Wi-Fi in the metro: look at the cable in the wall of the tunnel

Radiating cable - upgraded slot radiator
In February of this year, I participated in the launch of a pilot Wi-Fi zone on the Sokolnicheskaya metro line. The length of the line is slightly more than 26 kilometers. At the time of the test, the network was in two trains, now almost all of this distance (from Sokolniki to Sportivnaya station) can be completely online.
Technology
We used the already laid radiating cable in the tunnels. A 3G signal is transmitted over the cable at speeds up to 14 Mbit / s. In the train cars there are 3G-Wi-Fi routers that convert the 3G signal to Wi-Fi.
')
One of the serious technical difficulties in equipping subway cars was in a non-standard power supply in cars +75 V, given the fact that Wi-Fi equipment was not designed for such a network voltage.
In a very short time (our technicians were allowed to work with the equipment only a week before testing) had to look for manufacturers who work with power sources designed for such voltage. The closest such manufacturer was found in St. Petersburg, as soon as our employees completed the equipment supply transaction and brought it to Moscow, during the day it was installed in the wagons.
Why was chosen precisely Sokolnicheskaya line?
This is the very first line of the Moscow Metro, launched in 1935. It connects many stations, above which are located objects of culture, education, business centers. What is important, the share of people with smartphones, tablet computers and other devices with a Wi-Fi module is large on this thread. The branch is not overloaded with passengers, it is convenient to ride on it with Internet access devices, and it is long enough to enjoy Wi-Fi.
Why not ring?
The ring line is the most inconvenient in terms of Internet use:
- This is a short line.
- Each transfer station, a lot of incoming and outgoing
- On the ring line, most of the people go to 1-2 stations before the transplant
How does this work in detail?
From the base station operating in the 2G / 3G standard, a radiating cable is laid along the tunnel, which provides GSM / UMTS carriages with a signal all along the way.

It is a modernized slot emitter. In fact, this is a coaxial cable (operating frequency of 800 MHz - 2700 MHz) with holes on which dipole antennas (so-called “nails”) are wound.
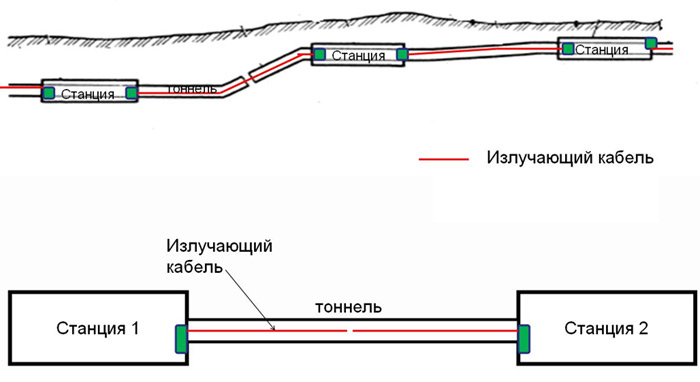
Along the way, seamless roaming is provided for subscriber devices.
The mobile router installed in the car converts the received cellular signal (3G / EDGE / GPRS) to the WiFi standard (802.11b / g) and distributes Internet traffic for subscriber devices inside the electric train cars.
And vice versa, passengers registered on the network transmit information from their gadgets to the Wi-Fi access point; they transfer traffic using a 3G modem to the Internet via the Beeline mobile network.
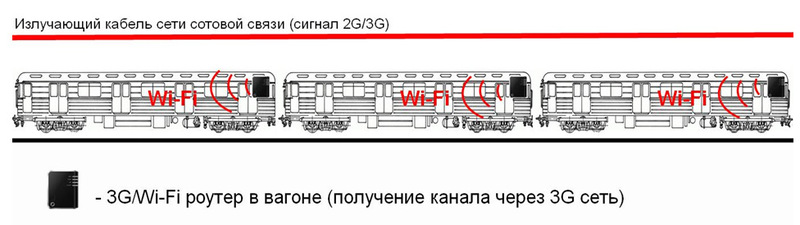
Now Wi-Fi access points are equipped with several trains plying along the Sokolnicheskaya metro line, there is a 3G coverage from Sportivnaya to Krasnoselskaya. Further development of the network in the metro will give:
- Continuous mobile communications.
- Fast mobile Internet access for passengers, and later for employees of the metro, which will allow to introduce various information services and install modern sensors, for example.
- This, in turn, will enable more detailed remote monitoring of systems.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/151430/
All Articles