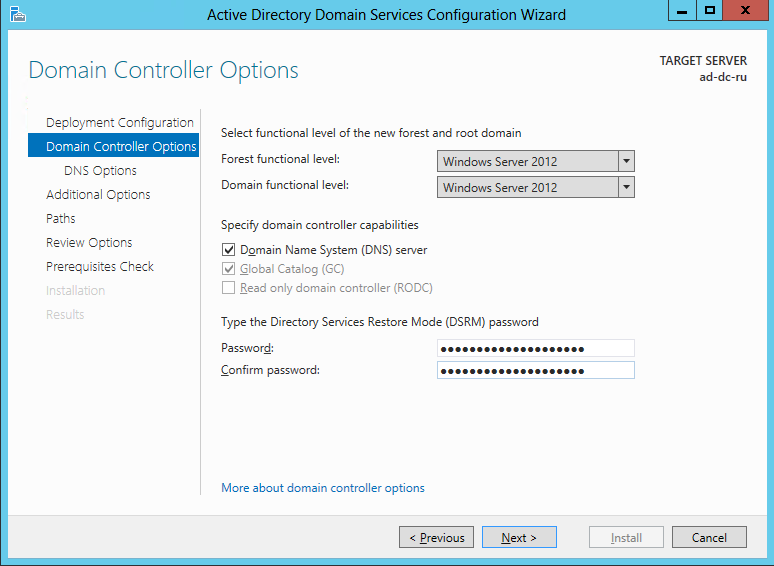
Domain Controller Options
In this practice, you will not integrate into your existing Active Directory environment, so click Next .

DNS creation warning message
For the repository for the Database , Log files, and SYSVOL folders, specify a recently formatted data disk (for example, F: \ NTDS for a database, F: \ NTDSLogs for logs, and F: \ SYSVOL for SYSVOL). Click Next to continue.
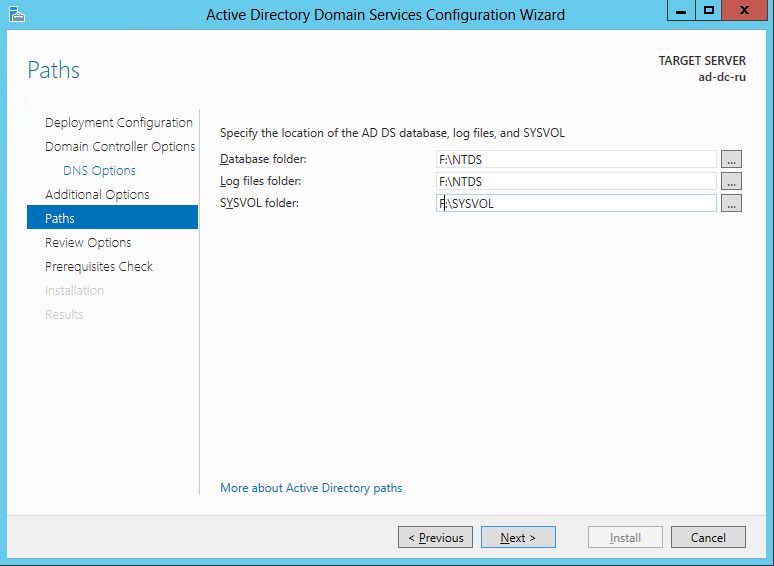
Settings for the location of the Database, Logs and SYSVOL folders
Finally, click Next again and wait for the Active Directory configuration process to complete, which may take several minutes. When prompted to restart, click Restart Now .
So we created a domain controller for the SharePoint 2013 farm.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/152655/
All Articles